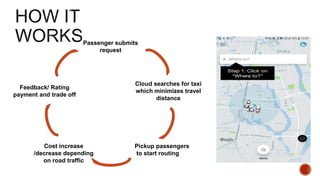
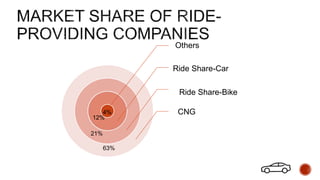
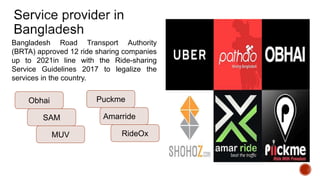
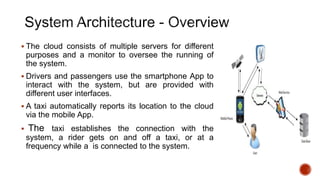
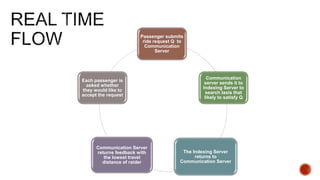
The document reviews ride-sharing platforms in Bangladesh, highlighting their impact on sustainable transport, market opportunities, and employment creation while addressing challenges like unprofessional drivers and inconsistent fare structures. It discusses the legal framework, including government regulations and tax issues, and the growth in ride-sharing services since the pandemic. Future success relies on improving service quality, addressing regulatory hurdles, and expanding reach to other cities.