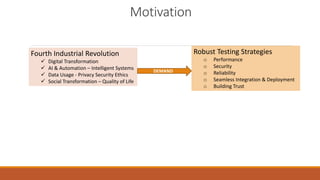
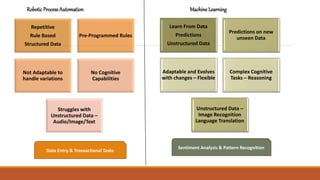
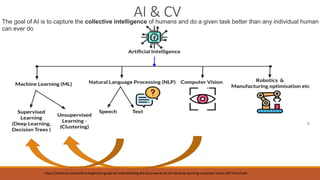
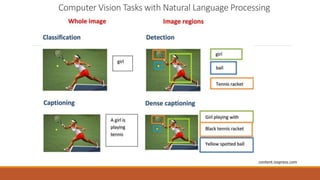
This document summarizes a presentation on robust testing strategies for machine learning models. The presentation covered:
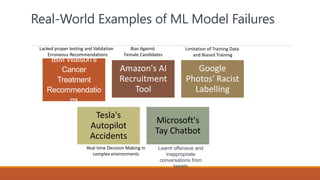
1) Examples of past ML model failures like IBM Watson's cancer recommendations and Microsoft's Tay chatbot.
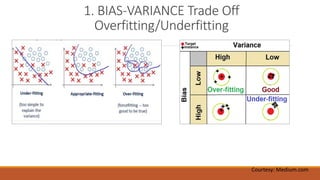
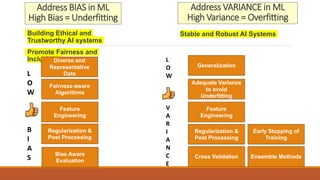
2) Key factors for robust ML testing like addressing bias-variance tradeoffs, using comprehensive training data, rigorous hyperparameter tuning, validation/evaluation techniques, and continuous monitoring.
3) The importance of developing reliable, inclusive, trustworthy and ethical ML systems through techniques like adversarial testing, validation, and ongoing performance monitoring.