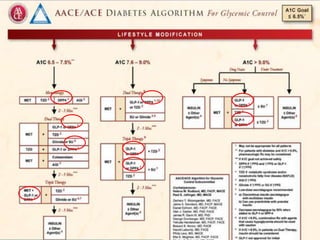
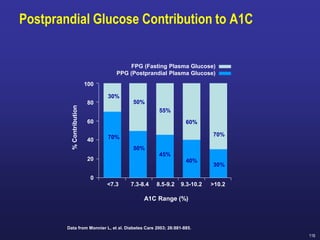
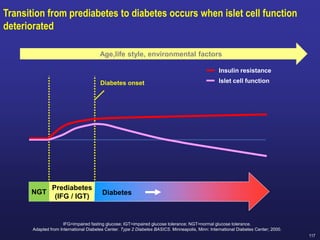
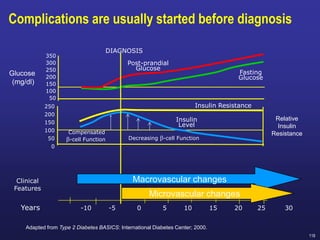
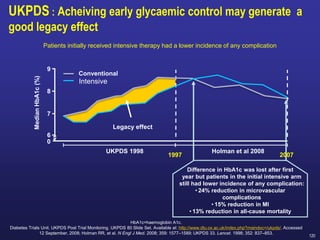
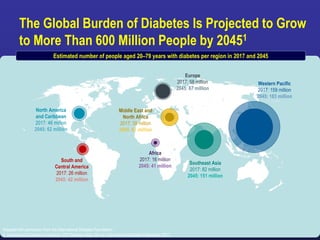
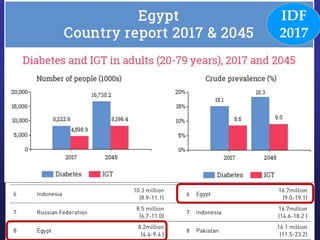
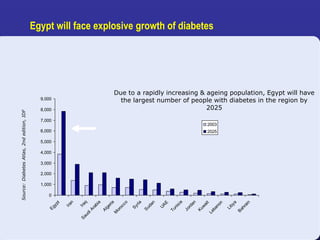
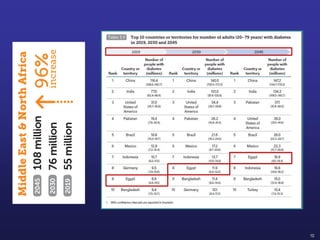
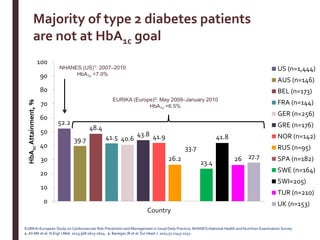
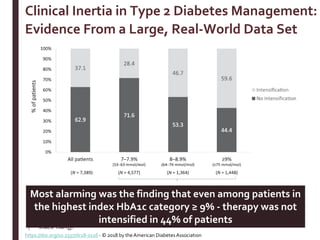
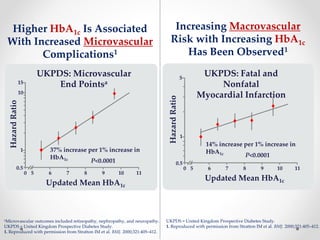
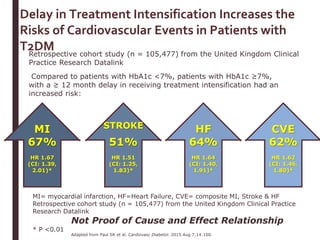
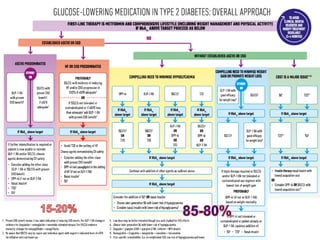
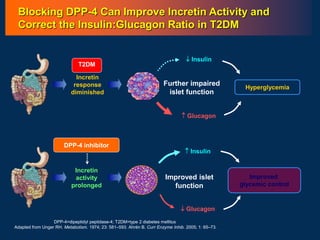
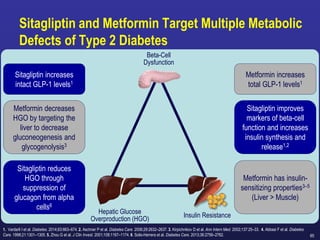
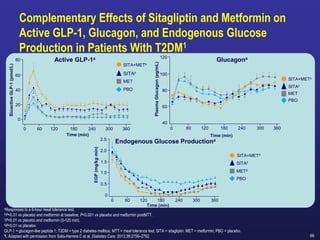
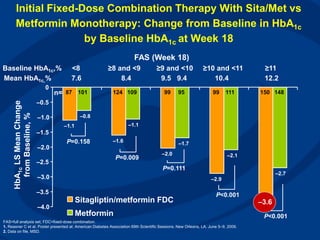
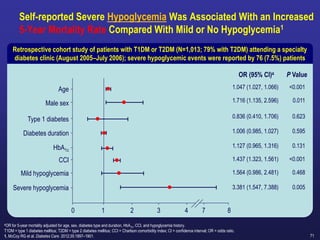
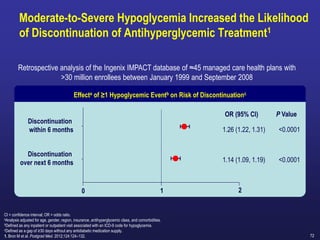
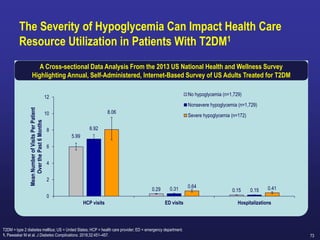
Recent studies have highlighted the growing global burden of type 2 diabetes, with over 600 million people projected to have the disease by 2045. In particular, Egypt will face explosive growth in cases. While control of blood sugar levels is important for reducing complications, most patients do not achieve treatment goals. Intensifying treatment in a timely manner when blood sugar is poorly controlled can reduce cardiovascular risks. Inertia on the part of both physicians and healthcare systems often limits timely treatment changes needed to improve outcomes for patients with type 2 diabetes.






![15
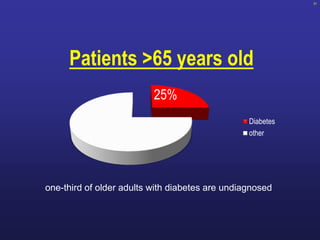
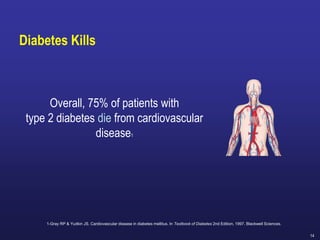
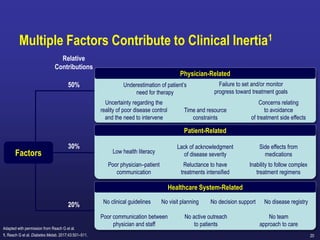
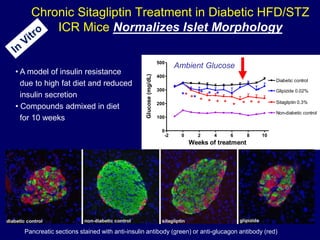
Diabetes is a Serious Chronic Disease
1 Fong DS, et al. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 [Suppl. 1]:S99–S102.
2 Molitch ME, et al. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 [Suppl.1]:S94–S98.
3 Kannel WB, et al. Am Heart J. 1990; 120:672–676.
4 Gray RP & Yudkin JS. In Textbook of Diabetes. 1997.
5 Mayfield JA, et al. Diabetes Care. 2003;26 [Suppl. 1]:S78–S79.
Diabetic
retinopathy
Leading cause
of blindness in working-age adults1
Diabetic
nephropathy
Leading cause of
end-stage renal
disease2
Cardiovascular
disease
Stroke
2- to 4-fold increase
in cardiovascular
mortality and stroke3
Diabetic
neuropathy
Leading cause of non-
traumatic lower extremity
amputations5
8/10 diabetic patients
die from CV events4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mimamsdpptprof-210527143706/85/sitagliptin-for-diabetics-15-320.jpg)





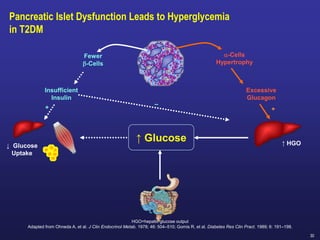
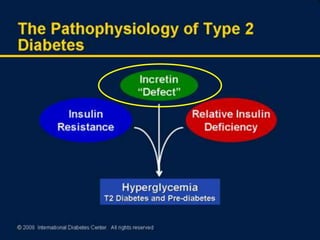

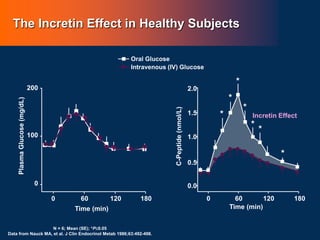
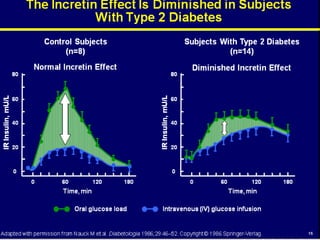
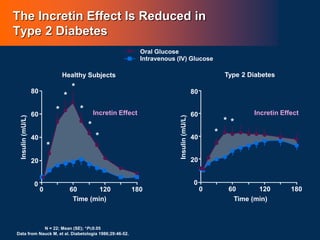
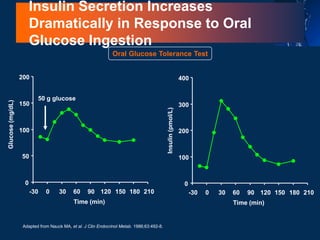
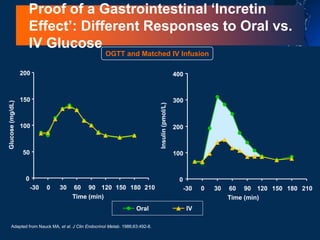
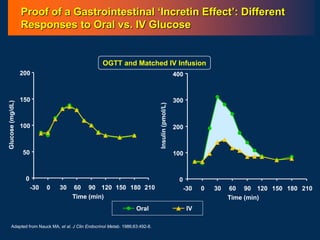






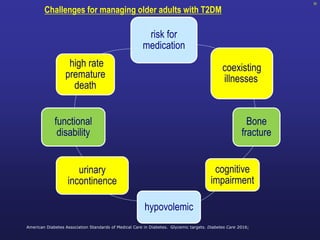
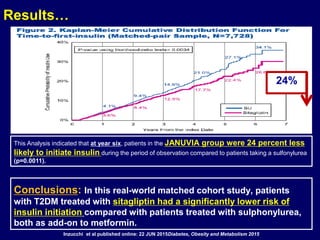
![L-Cell
(ileum)
Proglucagon
GLP-1 [7-37]
GLP-1 [7-36NH2]
K-Cell
(jejunum)
ProGIP
GIP [1-42]
GLP-1=Glucagon-Like Peptide-1; GIP=Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Peptide
Adapted from Drucker DJ. Diabetes Care. 26:2929-2940.
GLP-1 and GIP are Synthesized and Secreted
from the Gut in Response to Food Intake](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mimamsdpptprof-210527143706/85/sitagliptin-for-diabetics-45-320.jpg)
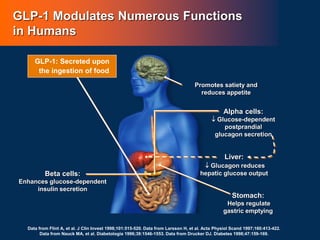
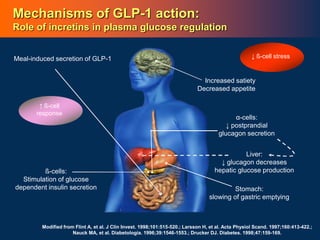
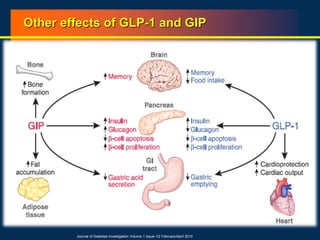





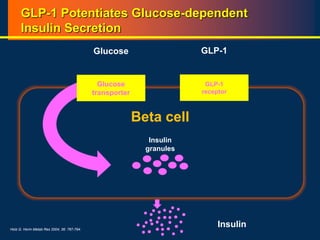
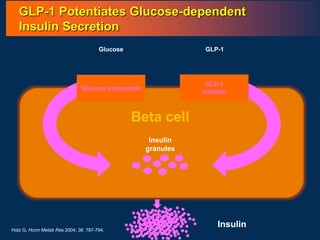


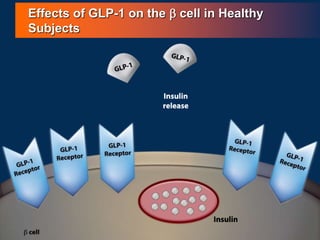
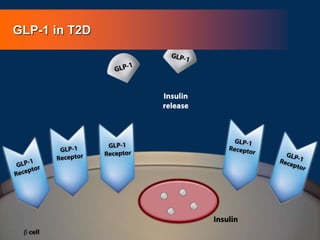

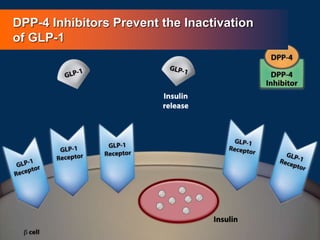



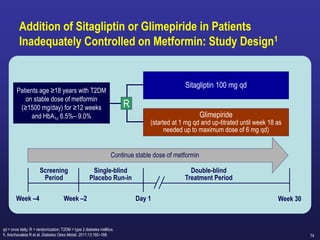

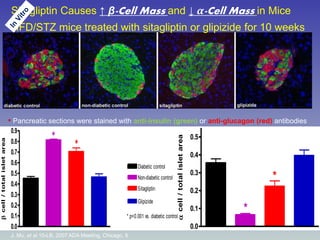


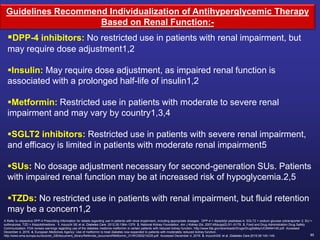
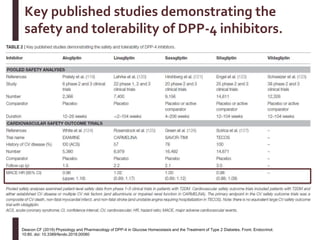
![86
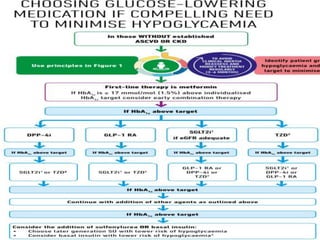
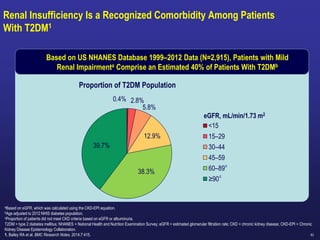
Dose Adjustment of Sitagliptin in Patients With Renal Impairment1–3
GFR = glomerular filtration rate; ESRD = end-stage renal disease.
1. JANUVIATM (sitagliptin) [Summary of product characteristics]. Merck. 2018. 2. Bergman AJ et al. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1862–1864. 3. Evans M et al. Diabetes Ther. 2015;6:1–5.
Dose adjustment of sitagliptin for patients with moderate to severe renal impairment or ESRD is
recommended to achieve plasma concentrations comparable to those in patients with normal renal function,
and not based on a risk of adverse effects or renal toxicity2,3
Normal renal function or
mild or moderate renal
impairment
(GFR ≥45 mL/min)
Sitagliptin 100 mg
Moderate renal
impairment
(GFR ≥30 to <45
mL/min)
Sitagliptin 50 mg
Severe renal
impairment
or ESRD, including
those requiring
hemodialysis or
peritoneal dialysis
(GFR <30 mL/min)
Sitagliptin 25 mg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mimamsdpptprof-210527143706/85/sitagliptin-for-diabetics-85-320.jpg)
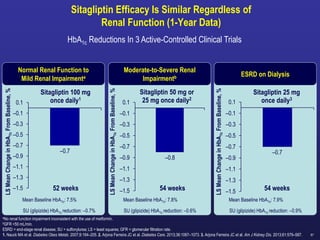
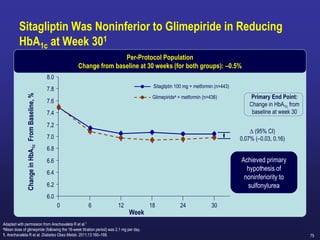
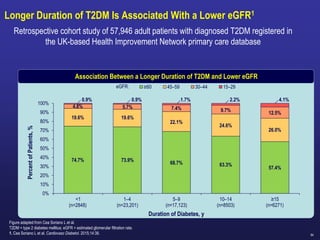
![88
Scott RS and col. Safety and Efficacy of Sitagliptin [SITA] Compared with Dapagliflozin [DAPA} in Subjects with T2D, Mild Renal Impairment and Inadequate Glycemic Control on
Metformin [MET] With or Without a Sulfonylurea. Poster presented at: ADA 2018; June 22–26, 2018; Orlando, Florida. 1142-P
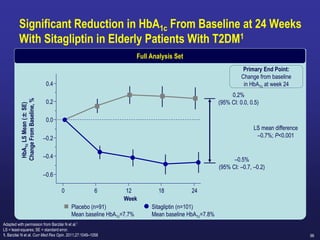
Change from Baseline in A1C through Week 24
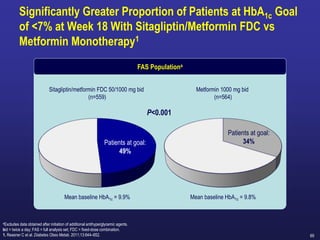
CompoSIT R Study:
Study Objective was:
To compare the efficacy and safety of the DPP-4 inhibitor
Sitagliptin with the SGLT-2 inhibitor Dapagliflozin in patients
with type 2 diabetes and mild renal impairment ,Mean eGFR:
78 mL/min/1.73m².
Sitagliptin treatment was associated with Greater reduction from baseline
in A1C compared to Dapagliflozin
2018 UPDATES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mimamsdpptprof-210527143706/85/sitagliptin-for-diabetics-87-320.jpg)
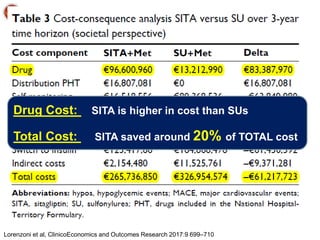
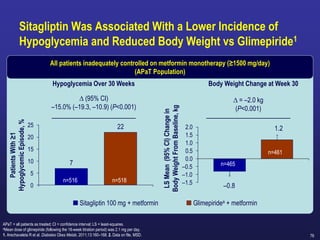
![89
CompoSIT R:-
Percentage of Patients at Goal of A1C <7% at Week 24
8
Scott RS and col. Safety and Efficacy of Sitagliptin [SITA] Compared with Dapagliflozin [DAPA} in Subjects with T2D, Mild Renal Impairment and Inadequate Glycemic Control on
Metformin [MET] With or Without a Sulfonylurea. Poster presented at: ADA 2018; June 22–26, 2018; Orlando, Florida. 1142-P
Conclusion:- In patients with type 2 diabetes and mild renal impairment with inadequate glycemic control on
metformin alone or in combination with a sulfonylurea agent:
• Treatment with sitagliptin for 24 weeks resulted in greater improvements in A1C relative to
treatment with dapagliflozin
• Treatment with sitagliptin and treatment with dapagliflozin for 24 weeks were generally well
tolerated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mimamsdpptprof-210527143706/85/sitagliptin-for-diabetics-88-320.jpg)