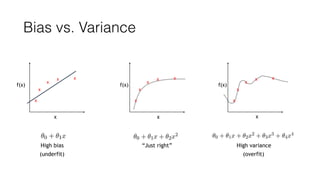
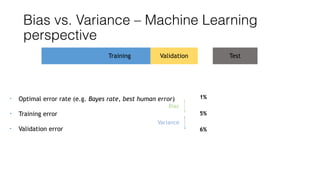
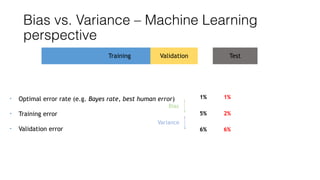
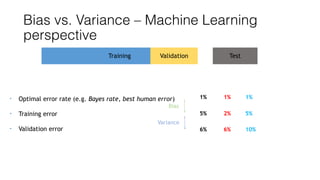
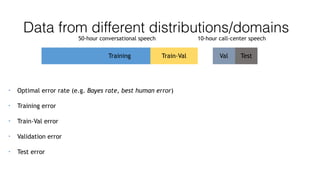
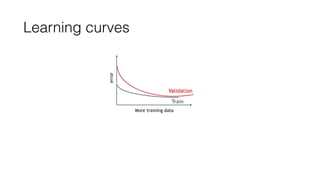
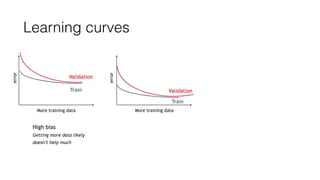
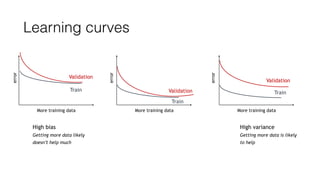
The document discusses several approaches to address a machine learning model that is making unacceptably large errors on new data. These approaches include collecting more training samples, reducing or increasing the number of features, adding regularization, using a bigger model, and tuning hyperparameters.