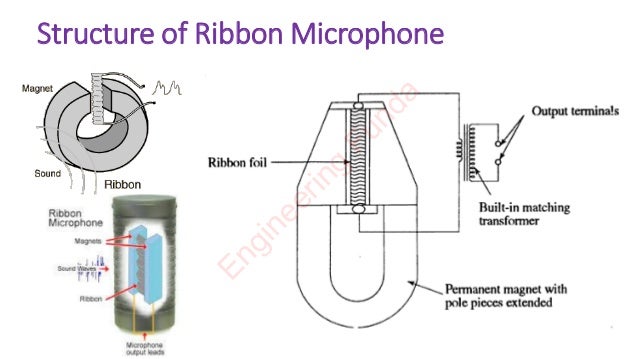
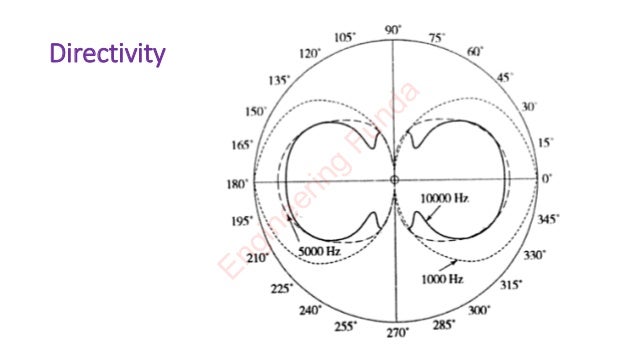
This document discusses the ribbon microphone. It describes the ribbon microphone's structure, which uses a lightweight aluminum ribbon placed in a magnetic field to function as both a conductor and a diaphragm. The ribbon microphone has a wide frequency response from 20-12,000 Hz due to its light ribbon. It has a figure-eight directivity pattern and is commonly used for drama recordings due to its ability to capture sound from both the front and back with dead sides.