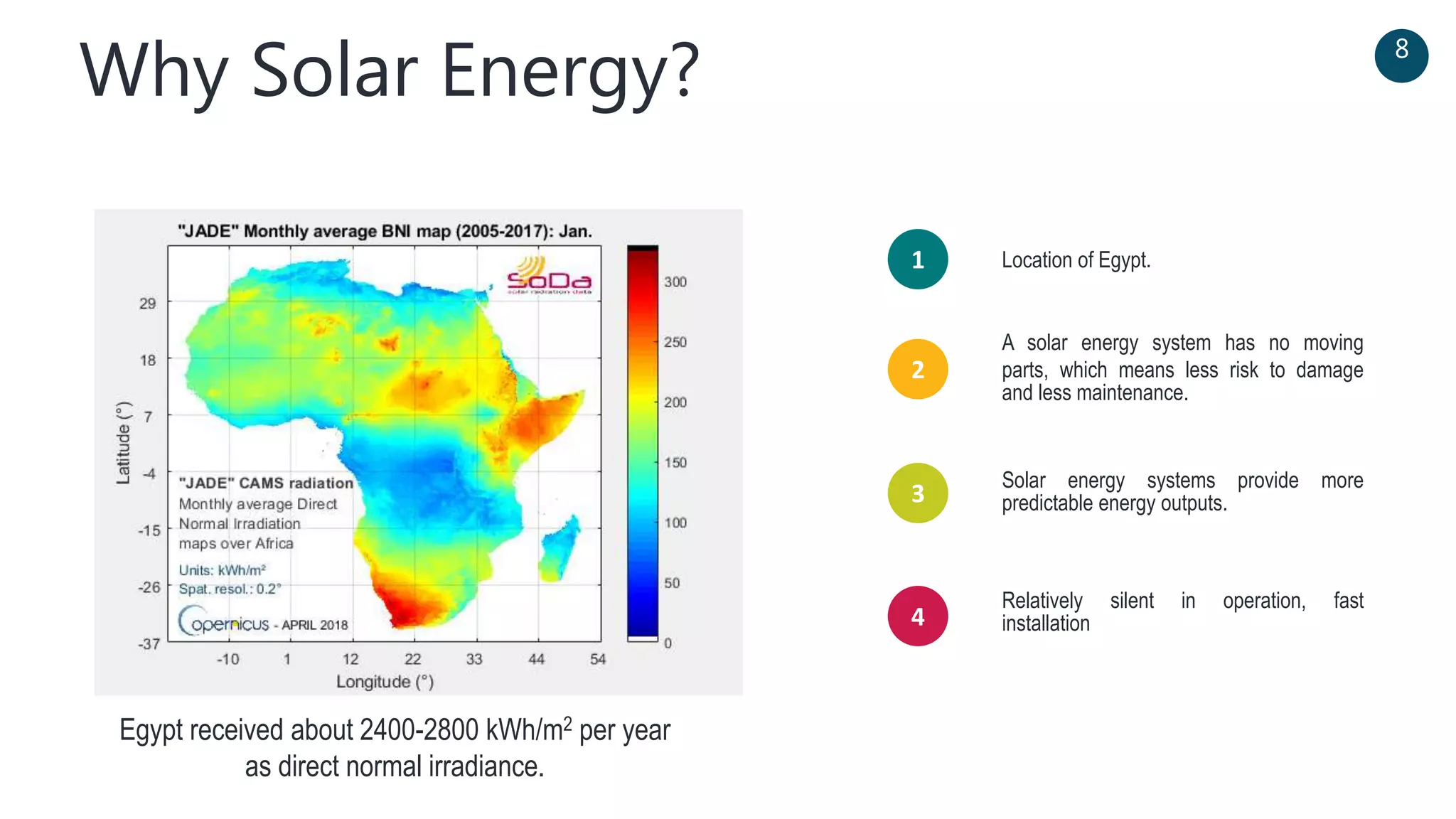
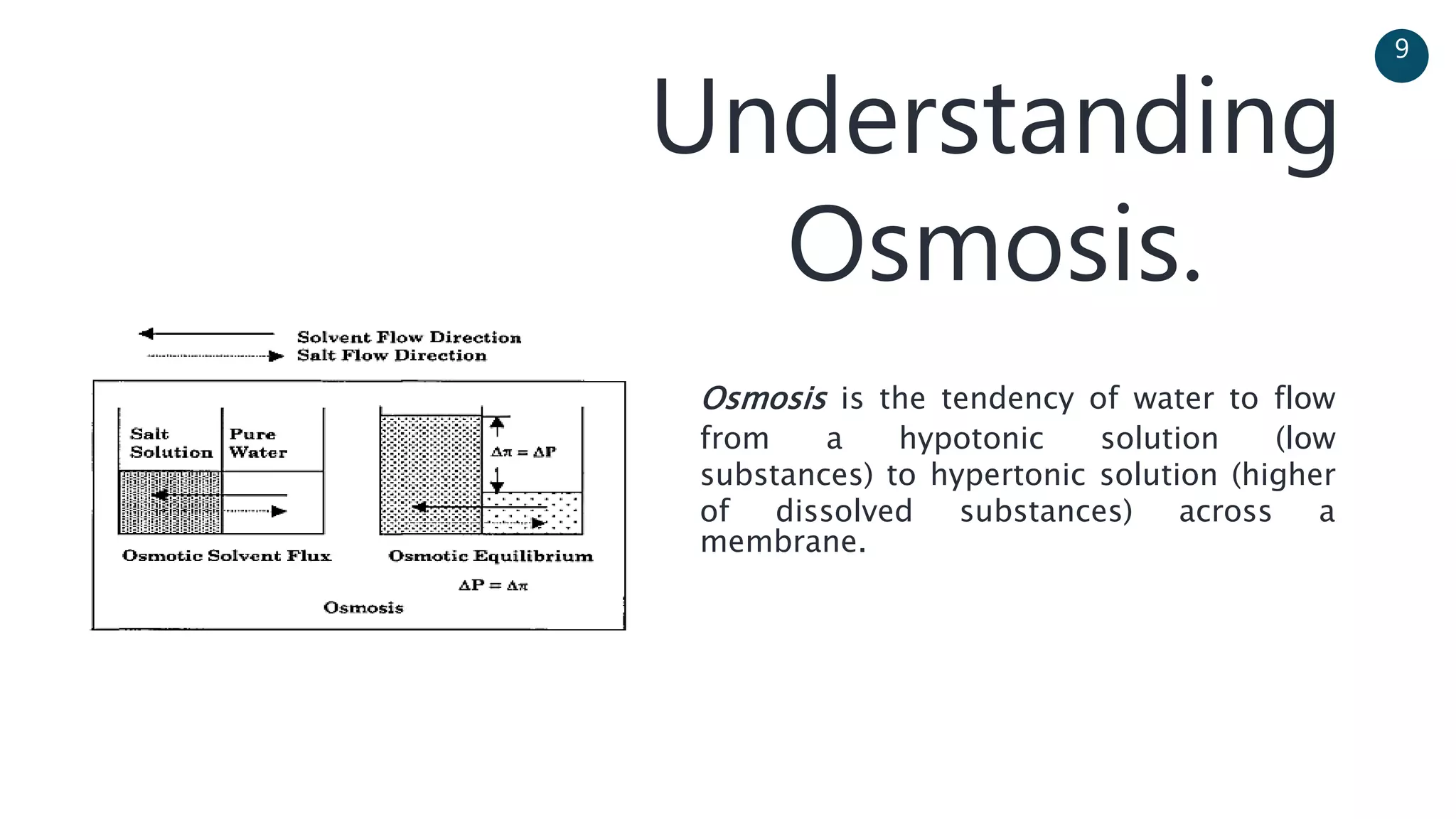
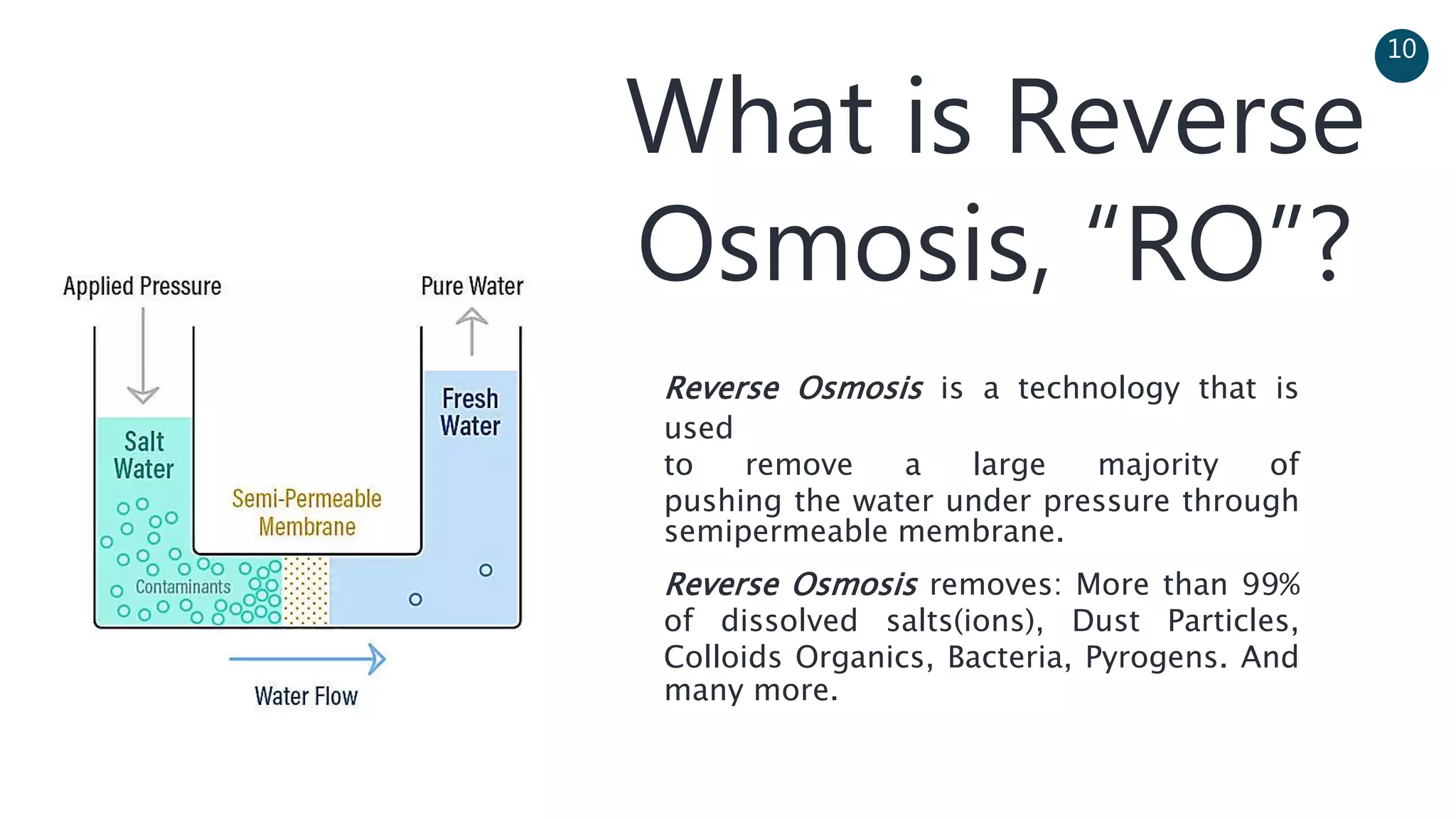
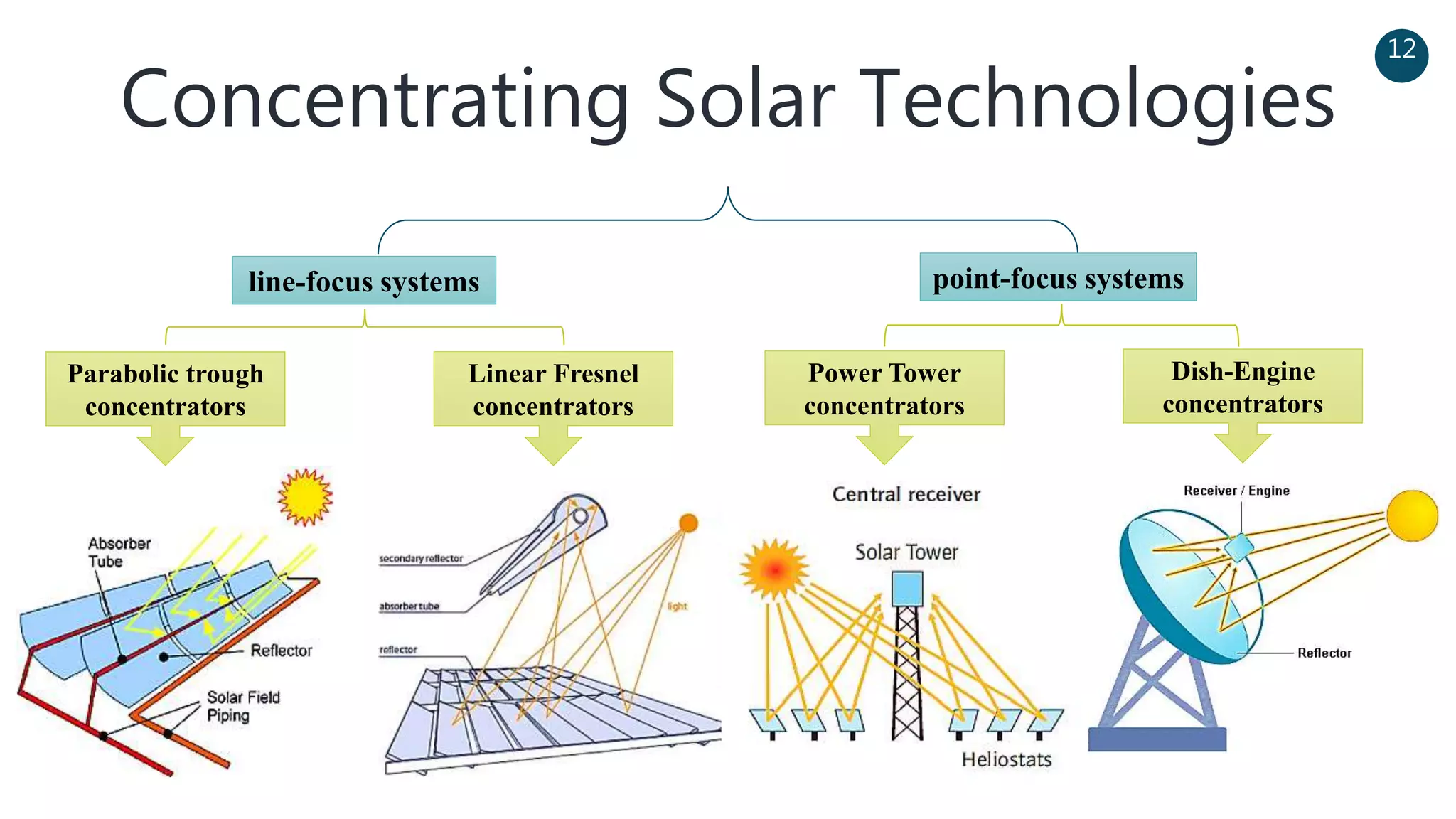
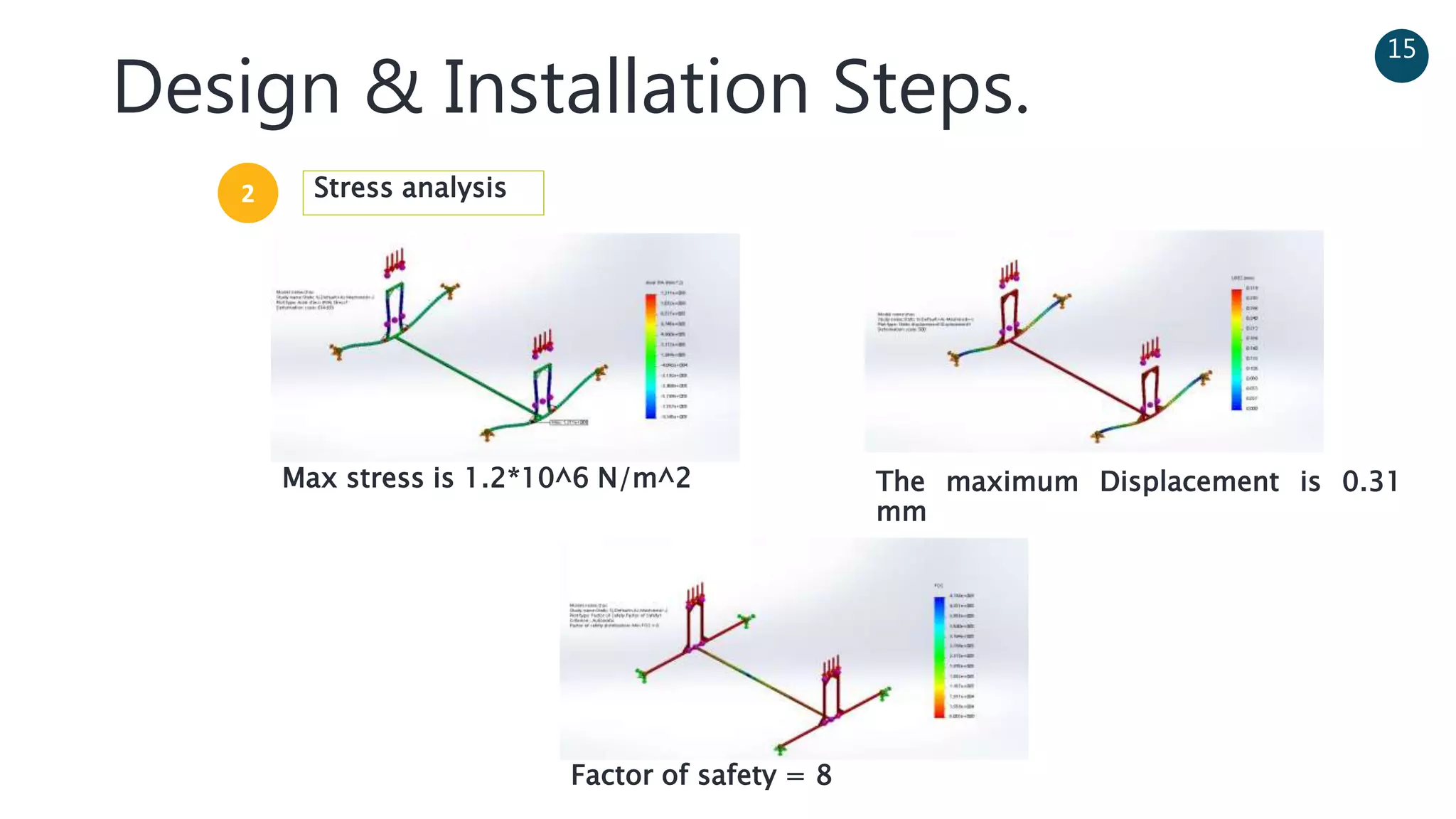
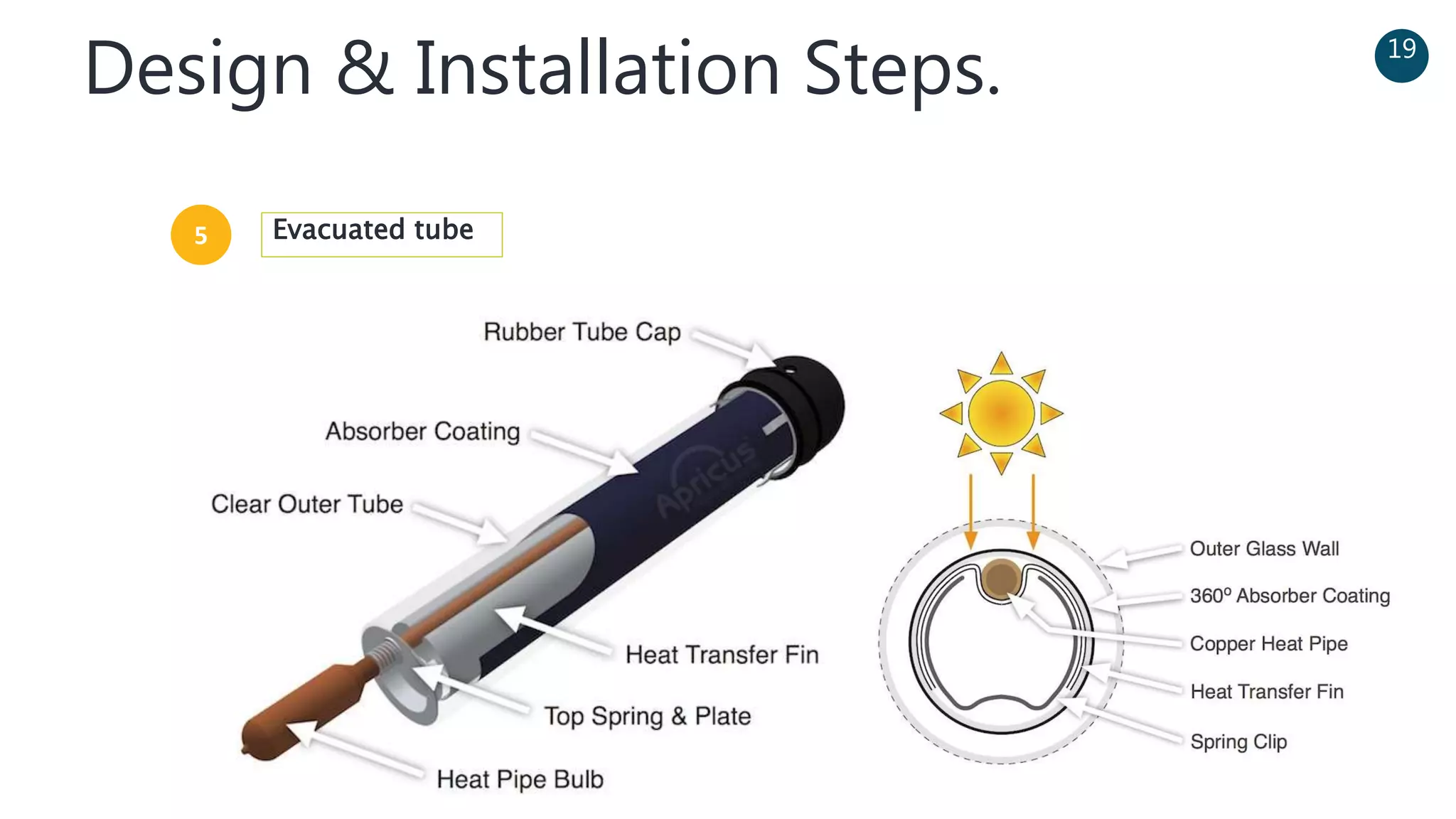
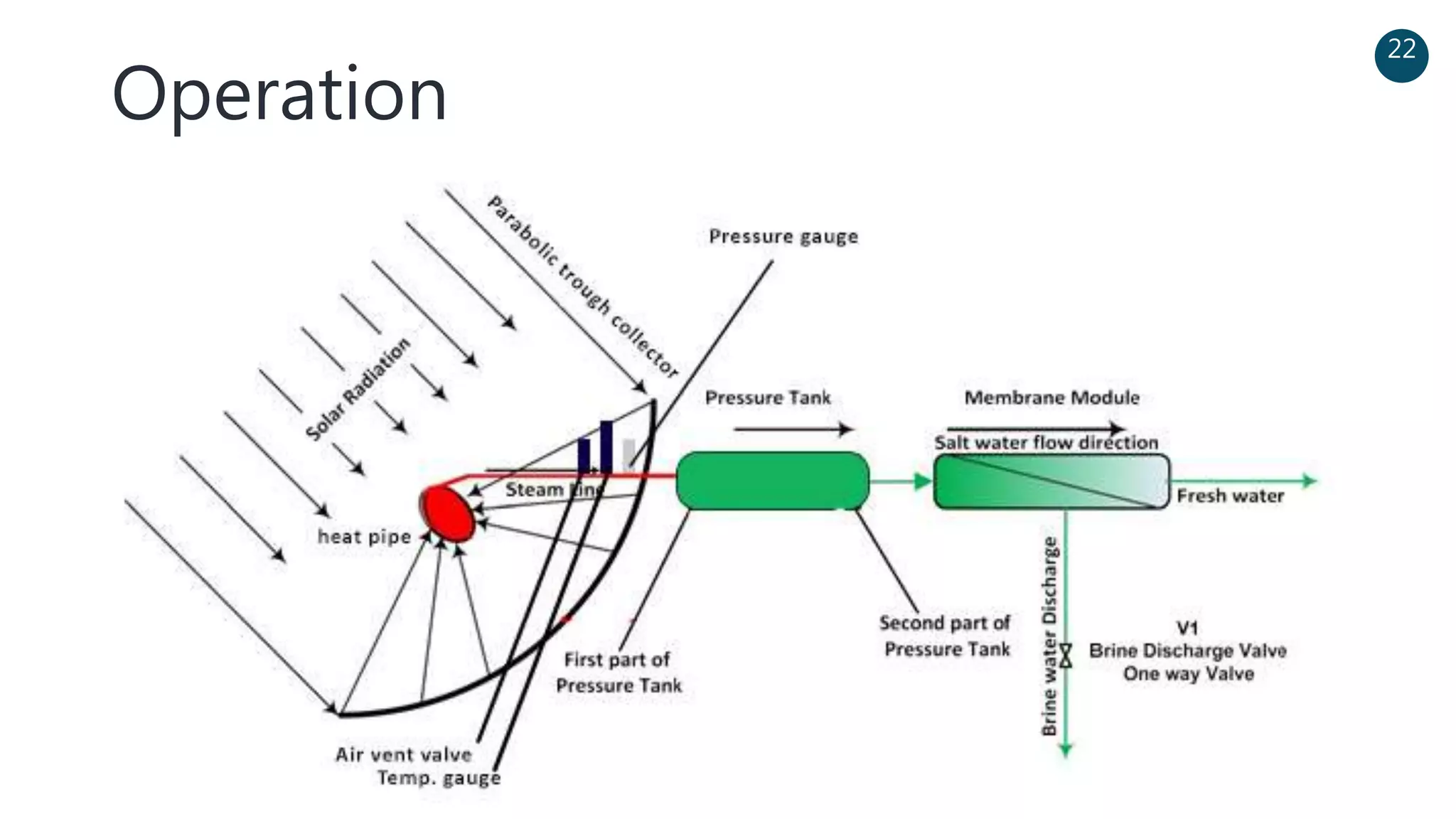
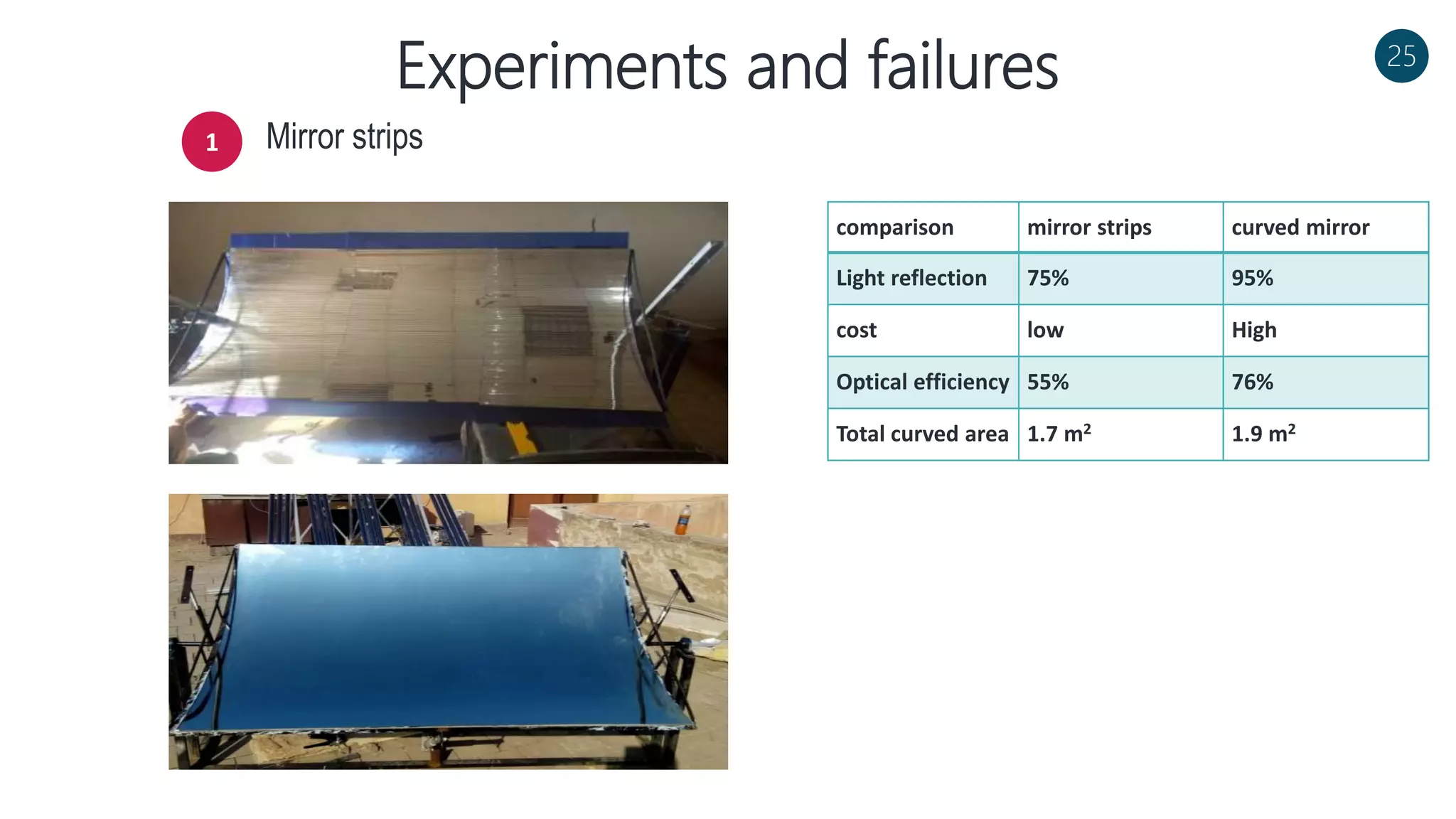
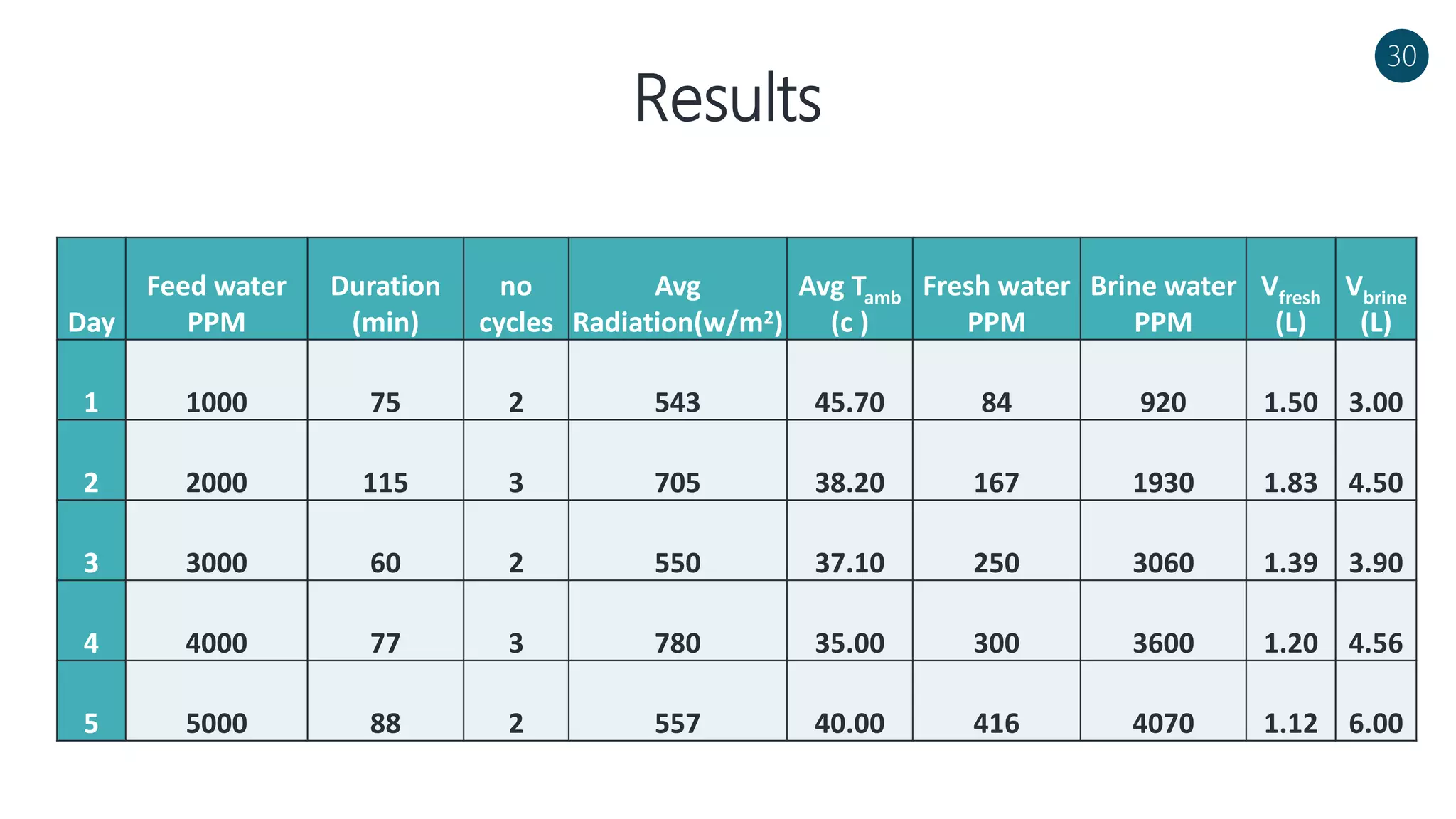
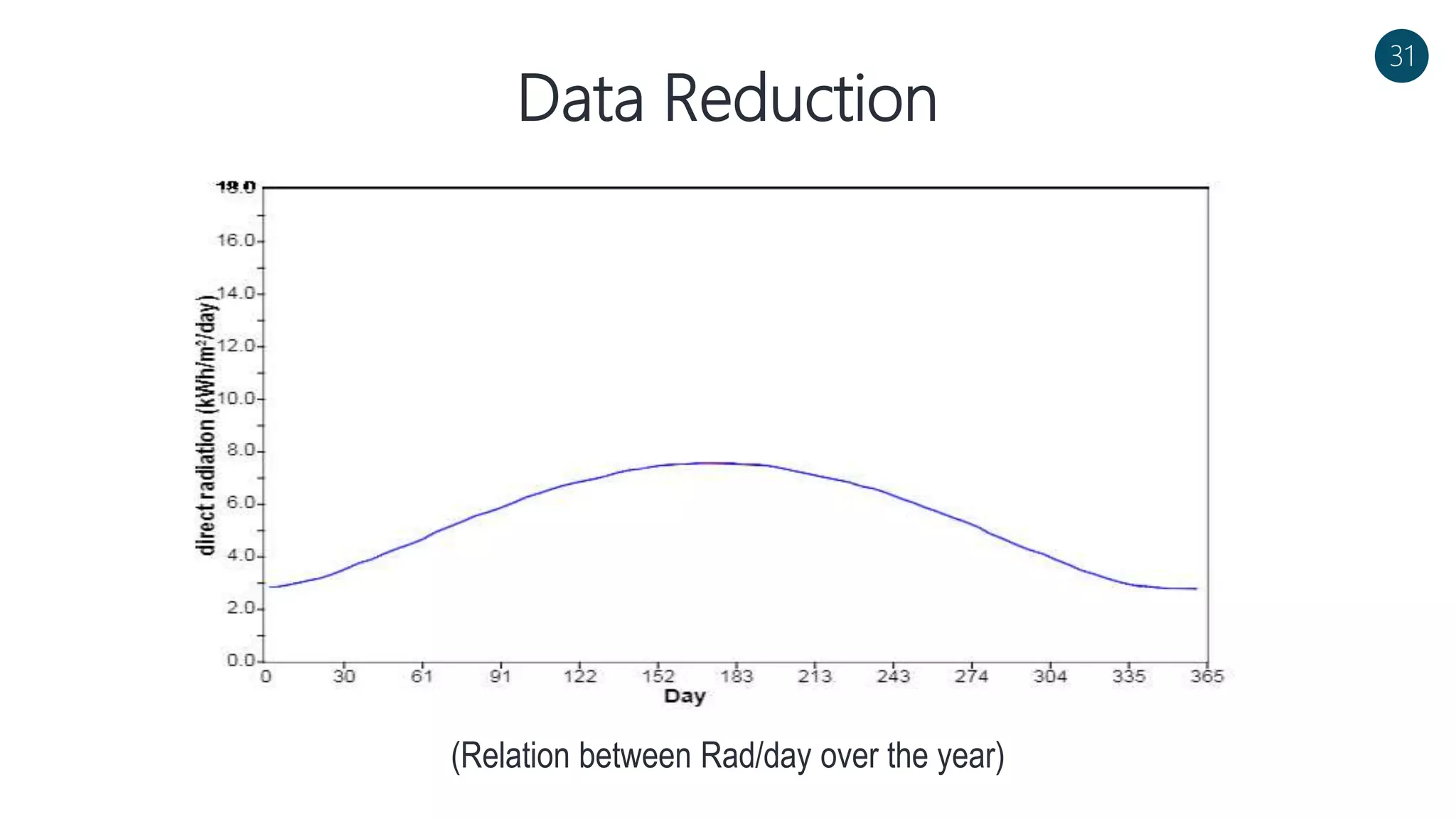
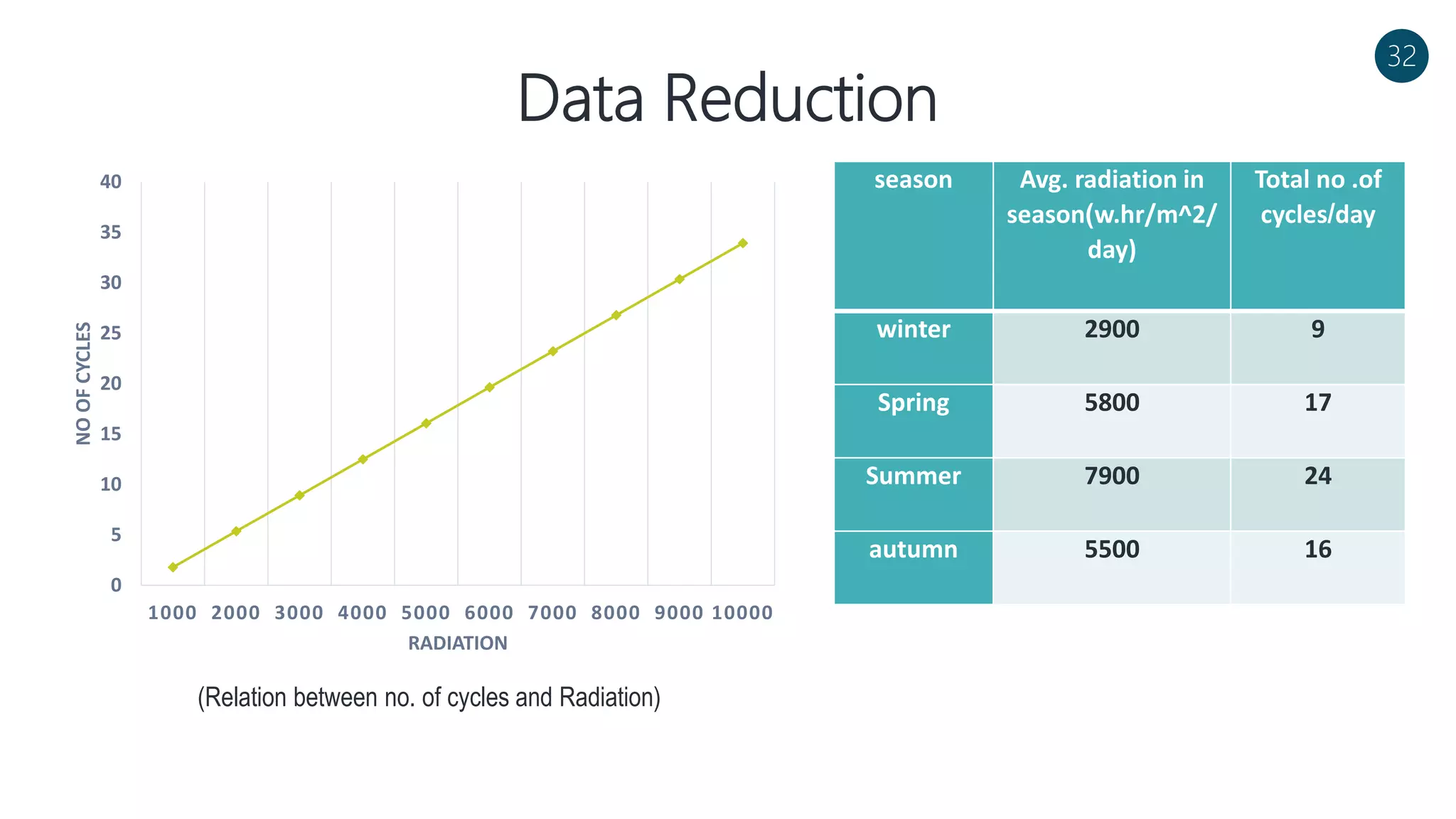
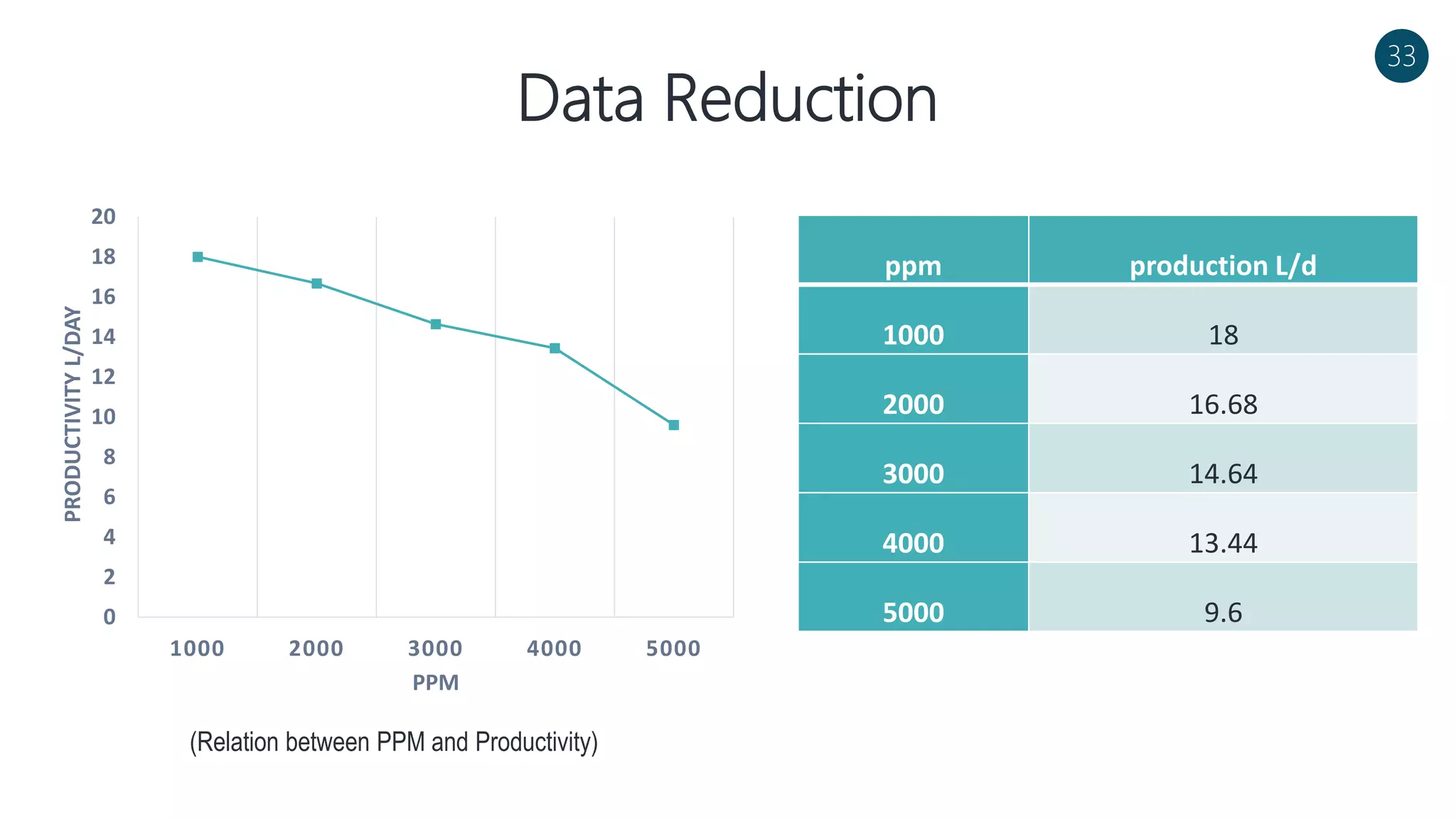
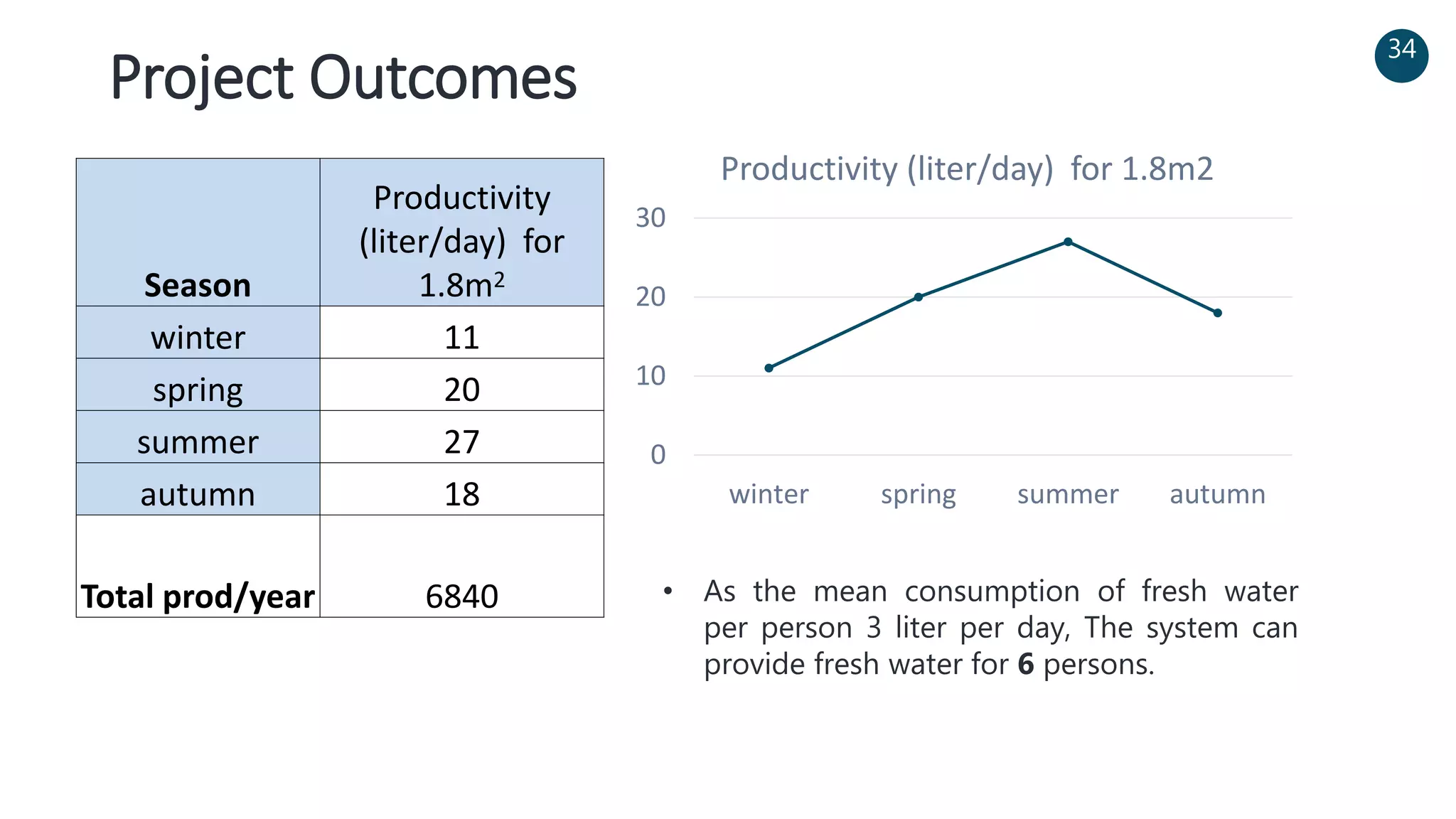
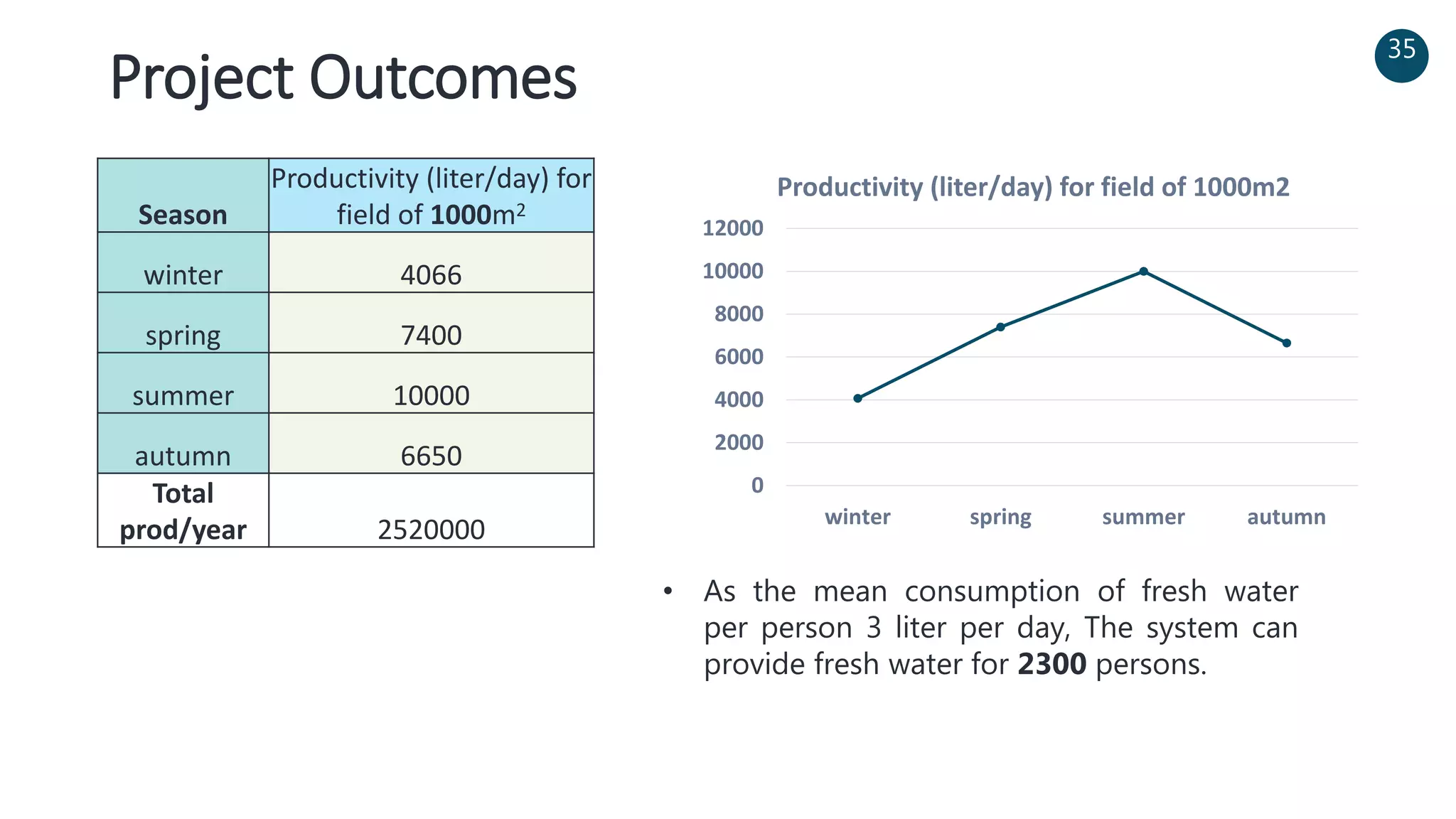
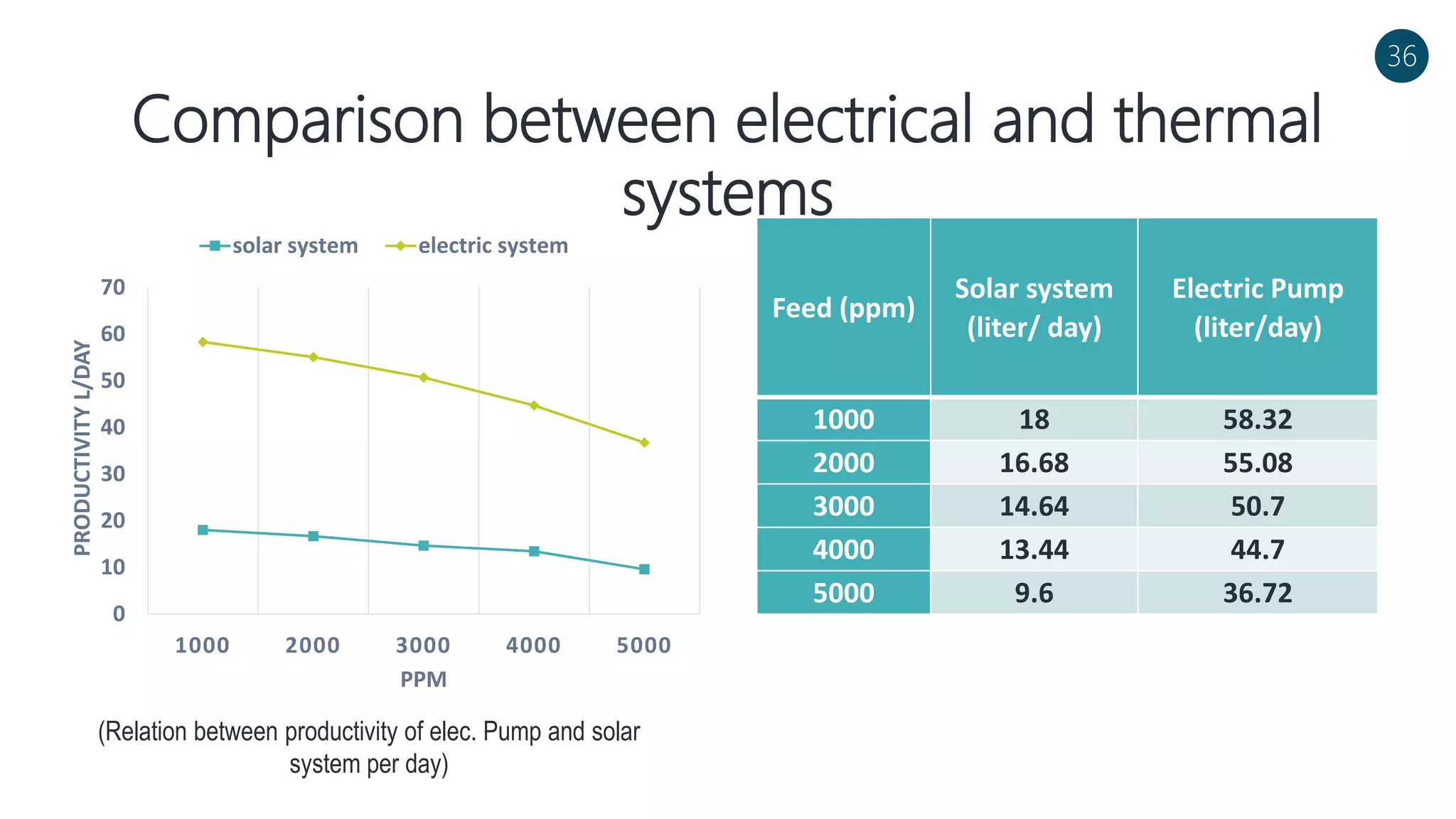
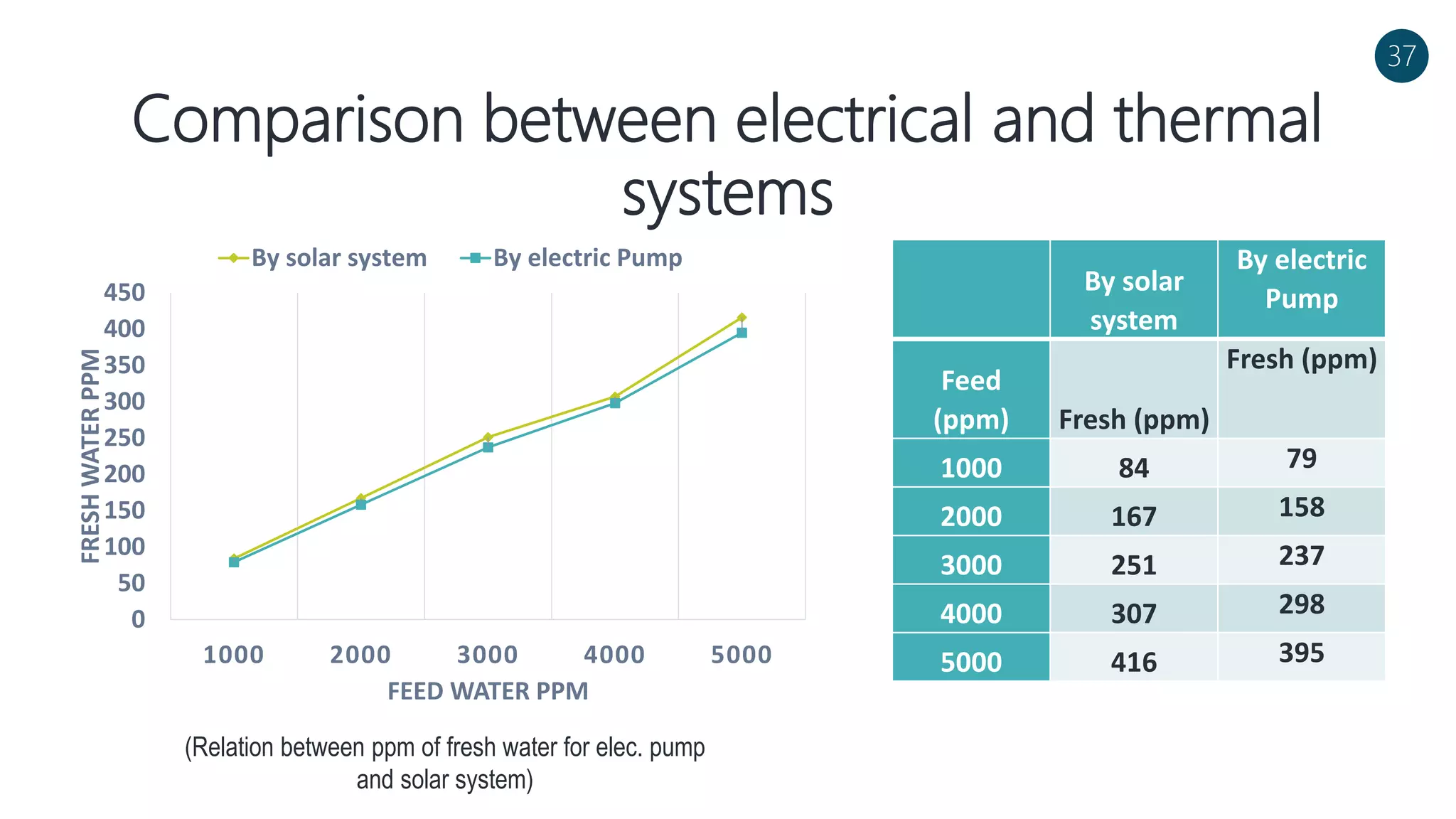
The document discusses a solar-powered water desalination unit designed to address fresh water scarcity using reverse osmosis technology. It highlights the advantages of renewable energy, particularly solar energy, as a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, detailing experimental setups, results, and productivity outcomes. The system aims to provide a significant amount of fresh water while reducing pollution and production costs.