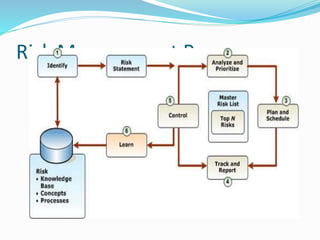
Risk management involves identifying and assessing risks, then minimizing their impact or maximizing opportunities through coordinated resource allocation. Risks can arise from uncertainty in markets, project failures, credit, disasters or attacks. The risk management process involves identifying risks, analyzing and prioritizing them, planning risk management strategies, tracking risk status and reporting, controlling risk through action plans, and learning lessons to improve the process.