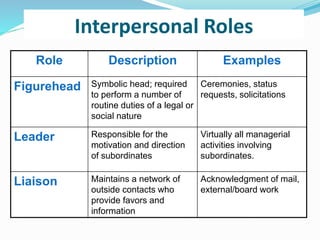
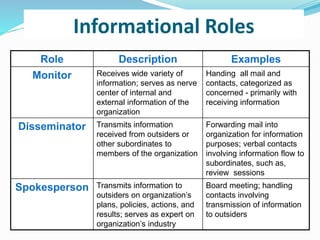
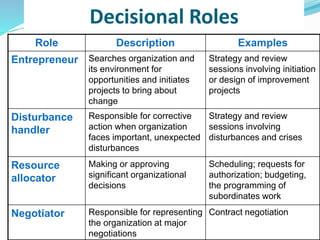
Managers perform three categories of roles: interpersonal roles, informational roles, and decisional roles. Interpersonal roles include figurehead, leader, and liaison. Informational roles consist of monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson. Decisional roles are entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, and negotiator. Each role has specific responsibilities and examples are provided to illustrate how managers fulfill these roles in their daily activities.