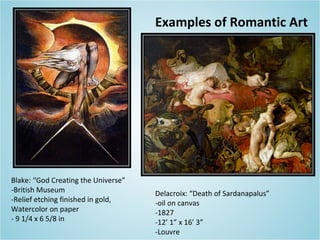
Neoclassicism began in the late 18th century as a reaction against Rococo styles and was adopted by leaders of the French Revolution who wanted to associate themselves with the stability and heroism of ancient Greek and Roman styles. Jacques-Louis David was a leading Neoclassical painter who appealed to republican sentiments with works like Oath of the Horatii. Romanticism emerged in reaction to Enlightenment rationalism and the Industrial Revolution, emphasizing emotion, imagination, and individualism in the arts. Romantic painters like Gericault, Delacroix, and Friedrich focused on landscapes, mythology, and exotic subjects to convey intense emotions.