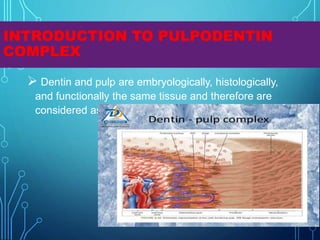
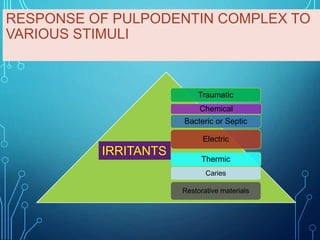
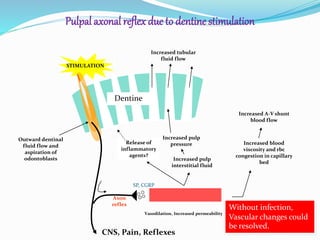
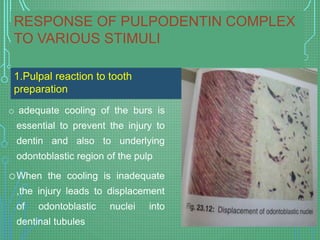
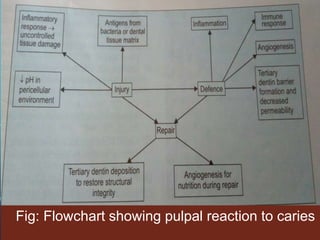
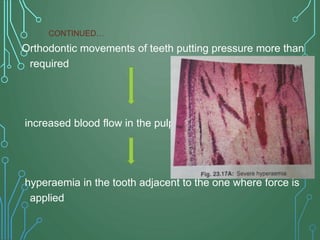
The document presents an overview of the pulpodentin complex and its responses to various stimuli, including traumatic, chemical, and thermal factors. It highlights the interdependence of dentin and pulp tissue, detailing how external factors like restorative materials and caries can provoke inflammatory responses or degeneration of the odontoblasts. Additionally, it discusses the effects of trauma, orthodontic movements, and local anesthetics on the pulpodentin complex and the potential outcomes of these influences.