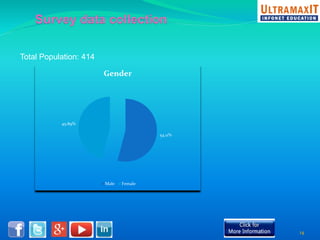
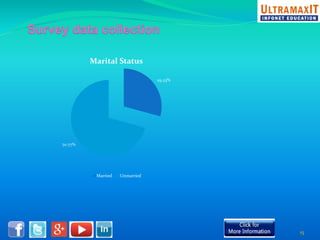
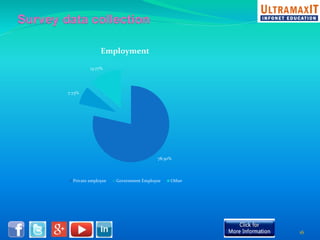
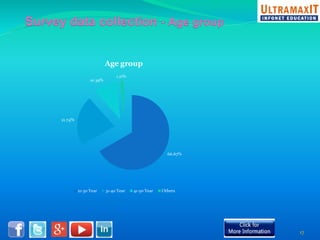
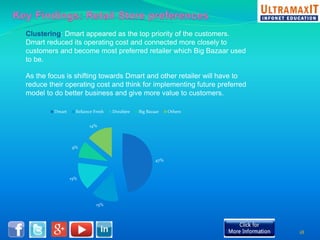
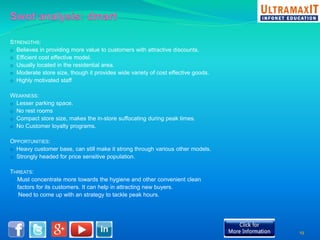
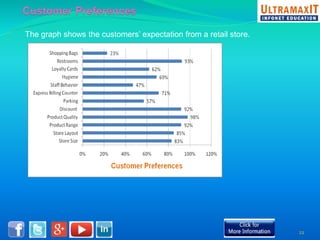
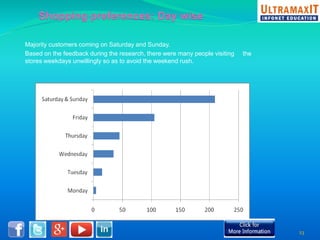
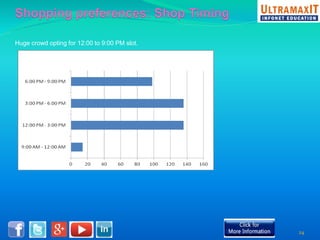
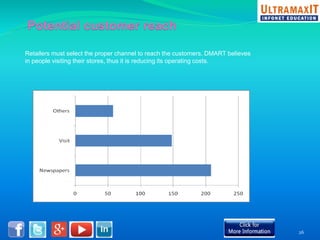
India's organized retail sector, valued at INR 16 trillion, is rapidly growing but faces challenges such as high operational costs, increased competition, and customer loyalty issues. Key insights from the analysis include the impact of unviable retail formats, significant lease costs, and the need for better backend investment. The report emphasizes the importance of adapting retail strategies through analytics to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency while exploring eco-friendly models to reduce costs.