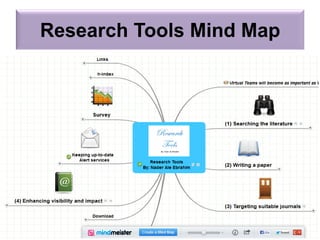
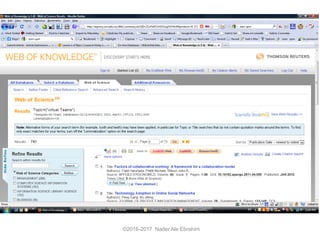
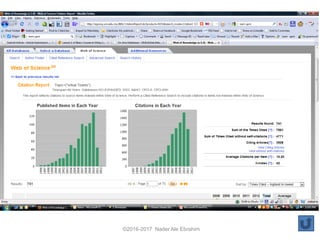
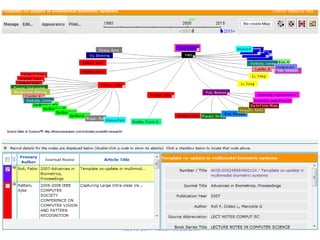
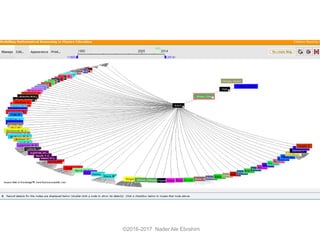
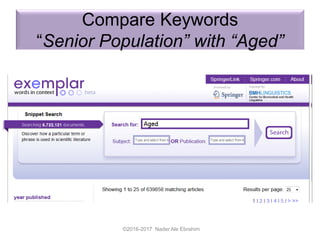
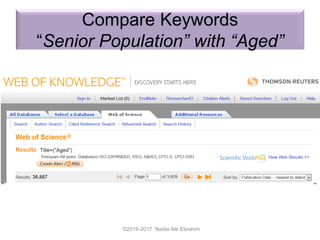
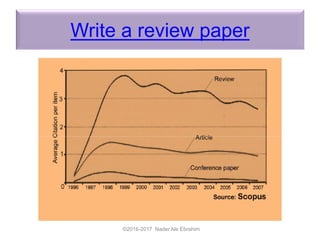
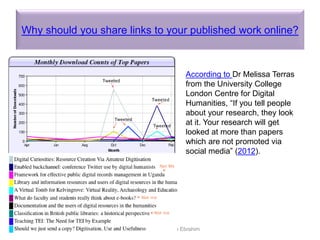
The document outlines a presentation by Dr. Nader Ale Ebrahim on various research tools designed to assist researchers in literature searches, writing, journal targeting, and enhancing research visibility. It highlights over 700 tools available to improve efficiency in research activities and addresses common problems faced by researchers regarding literature access and citation management. The seminar aims to equip researchers with skills to effectively utilize available resources for maximizing their research impact.