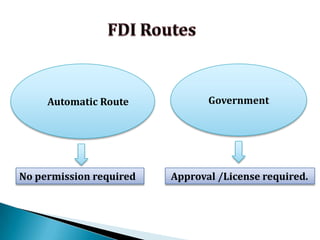
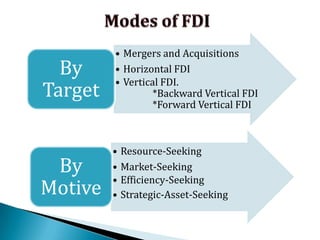
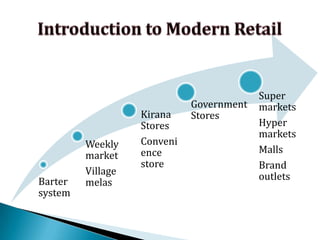
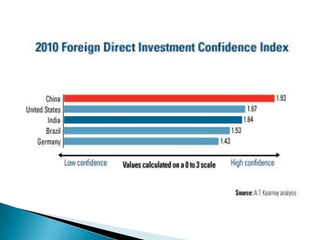
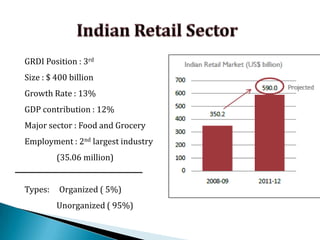
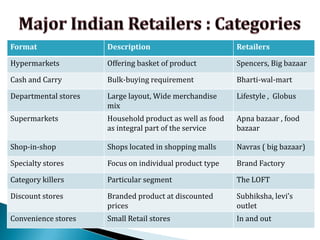
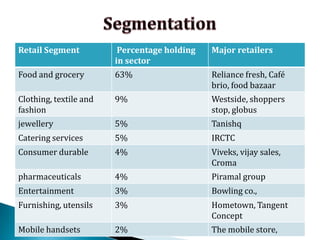
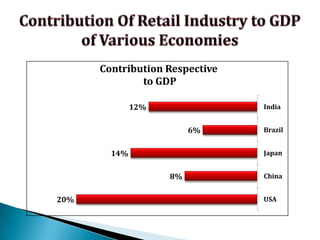
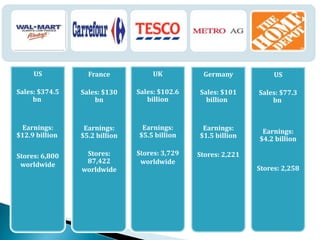
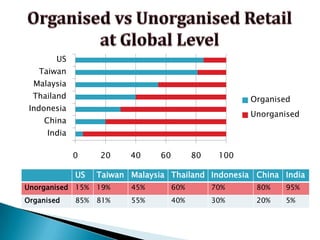
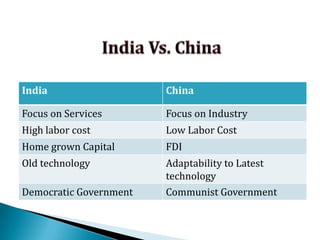
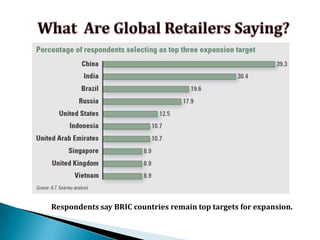
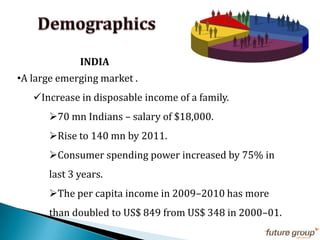
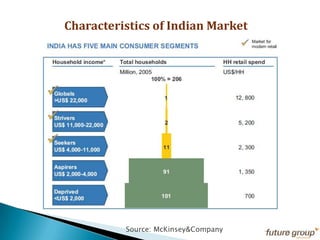
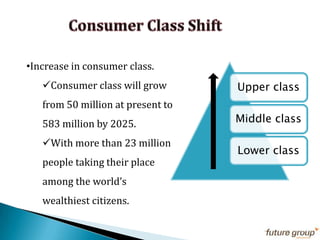
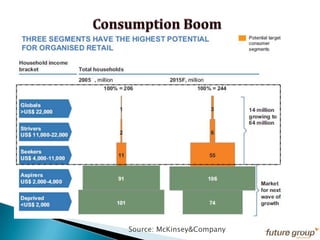
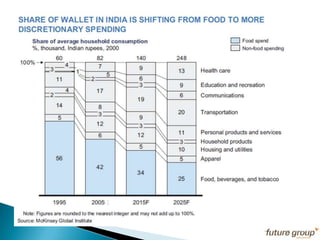
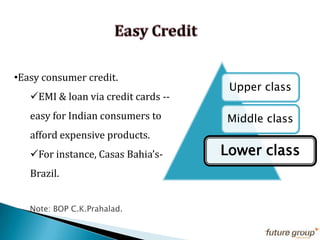
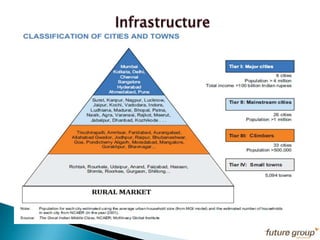
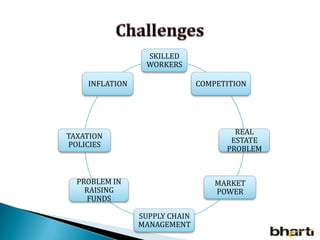
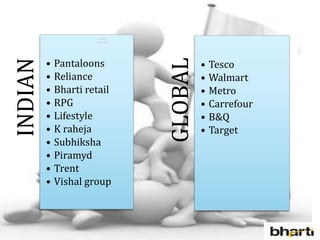
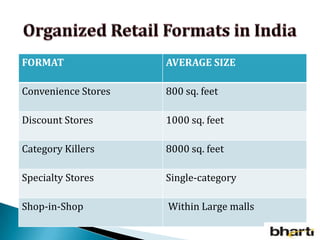
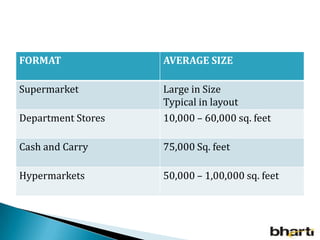
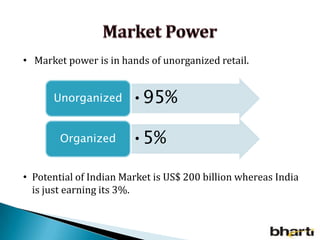
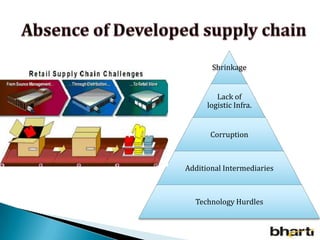
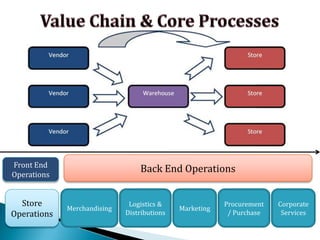
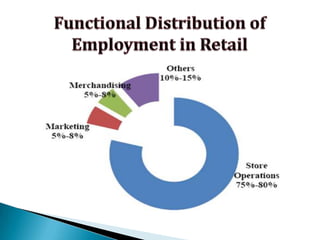
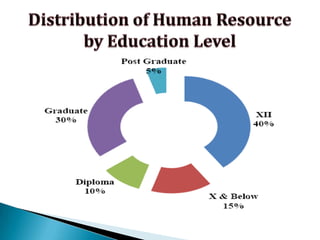
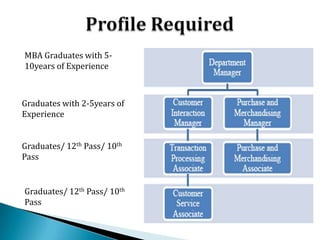
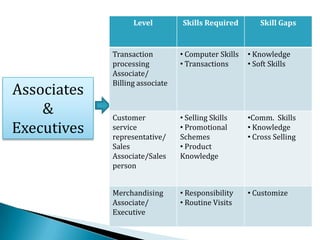
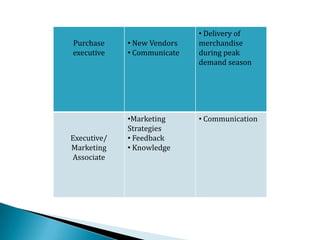
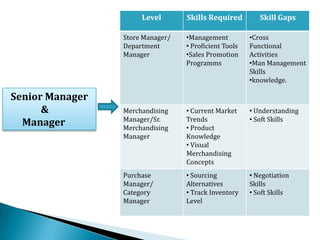
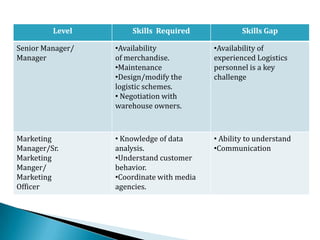
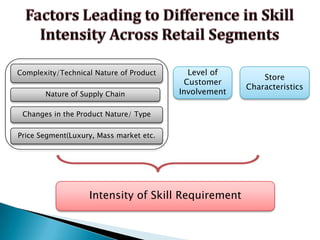
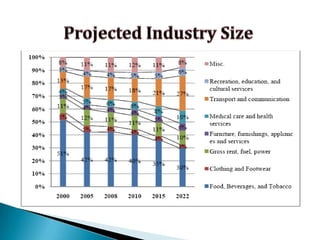
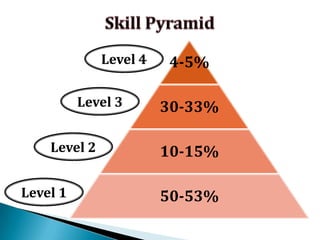
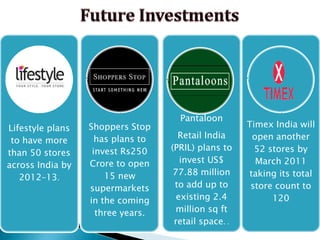
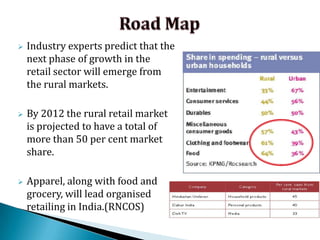
FDI in the retail sector in India presents both opportunities and challenges. It could boost the supply chain and bring investment in technology and skills development. However, there are concerns about the impact on small retailers and employment. If regulated properly with a gradual opening and conditions on investment in rural areas, FDI could benefit farmers and consumers while curbing inflation. The human resource challenges include developing skills to match the demands of the modern organized retail sector. Overall, FDI in retail has the potential to modernize retail and improve efficiency if risks are mitigated and inclusive growth is ensured.