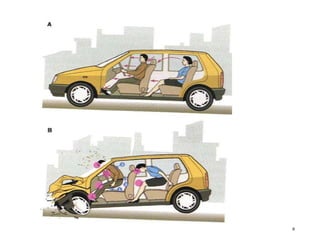
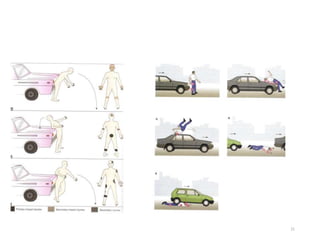
Motor vehicle accidents can cause a variety of injuries to occupants, pedestrians, and cyclists depending on the type and severity of impact. Common causes of injury include impact with interior vehicle surfaces, intrusion of objects into the passenger compartment, and ejection from the vehicle. Injuries may involve any body region. Autopsies of crash victims aim to determine cause of death and document findings for legal purposes. Investigations also examine crash scenes and vehicles to understand accident dynamics.