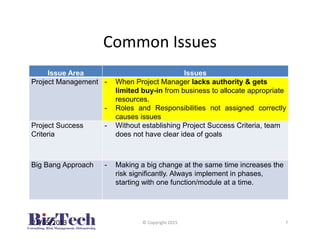
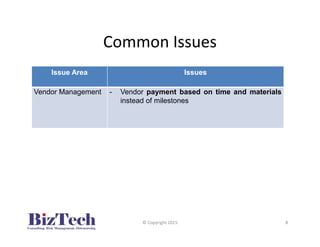
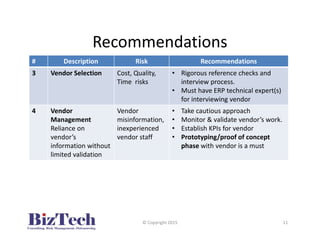
This document outlines recommendations for managing risks associated with ERP implementations based on common issues observed. It recommends establishing clear business requirements, selecting experienced implementation vendors through rigorous evaluations, implementing in phases, establishing milestones-based payments, and conducting comprehensive testing. Strong project management with well-defined roles and executive support are also advised to help ensure ERP implementations meet expectations.