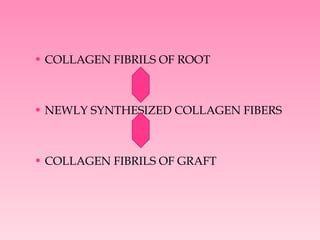
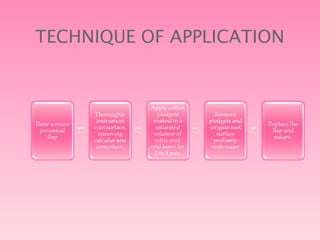
The document discusses root conditioning agents used in periodontal treatment. It focuses on citric acid, tetracycline, and fibronectin. Citric acid works by removing the smear layer and demineralizing the root surface, exposing collagen fibers to promote new attachment of fibroblasts. Tetracycline also demineralizes roots but requires higher concentrations and longer application times than citric acid. Fibronectin enhances new attachment by promoting cell proliferation and acting as a fibrin sealant during wound healing. While not fully proven in human studies, these agents provide benefits over scaling and root planing alone by detoxifying roots and enhancing new attachment.