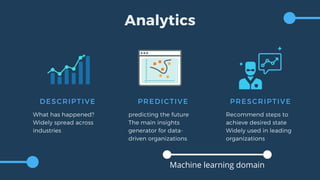
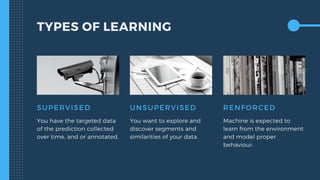
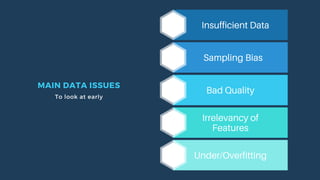
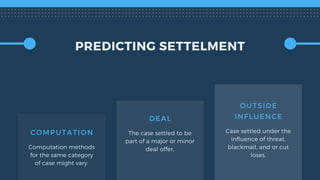
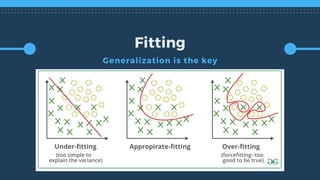
The document outlines key aspects of implementing machine learning (ML), including defining problems, understanding data quality, and selecting appropriate learning types. It emphasizes the importance of effective feature engineering, data representation, and performance metrics while managing ML projects and expectations. The presentation also offers practical tips for project management, such as starting with a minimum viable product and leveraging A/B testing.