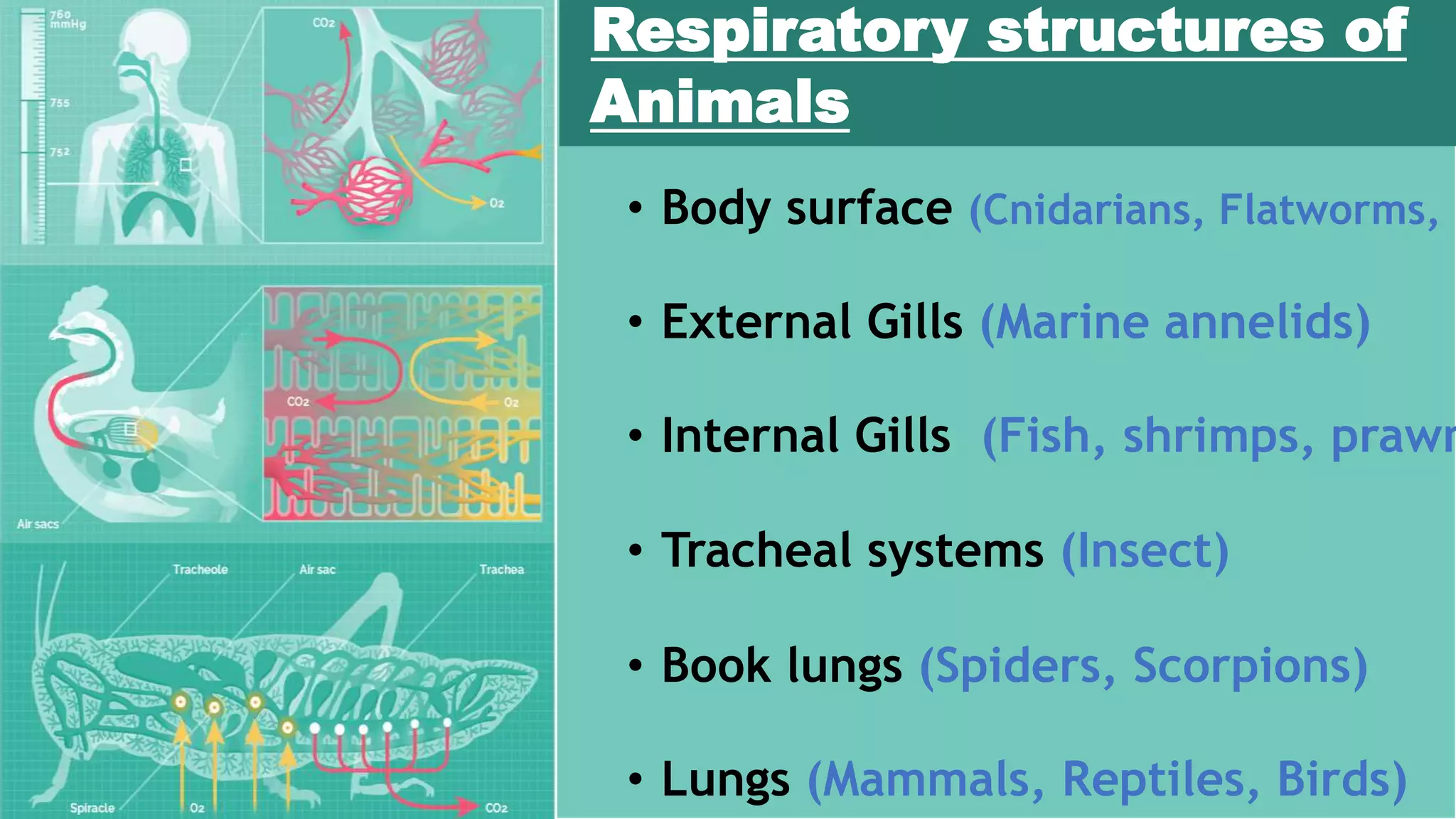
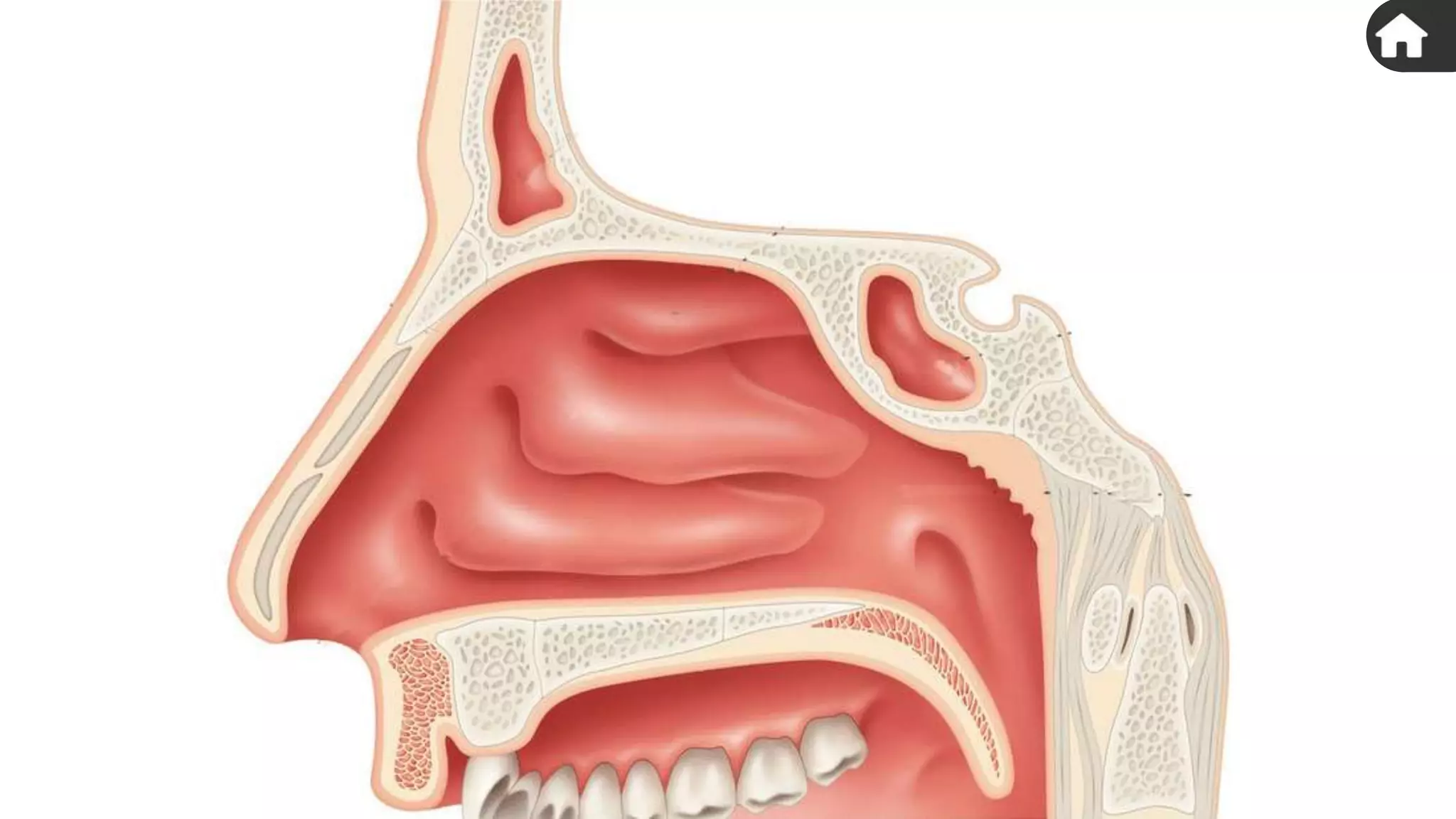
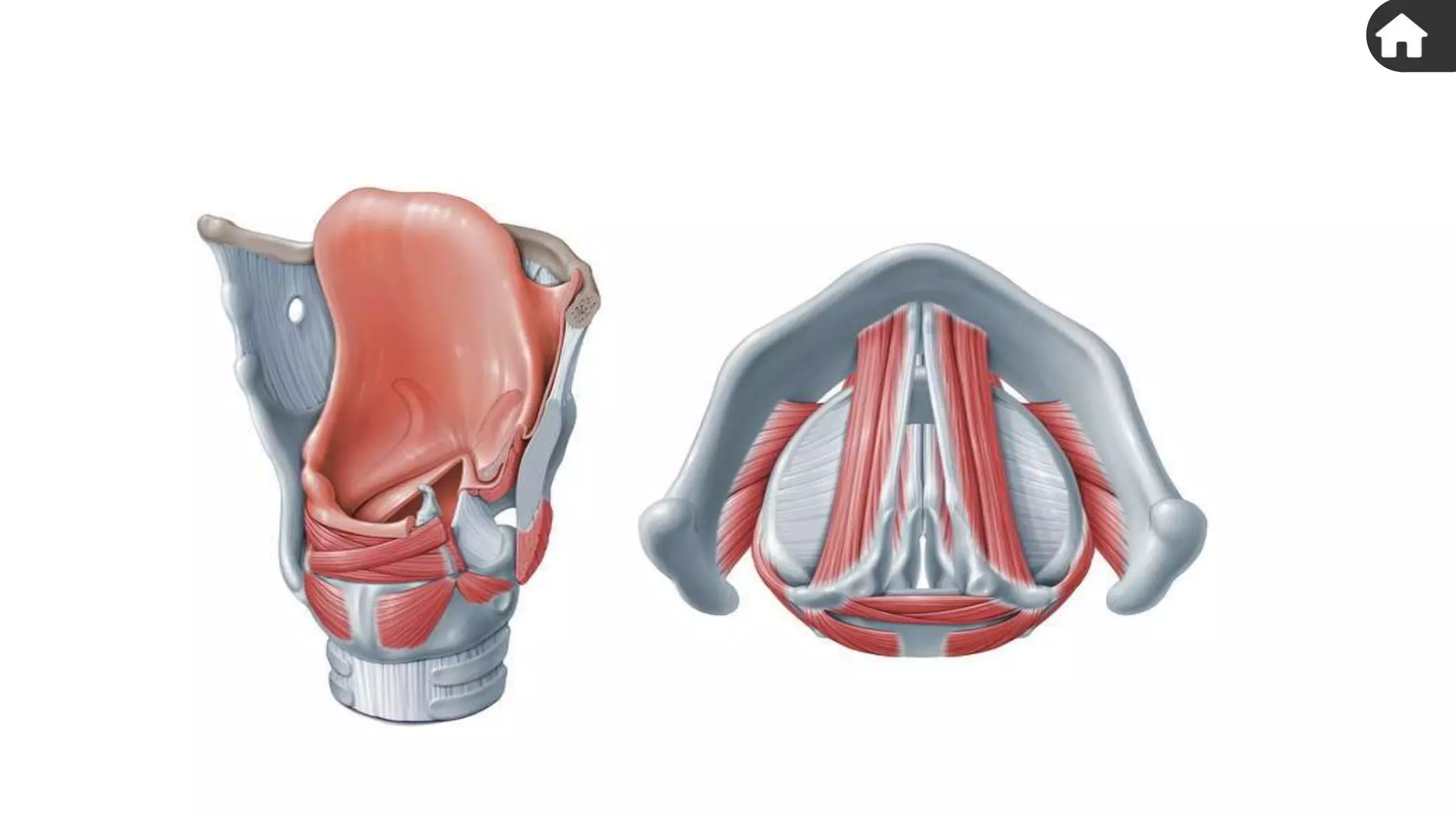
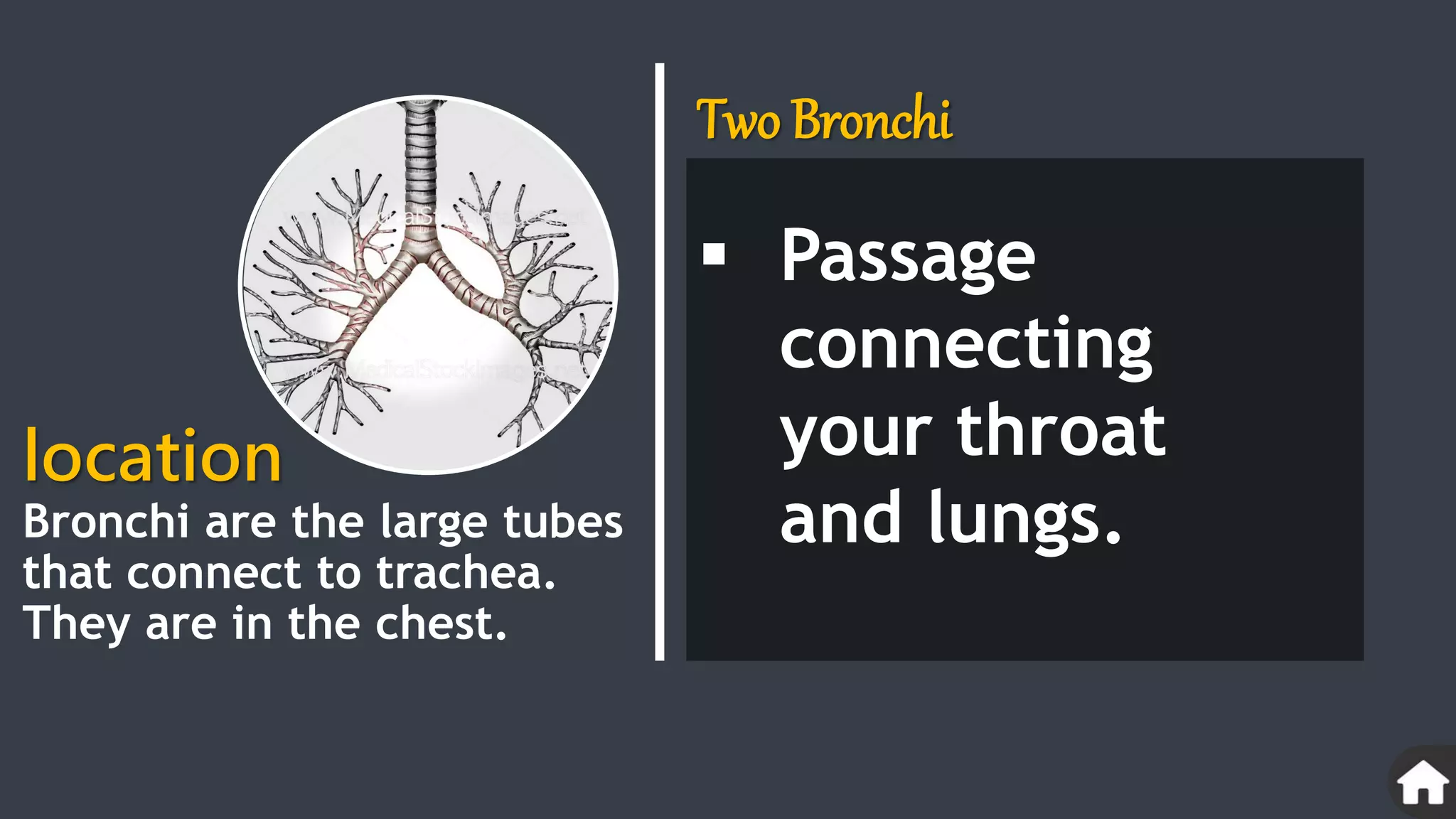
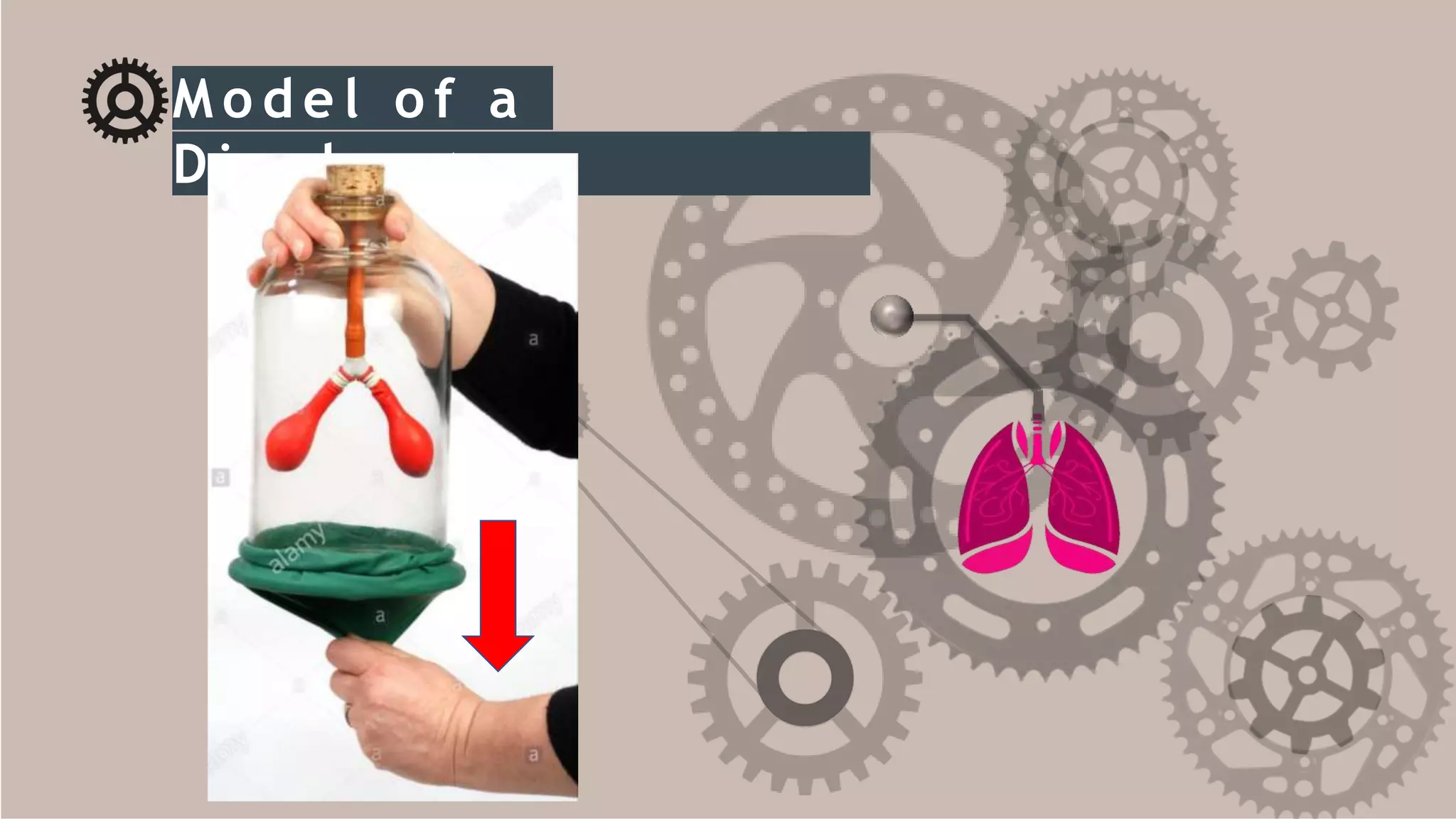
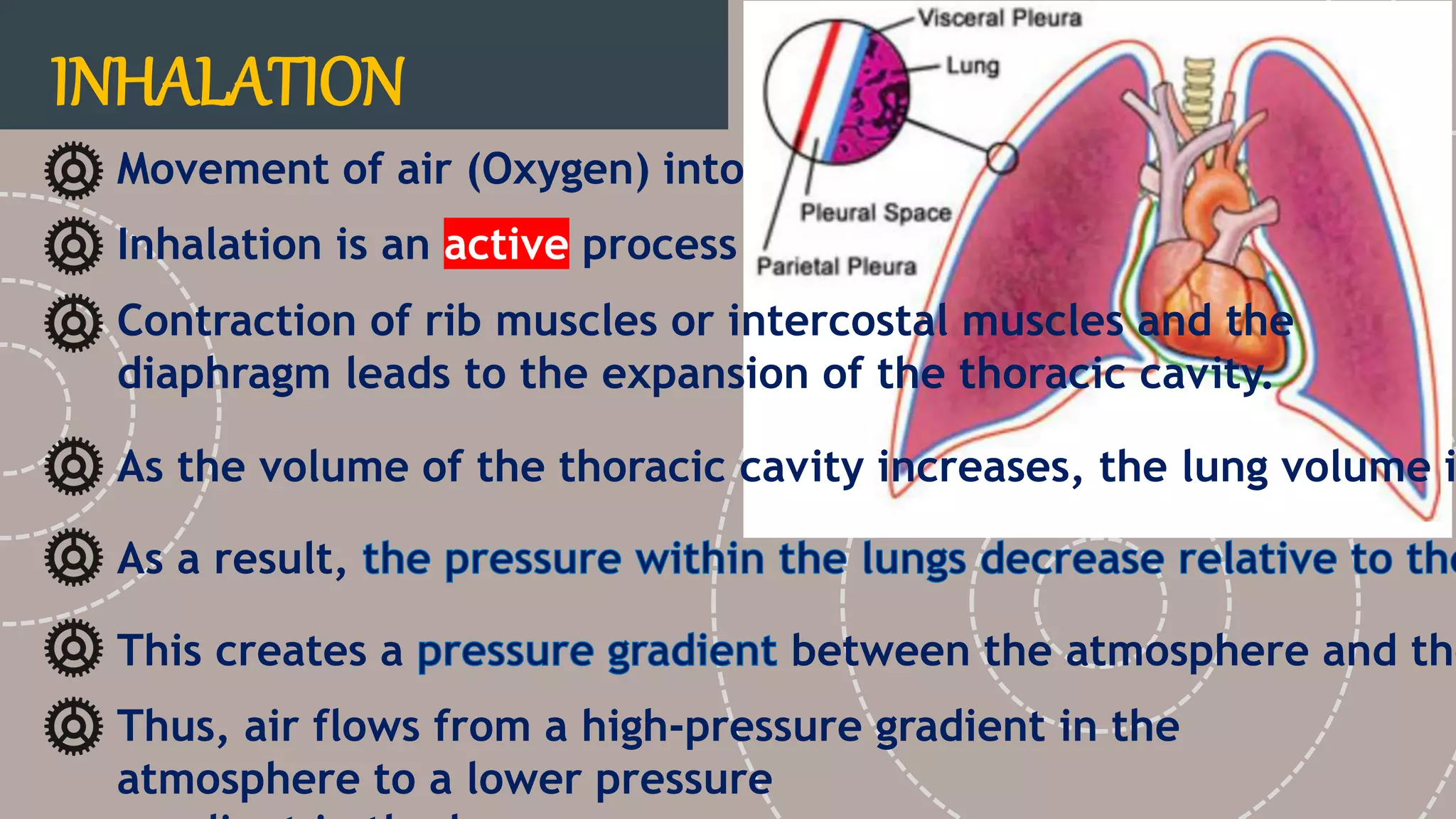
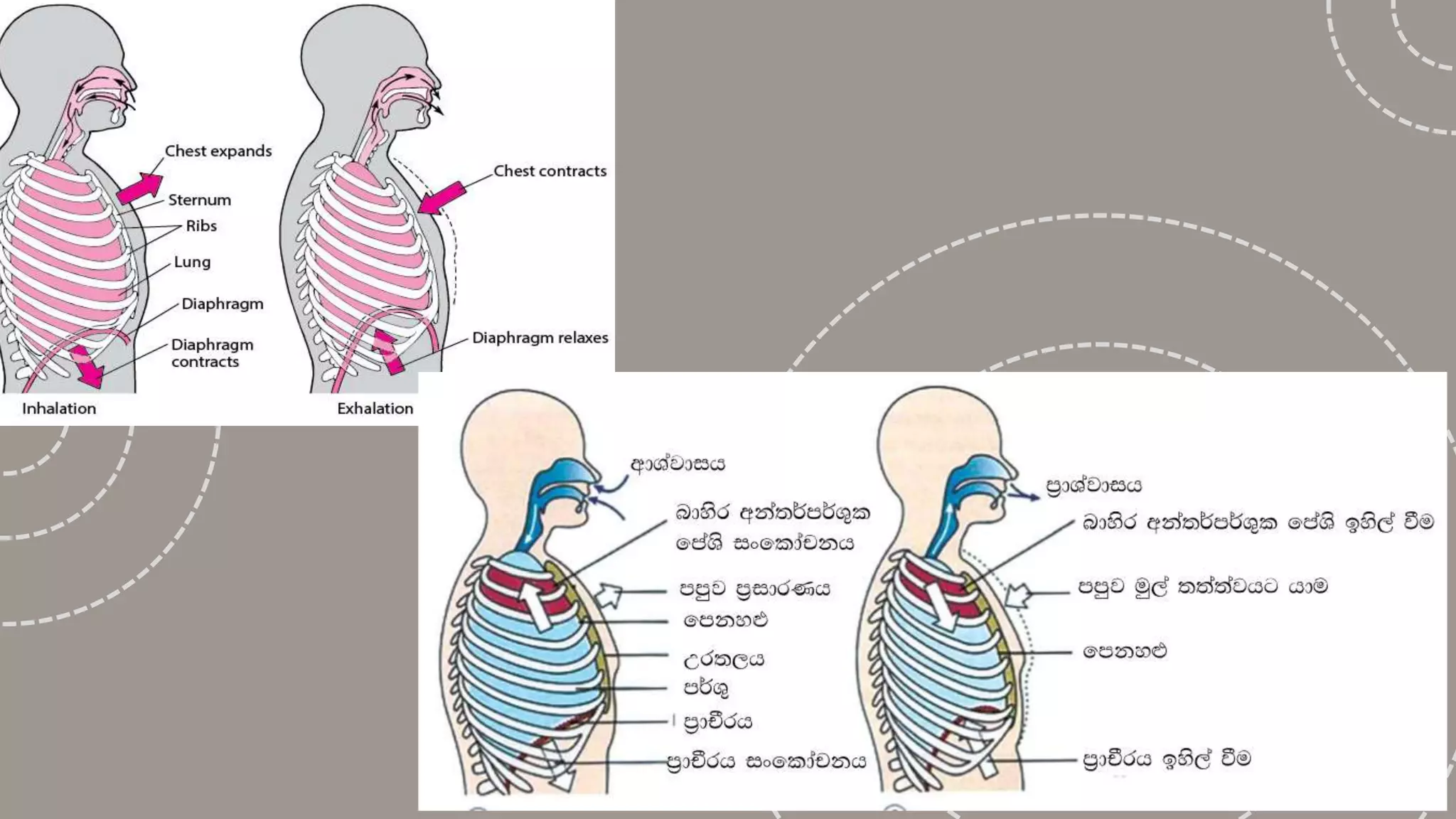
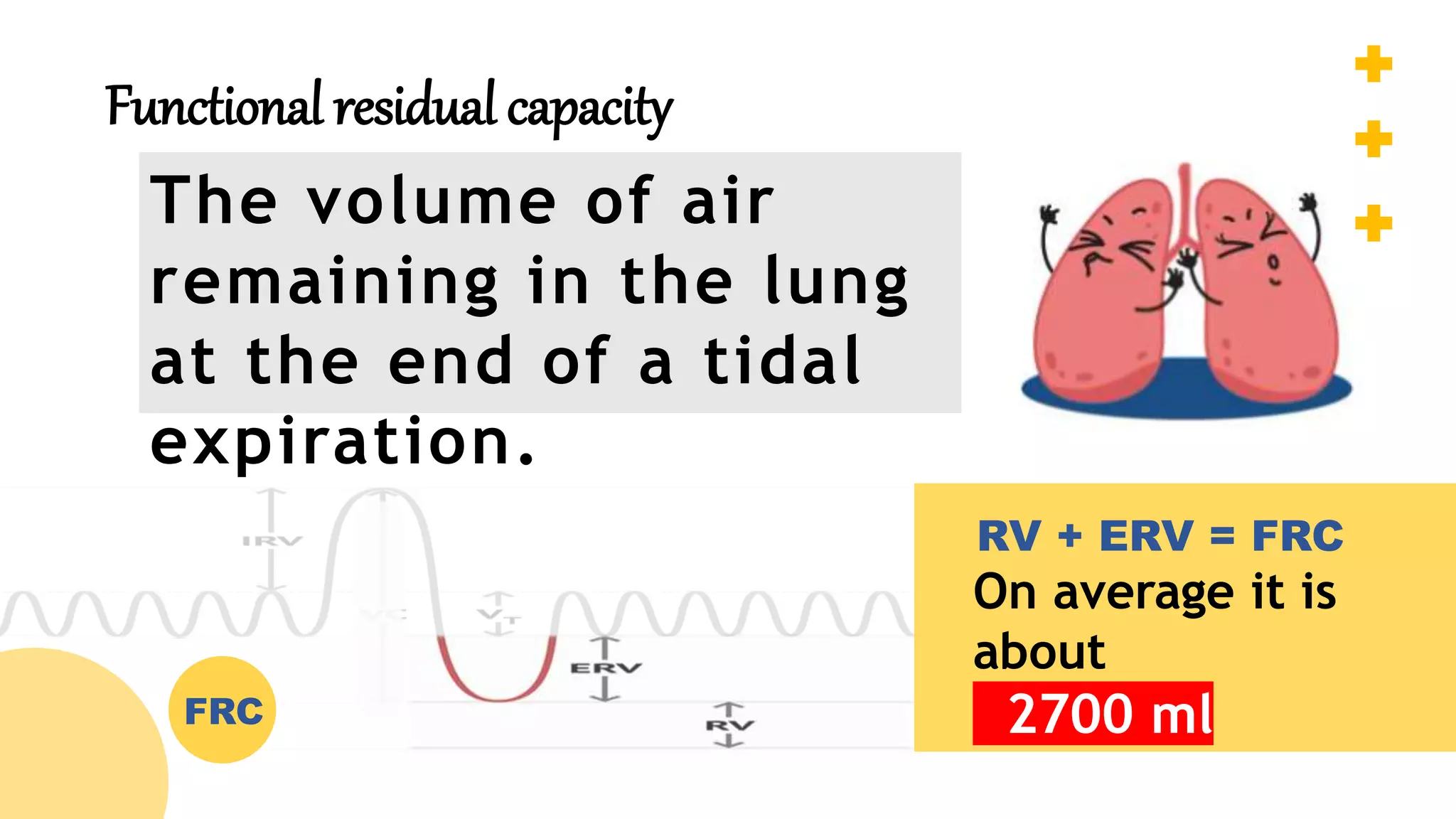
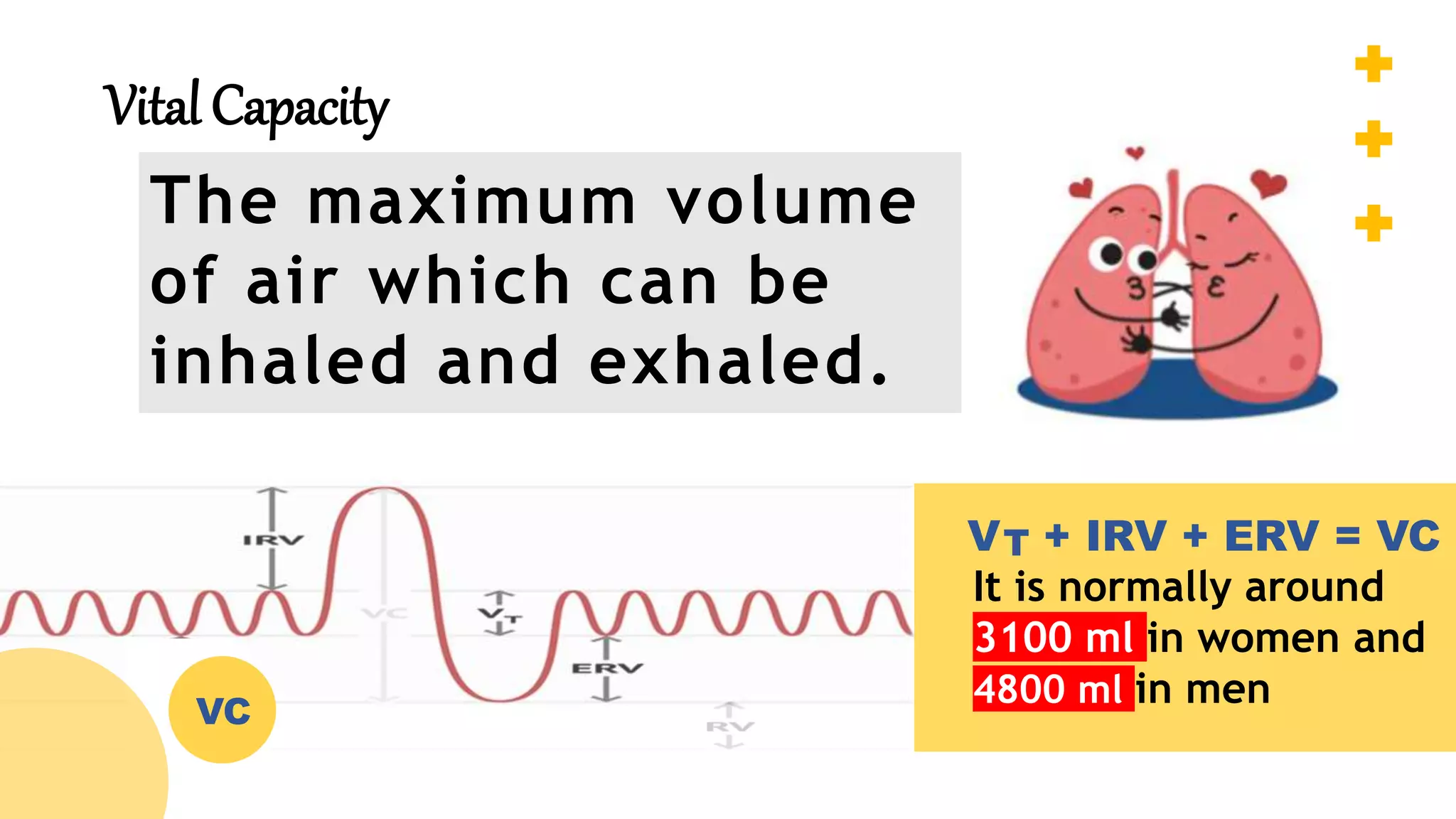
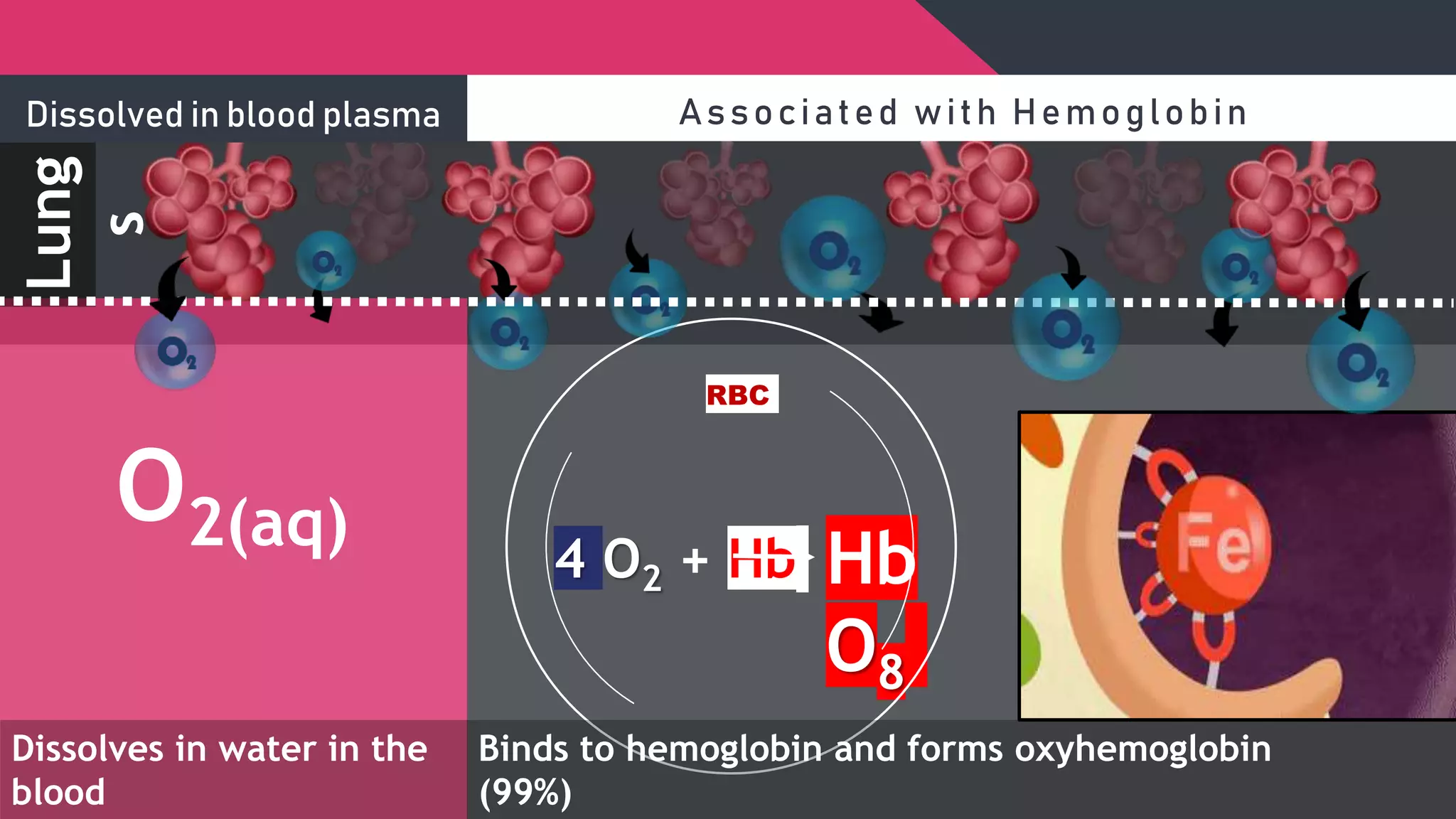
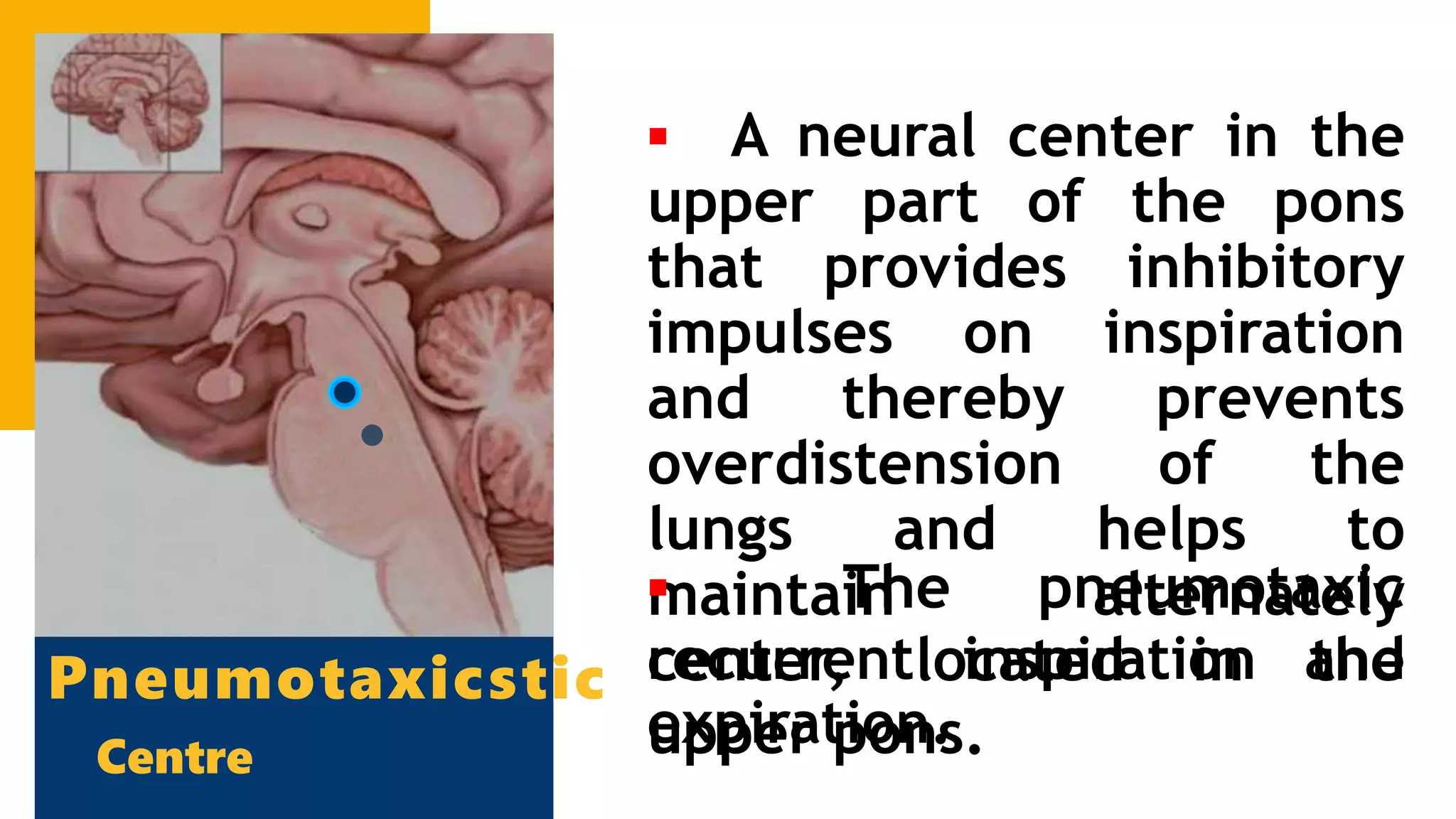
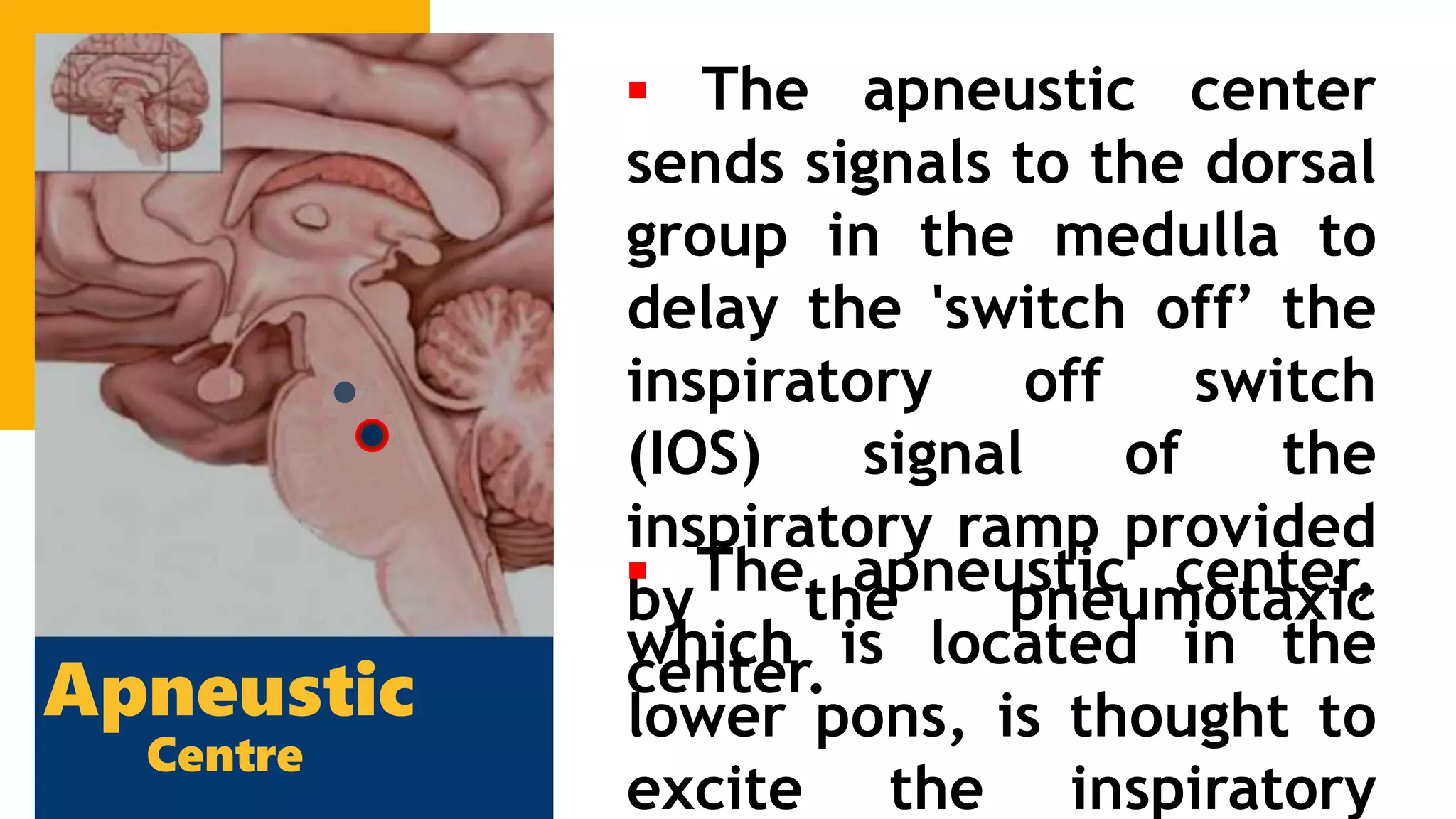
The document describes the human respiratory system, detailing the anatomy and functions of various respiratory structures such as the nose, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, emphasizing the importance of gas exchange. It outlines the processes of inhalation and exhalation, the roles of different lung volumes and capacities, and how gases are transported in the blood. Additionally, the document highlights respiratory disorders, their causes, and the detrimental effects of smoking on lung health.