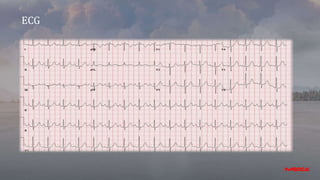
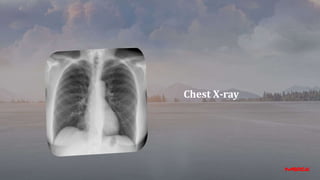
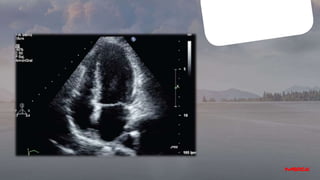
- This document appears to be notes from a case presentation and discussion of treating hypertension. It describes a 50-year-old male patient presenting with shortness of breath, palpitations, and a blood pressure of 160/115 mmHg. Various investigations were conducted.
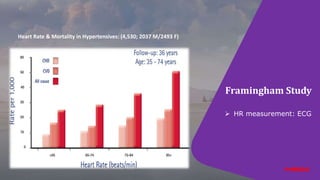
- The discussion centers around hypertension treatment guidelines and determining the appropriate treatment strategy for this patient. Various medication options and their effects are considered. The document recommends starting treatment with a bisoprolol and amlodipine combination to control the patient's blood pressure and heart rate.