Respiratory organ in man By Dr. Jayvardhan V Balkhande
- 1. Respiratory organ in man Prepared by Dr. Jayvardhan V Balkhande Assistant Professor Department of Digambarrao Bindu ACS College, Bhokar Dist. Nanded.(Maharashtra) Email: cageculture2014@gmail.com S. R. T. M. University, Nanded. B.Sc. Second Year (Zoology) Sem III
- 2. Respiratory organ in man Respiration is simply defined as the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide into the body. The released energy is utilized to perform various life activities. The metabolic waste like CO2 is removed from the body through lungs.The compounds oxidized in respiration are called respiratory substrates.
- 3. • Respiration is categorized into two types on the basis of site of gaseous exchange: • i. - exchange of gases between lungs and blood. It is the process of absorption of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide from the body through lungs. • ii. exchange of gases between blood and cells. It is the process of utilization of oxygen to produce energy and carbon dioxide by oxidation of food material inside the cell.
- 4. • Respiration is of two types on the basis of availability of oxygen: • i. Aerobic respiration: The process which consists external and internal respiration occurs in higher animals including human beings are called aerobic respiration. • ii. Anaerobic respiration:
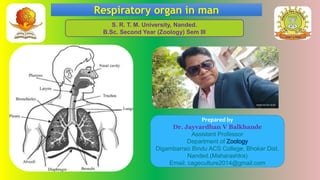
- 5. Respiratory organs Organs involved in respiratory system are: • 1.Nose and nasal cavity • 2.Pharynx • 3.Larynx • 4.Trachea • 5.Bronchi • 6.Lungs • 7.Alveoli
- 6. 1. Nose and nasal cavity Nose is a part of respiratory tract lying above mouth. It is made by hyaline cartilage.It is divided into right and left nasal cavity by nasal septum. Its anterior portion is cartilaginous and posterior portion bony. The nasal cavities open outside through nostrils or external nares. The nasal cavities open posteriorly into the nasopharynx through internal nares. The opening of paranasal sinuses and nasolacrimal ducts lie in the nasal cavities. Internally, nasal cavity is lined with mucous membrane and ciliated columnar epithelium. It contains nasal hairs. Function ü It prevents the entry of dust particles into the lungs by trapping those dusts on mucus or by nasal hair. ü The ciliated epithelium prevents infection by sweeping out microorganisms. ü It warms the cold air and moistens the dry air. It detects smell. The superior one third of nasal mucosa is the olfactory area which contains olfactory cells. These cells are involved in perception of smell
- 7. 2.Pharynx • It is both digestive and respiratory organ. It is a tube of 12- 14 cm that extends the base of skull to the level of 5th cervical vertebra. It lies behind mouth, nose and larynx. It is connected to nasal cavity through the internal opening of nares and to the mouth. • It is divided into three parts: • a. Nasopharynx • b. Oropharynx • c. Laryngopharynx • a.Nasopharynx • It is the nasal part of pharynx,lies behind the nose and superior to the soft palate. It lined with ciliated epithelium that help in cleaning inspired air. On the lateral wall, there are two opening of auditory tubes and on posterior wall, there is a pharyngeal tonsils, consisting of lymphoid tissues.
- 8. 2.Pharynx • b.Oropharynx • Oral part of pharynx Lies at the posterior part of mouth, extends from soft palate to epiglottis. It is separated from mouth by a pair of membranous narrow passage called fauces. • c.Laryngopharynx • It is the lower most portion of pharynx and has a slit like aperture called glottis. This can be closed by leaf like bilobed cartilage, epiglottis, during swallowing of the food. • Function • Pharynx helps in passage of air from nose to trachea. • The air is further warmed and moistened as it passes through pharynx. • There are olfactory nerve endings of the sense of smell. • Protection: The lymphatic tissue of the pharyngeal and laryngeal tonsils produces antibodies in response to antigen. • Hearing: The auditory tube, extending from the nasopharynx to each middle ear, allows air to enter the middle ear.
- 9. 3.Larynx • It is also called sound box or voice box. It is situated in the anterior neck i.e. in front of esophagus. • It is small, thin walled, tubular part present in the neck at the apex of trachea. • It connects the lower part of pharynx and trachea. Pharynx opens in larynx through glottis which is guarded by a leaf like unpaired cartilage which is called epiglottis. It prevents the entrance of food into trachea. It is composed of several irregular shaped cartilages- they are: 1 thyroid cartilage, 1 cricoid cartilage and 2 arytenoids cartilage. They prevent the larynx from collapsing. There are two vocal folds (true vocal cords) situated in the cavity of larynx between thyroid and arytenoid cartilage. Also a pair of vestibular folds is protective in function. • Function • It plays important role in sound production. • It links pharynx with trachea, thus it allows passage of air. • Speech is produced when sound produced by vocal cords are manipulated by tongue, cheeks and lips. • During swallowing the larynx moves upward, blocking the opening into it from the pharynx. In addition the epiglottis also closes over the larynx. This ensures the food passes into oesophagus and not into trachea.
- 10. 4.Trachea (Wind pipe) • It is hollow tube of about 11-12 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter. • It extends from the base of larynx to thoracic cavity. It runs in the neck in front of oesophagus. • It is supported by 16-20 C-shaped cartilaginous tracheal rings. These rings prevent the trachea from collapsing due to continuous relaxation and expansion. • Internally, the wall of trachea is lined by pseudostratified ciliated epithelium with mucus secreting goblet cells. • The secretion of mucus cells keep the wall of tube moist and trap dust particles. • The mucus lubricates the passage and cilia help to filter out dust. • The constant beating of cilia carry mucous and debris upward into pharynx where upon it is swallowed or coughed up. • Help in cough reflex. It supports head and neck.
- 11. 5.Bronchi • As the trachea reaches into the thoracic cavity, it divides into two branches called bronchi- right and left bronchi. • Each bronchus has the structure similar to trachea. The right bronchus is wider and shorter than left bronchus. • It is about 2.5 cm long and left bronchus is about 5 cm in length. • Each bronchus when enter into corresponding lungs, it divides into smaller secondary bronchi and then into tertiary bronchi. • These bronchi progressively subdivide into smaller and smaller tube called bronchioles and then into terminal bronchioles. • Bronchioles continue to branch, and open into respiratory bronchioles which in turn branch into alveolar duct that lead into alveoli (microscopic air sac). • Function • Bronchi connect the trachea to the lungs, allowing air from external respiratory openings into the lungs.
- 12. 6.Alveoli • Bronchioles continue to branch, and open into respiratory bronchioles which in turn branch into alveolar duct that lead into microscopic air sac called alveoli. • Gaseous exchange takes place in alveoli. The alveoli are richly supplied with blood capillaries. • The wall of alveoli is lined with type I pneumocytes which help in gaseous exchange and type II pneumocytes produce surfactant. • The surfactant reduces the surface tension so that the lungs do not collapse. • Function • Alveoli help in purification of blood and allow exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
- 13. 7. Lungs • Lungs are a pair of conical organ situated one on either side of thoracic cavity. • They are hollow, soft, spongy, elastic, light and pink colored. There are one pair of lungs- they are right lung and left lung. • Lungs are externally surrounded by two layers called pleural membrane. • The outer membrane is called parietal pleural membrane and the inner layer is called visceral pleural membrane. • These membranes protect lungs and stop leaking of air into thoracic cavity. The space between two layers is called pleural cavity which is filled with pleural fluid. • The pleural fluid performs following function: • i. Allows smooth/ free frictionless movement of lungs. • ii. Protects the lungs from mechanical shocks. • iii. Keeps the pleura together and lungs expanded.
- 14. • Lobes of lungs • Lungs are divided into distinct lobes. Right lung has three lobes- right superior, middle and inferior lobe. These lobes are demarcated by transverse and oblique fissures. • Left lung has two lobe- superior and inferior lobe. The left lung is smaller than right lung and has a cardiac notch to accommodate heart.