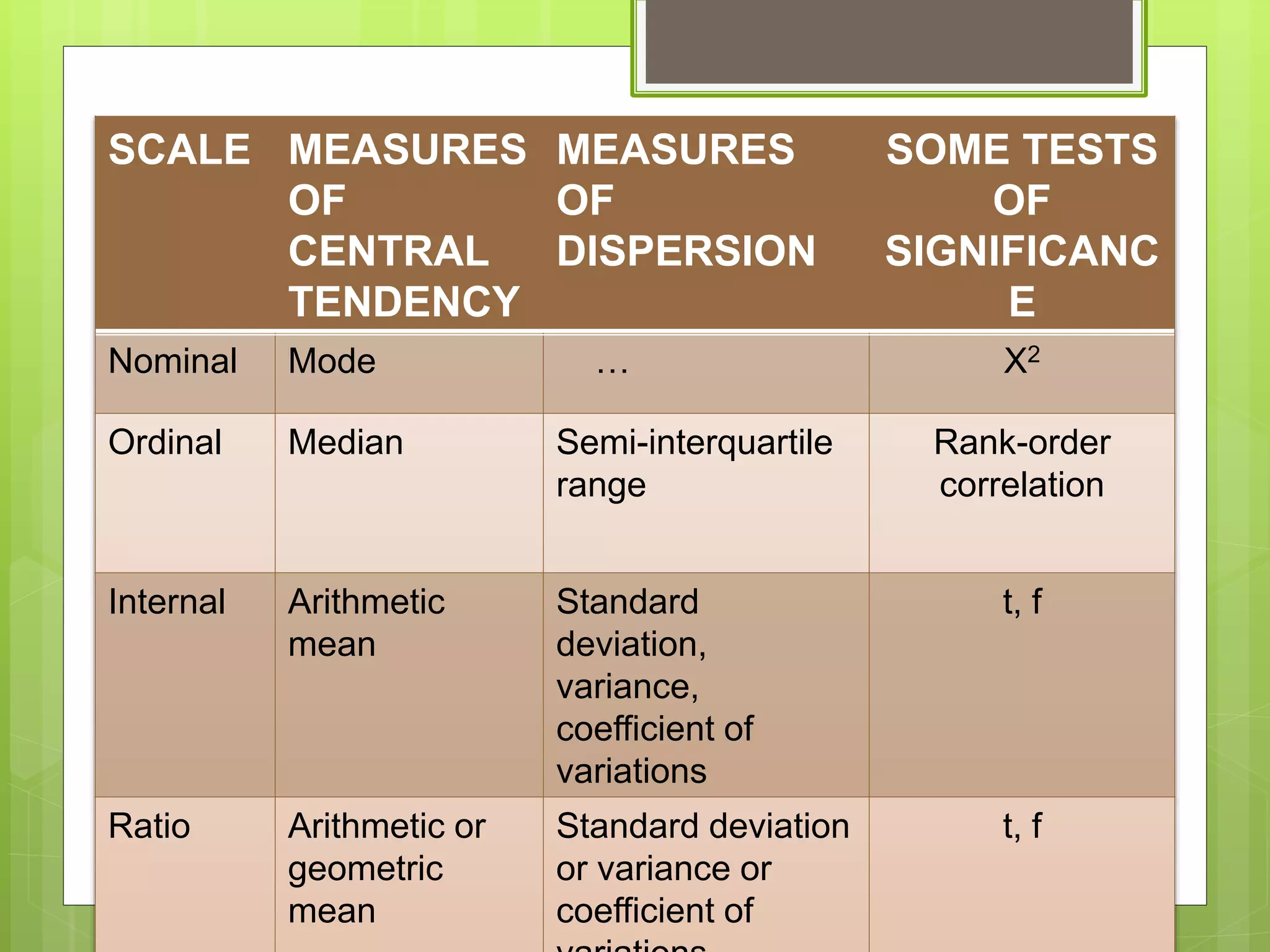
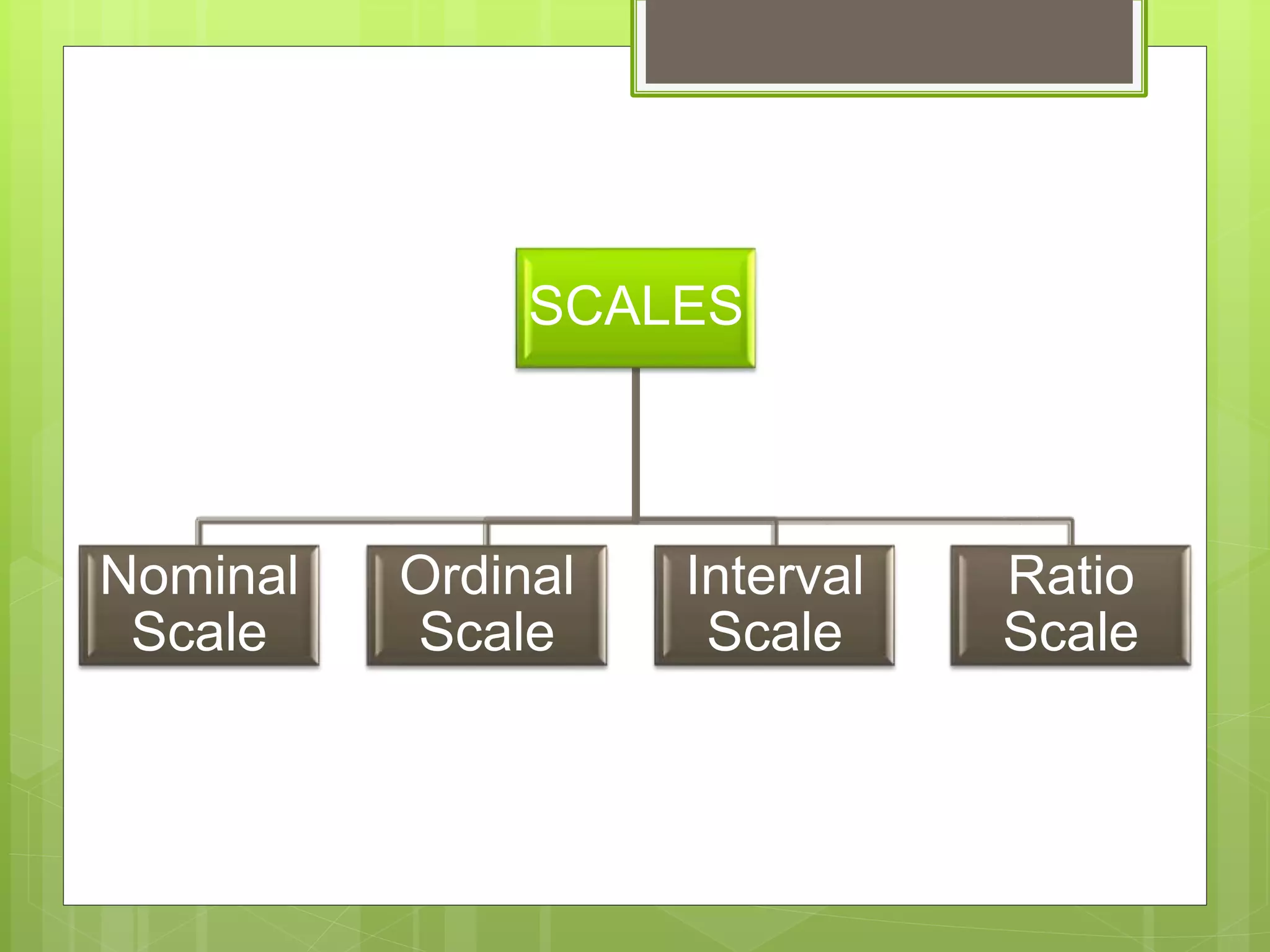
Scales are tools used to measure how individuals differ on variables of interest. There are four main types of scales: nominal scales assign subjects to categories, ordinal scales denote differences and rank categories, interval scales allow arithmetic operations on data, and ratio scales measure magnitude and proportions of differences. Examples provided include using Likert scales to rate agreement, ranking apps, and comparing boys and girls in a ratio. Various other scale types were also outlined such as dichotomous, category, semantic differential, numerical, Stapel, graphic rating, and forced choice scales. The presentation concluded with describing measures of central tendency and dispersion that correspond to each scale type, along with some common tests of significance.







![Semantic differential scale
• several bipolar attributes are identified
• respondents are asked to indicate their attitudes
For example: Courageous Timid
Honest
Dishonest
Numerical scale
• The scale provides number on a five-point or seven
point
• with bipolar adjectives at end
For example: Honest [7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ] Dishonest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rmtypesofscaling-150915090811-lva1-app6891/75/Research-Methodology-types-of-scale-9-2048.jpg)