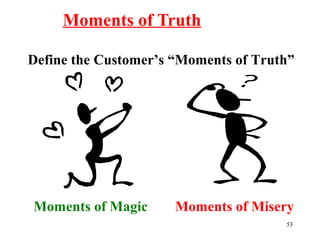
The document outlines the evolution and current trends of retailing in India, emphasizing the importance of customer engagement and satisfaction. It discusses various retail formats, store operations, and the role of technology in enhancing customer experiences. Additionally, it highlights the significance of service quality and effective complaint management in maintaining customer loyalty.