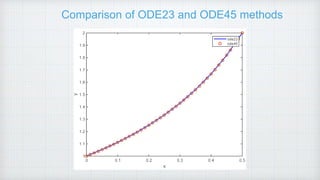
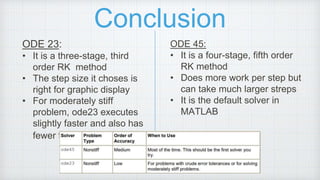
The document outlines the implementation of the Runge-Kutta methods (ode23 and ode45) in MATLAB for solving ordinary differential equations and includes a comparison of their performance. It discusses the step-by-step process of defining a function, setting the domain, and plotting results, highlighting the exact solution as well as the numerical approximations. The conclusion emphasizes the characteristics and advantages of both methods in various scenarios.



![Script File
f=@(x,y) x*y^2+y
[x,y] = ode23(f,[0,0.5],1)
plot(x,y,'r','linewidth',1.5)
hold on
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y’)
f=@(x,y) x*y^2+y
[x,y] = ode45(f,[0,0.5],1)
plot(x,y,'r','linewidth',1.5)
hold on
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20463988-230523151902-d4de2021/85/Runge-Kutta-Method-4-320.jpg)
![Output
Numerically approximate the solution of the first
order differential equation
Dy/dx = xy2 + y, y(0) = 1, on the interval x ∈ [0,
0.5].
For any differential equation in the form y’= f(x,
y), we begin by defining the function
f(x, y). For single equations, we can define f(x, y)
as an anonymous function. The basic syntax for
the MATLAB solver ode45 is
ode45(Function, Domain, Initial Condition)
For this example, we use
MATLAB returns two column vectors. The first
with values of x and the second with values
of y. Since x and y are vectors with
corresponding components, we can plot the
values with
which creates the figure below](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20463988-230523151902-d4de2021/85/Runge-Kutta-Method-5-320.jpg)