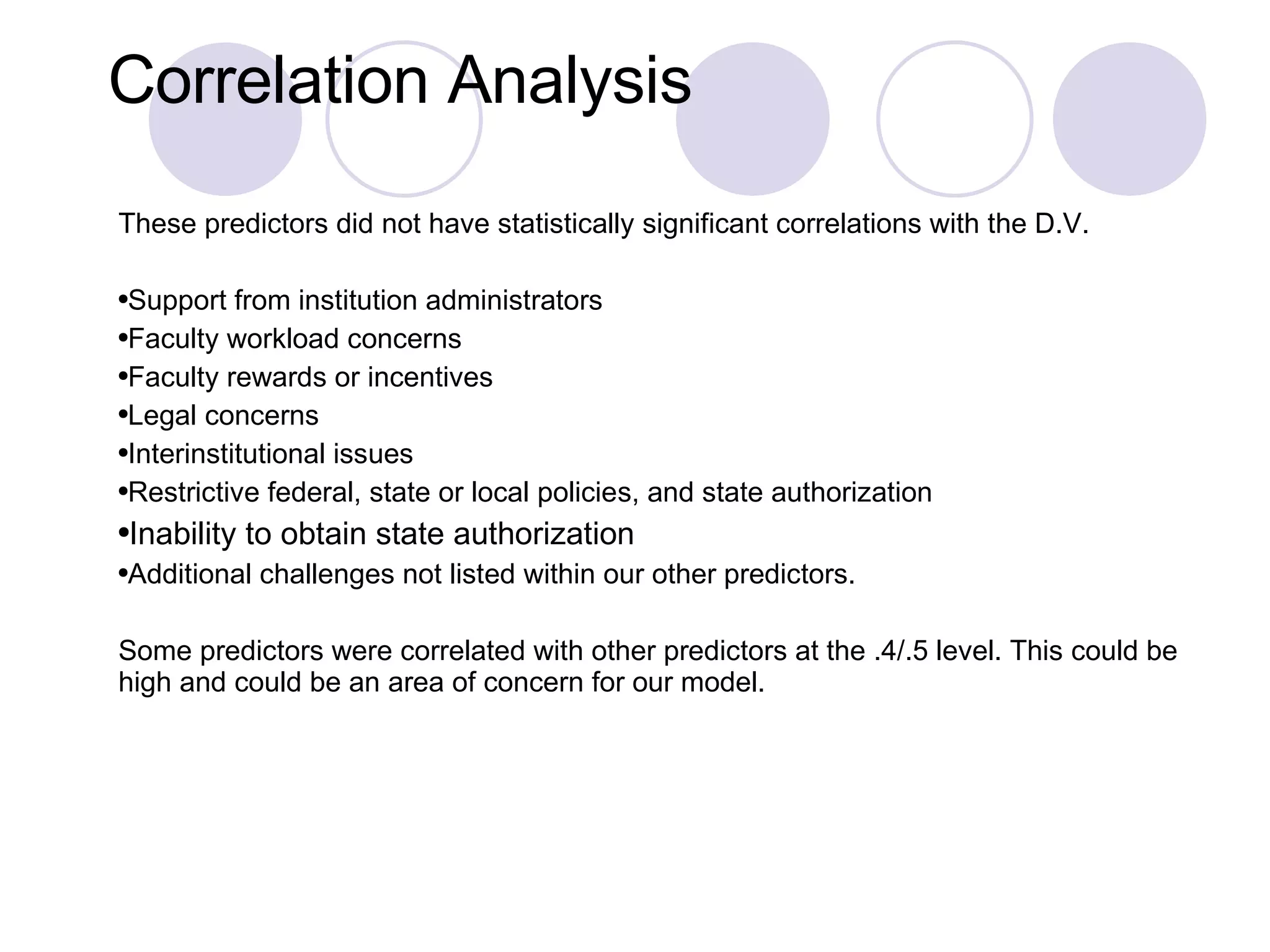
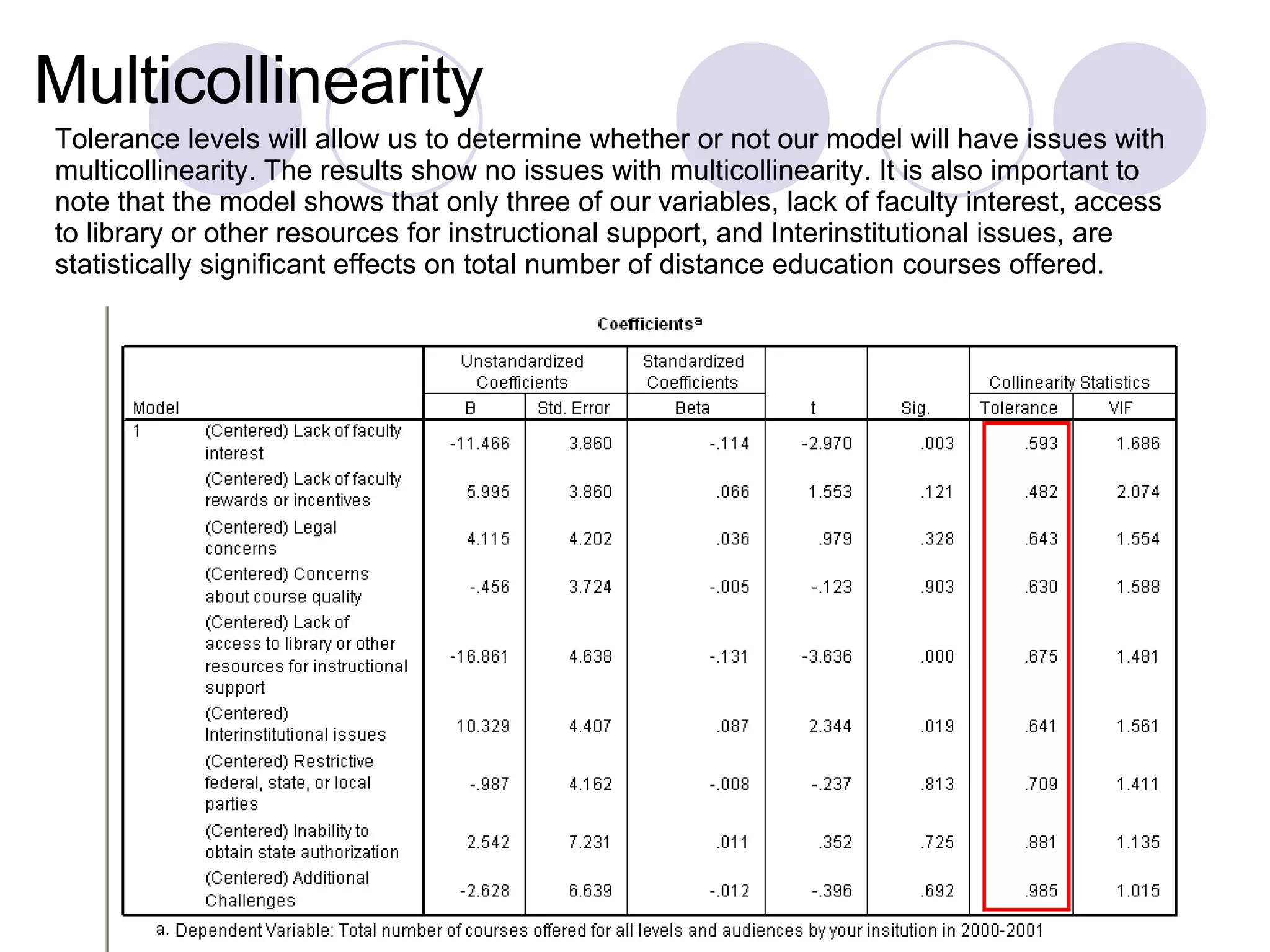
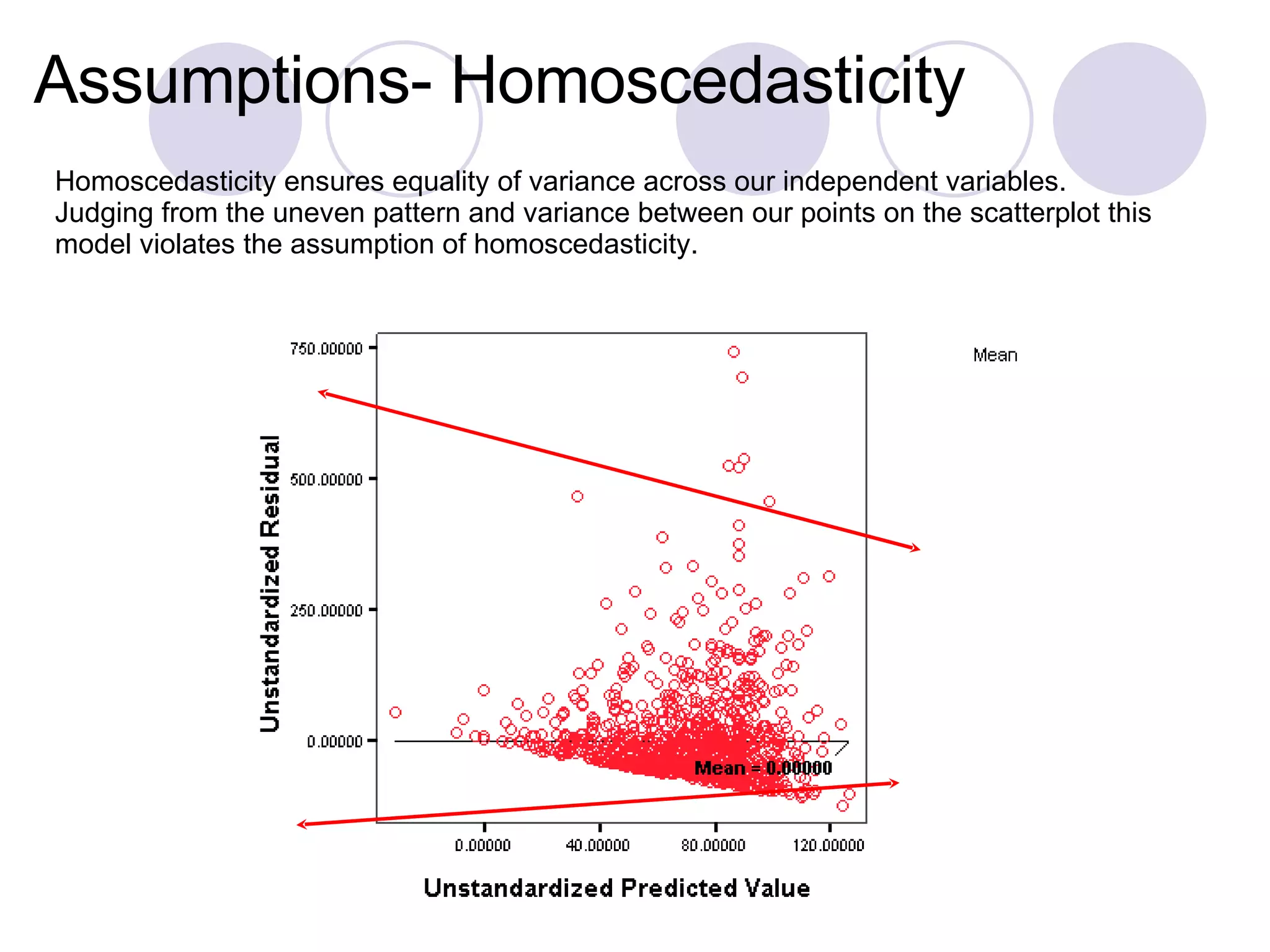
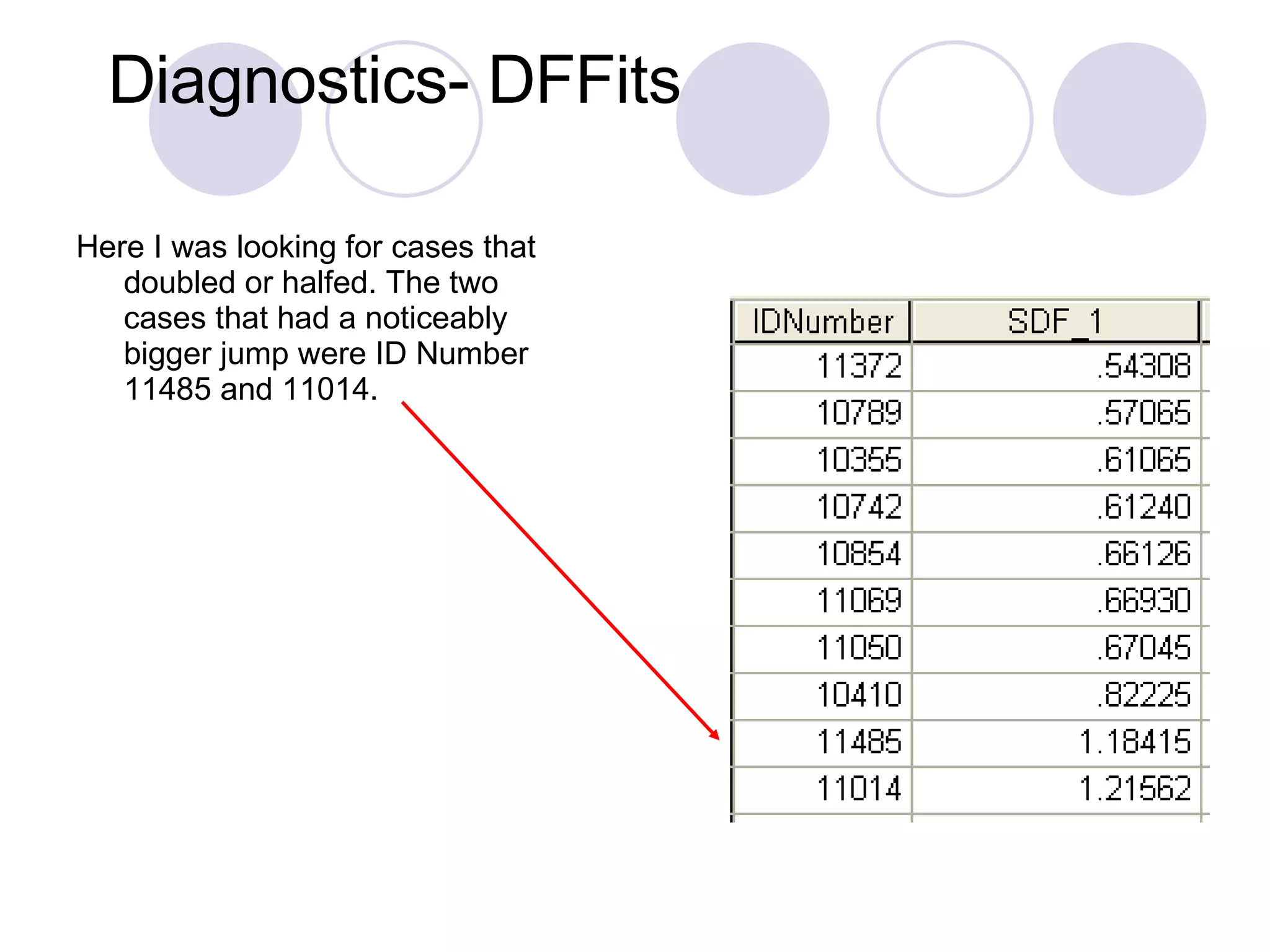
This study examines 16 factors that may influence institutions' decisions to offer distance education programs. The researcher analyzed data from 1,500 institutions regarding their distance education offerings in 2000-2001. The regression model found that lack of faculty interest, limited access to instructional resources, and interinstitutional issues significantly impacted the number of distance education courses offered. However, the model violated assumptions of homoscedasticity and normality of residuals, indicating the relationships may not be reliable. Further analysis of outliers and interactions showed some cases had disproportionate influence on the model.