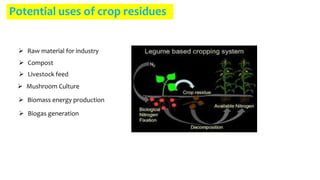
Crop residue management involves maintaining at least 60% soil cover after harvest to protect water quality and soil from erosion. It conserves soil moisture and organic matter while improving soil aeration, infiltration, and structure. Crop residues left after harvest include stalks, leaves, and stems. They can be burned, which causes air pollution, or left in fields, where they interfere with tilling but maintain soil nutrients and moisture levels. Potential uses of crop residues include producing biomass energy, livestock feed, compost, biogas, and industrial materials.