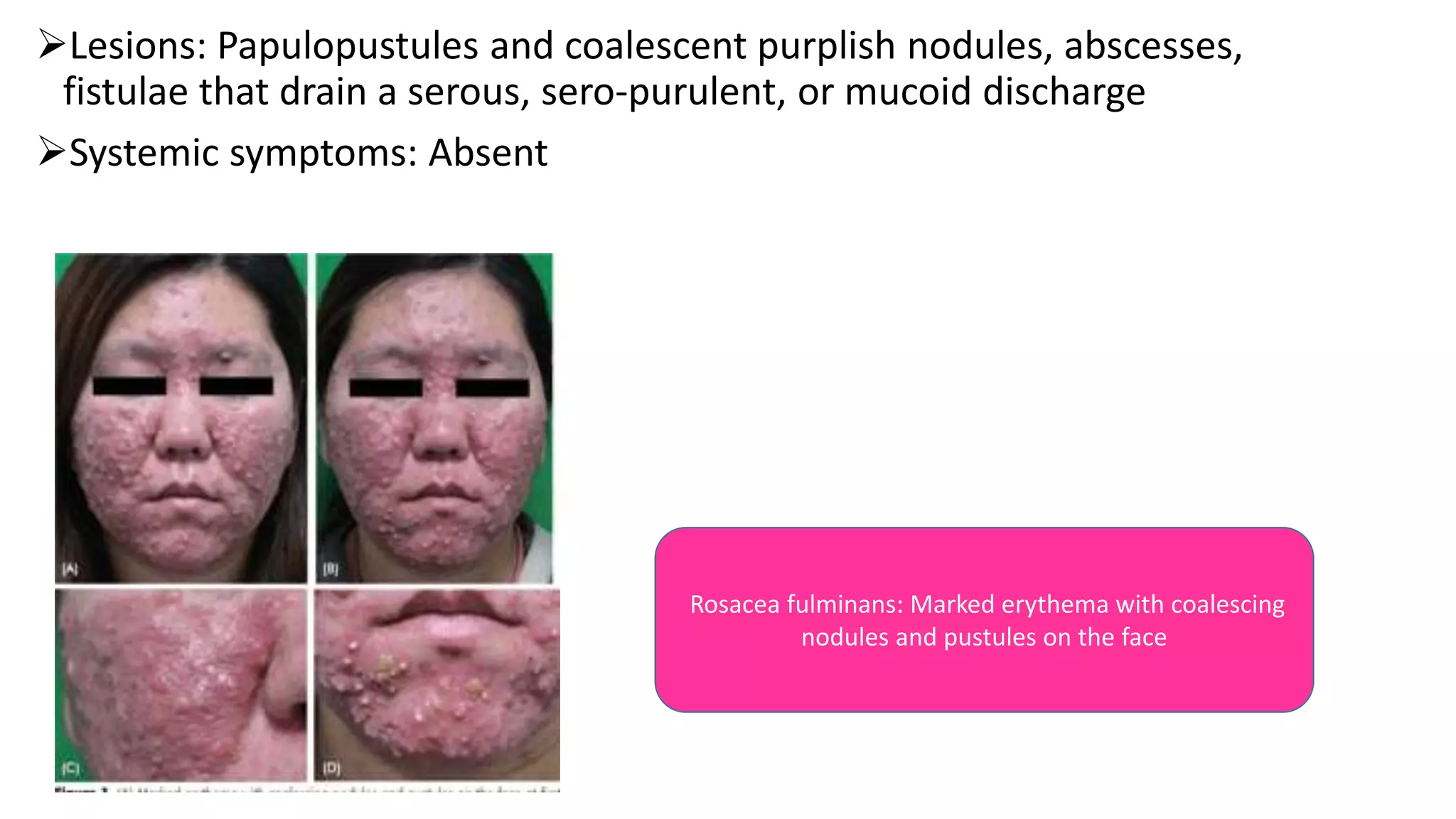
This document provides information on rosacea, including its epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Rosacea commonly affects fair-skinned individuals between 30-50 years of age and is characterized by prolonged flushing, erythema, telangiectasia, papules, pustules, and phymatous changes. Its exact cause is unknown but may involve factors such as genetics, microbes like Demodex folliculorum, innate immune system alterations, and environmental triggers. Treatment involves avoiding triggers, photoprotection, topical medications, oral antibiotics or isotretinoin, and procedures for advanced cases.