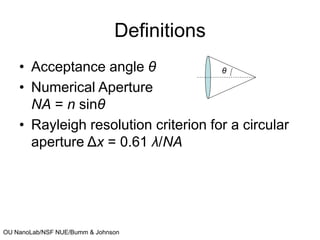
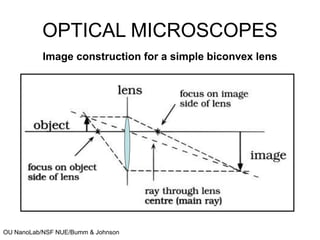
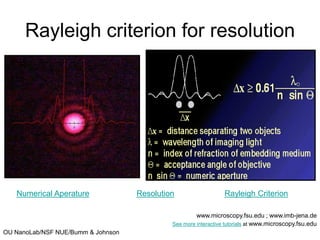
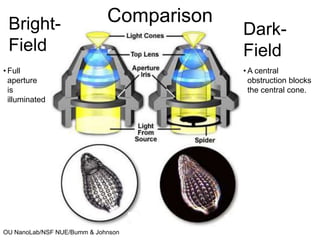
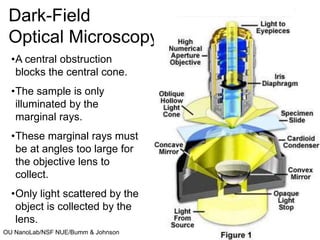
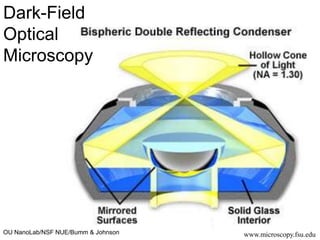
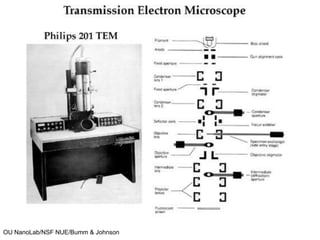
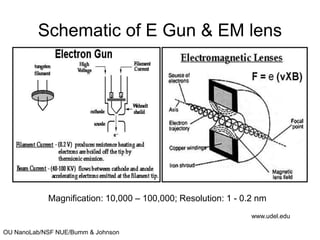
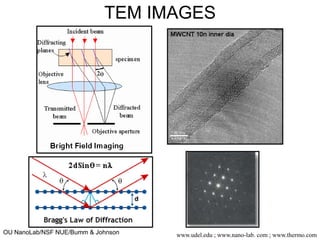
This document discusses microscopy techniques and their resolutions. Optical microscopes have a resolution of around 200 nm while electron microscopes can achieve resolutions as low as 0.1 nm. It explains the Rayleigh resolution criterion and how numerical aperture affects resolution. Dark-field optical microscopy is described as using marginal rays and blocking the central cone to only image scattered light. Components of transmission electron microscopes are outlined, noting they use electrons rather than light for higher resolutions down to 1-0.2 nm.