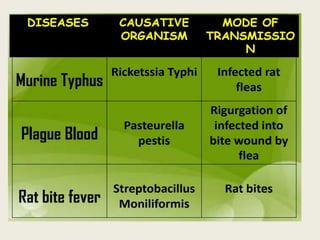
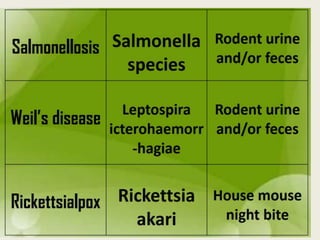
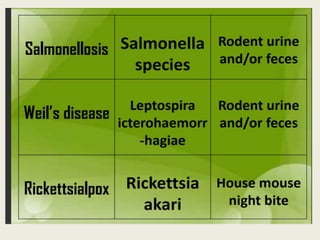
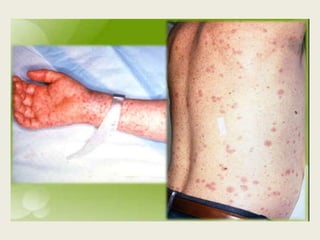
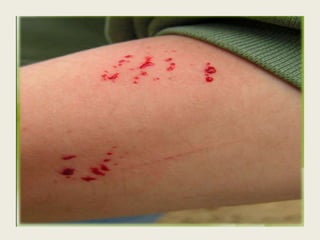
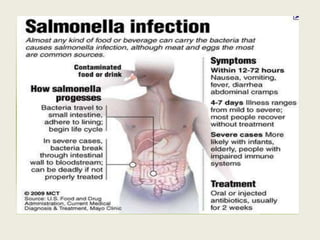
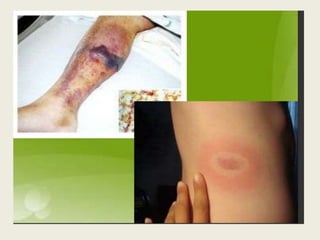
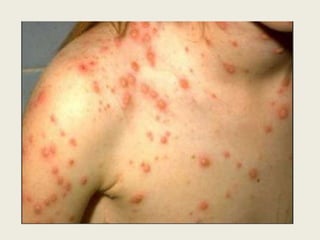
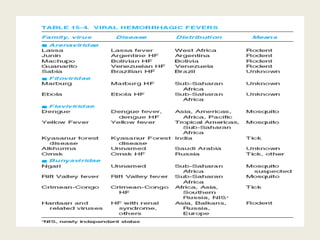
Rodents can spread over 35 diseases to humans directly through contact with rodents or indirectly through ticks/mites/fleas that fed on infected rodents. These diseases include plague, tularemia, salmonellosis, Lassa fever, viral hemorrhagic fevers, hantavirus, and Lyme disease. Changes to rodent populations from food surpluses, deforestation, or climate change can increase risk of transmission to humans. Several specific diseases transmitted include murine typhus from flea bites, rat bite fever from rodent bites/secretions, salmonellosis from Salmonella bacteria, and Weil's disease from contaminated water exposure. Rickettsialpox results from rod