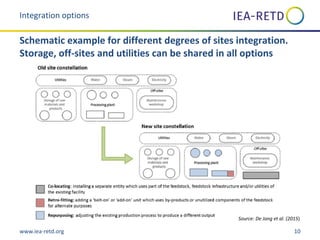
This document summarizes a study on integrating conventional (1st generation or 1G) and advanced (2nd generation or 2G) biofuel production sites. The study analyzed the technical feasibility and costs/benefits of integration options like co-location, retrofitting, and repurposing existing 1G sites for 2G biofuel production. It found that integrating 2G bioethanol production is more feasible than biodiesel production and can provide cost savings of 5-10% through improved resource efficiency. However, further research is still needed to fully understand the economic potential of specific integration strategies and their impacts.