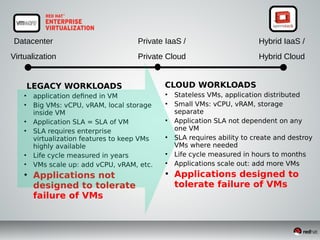
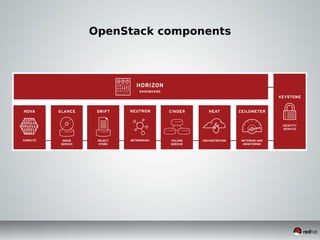
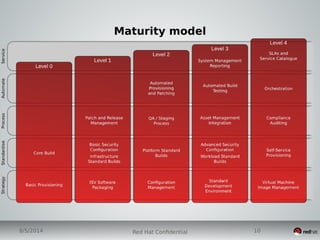
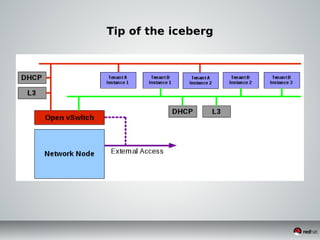
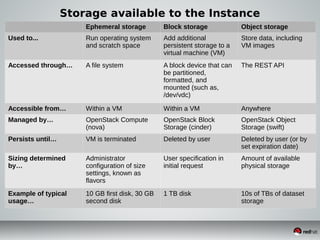
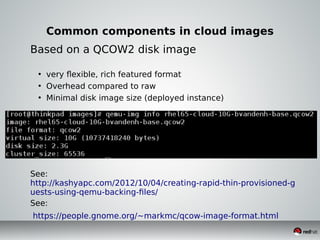
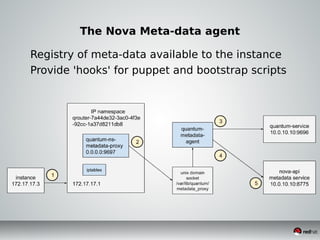
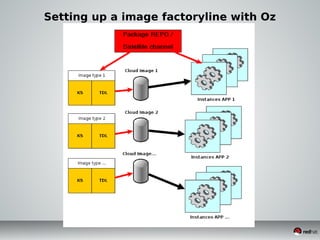
This document discusses Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and creating cloud images using OpenStack and Oz. It provides an overview of IaaS and OpenStack components available to instances. It then covers creating cloud images, including using Oz to automate image creation through kickstart files and template definition language files. Finally, it briefly discusses setting up an image factory line with Oz.