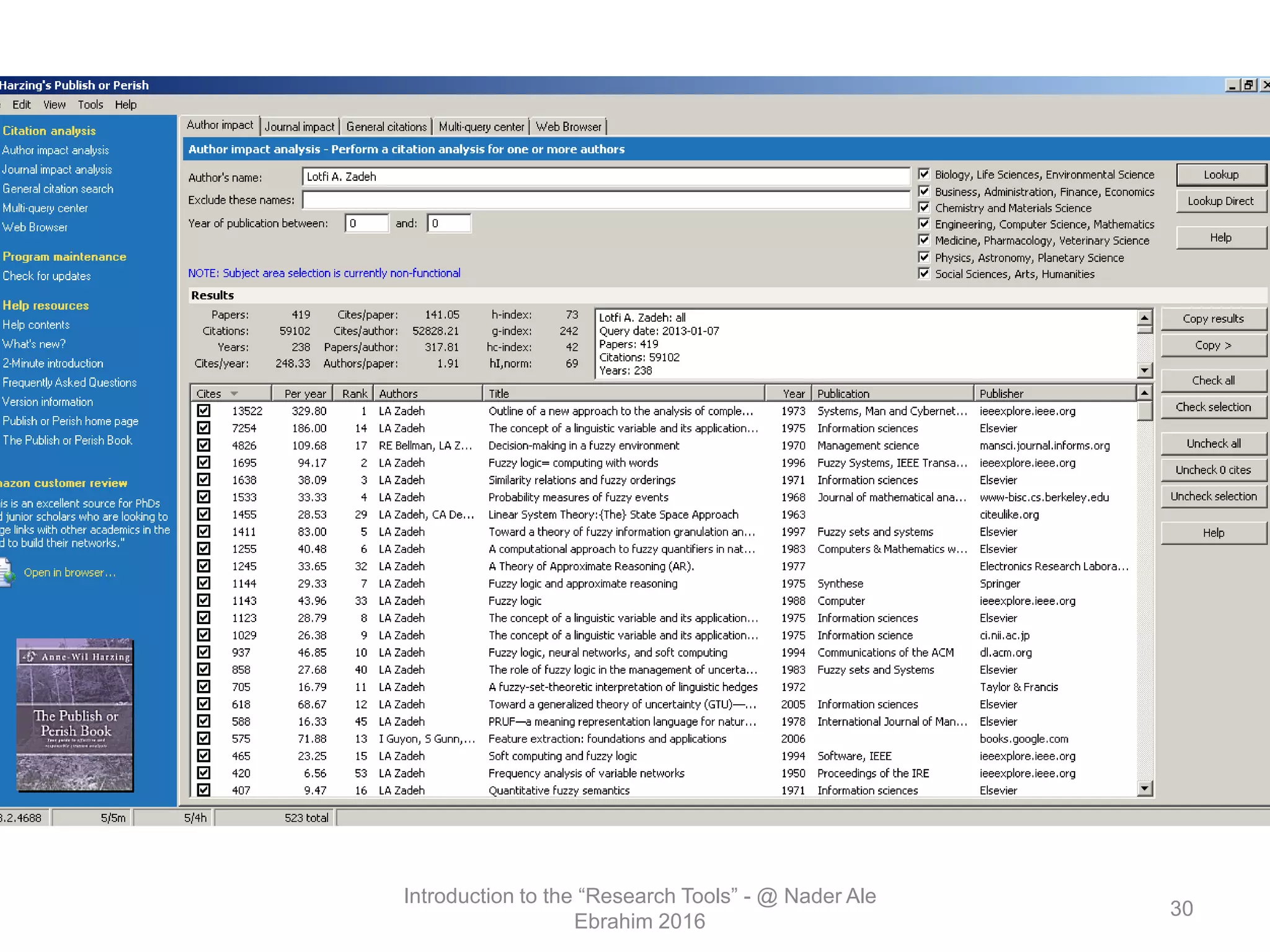
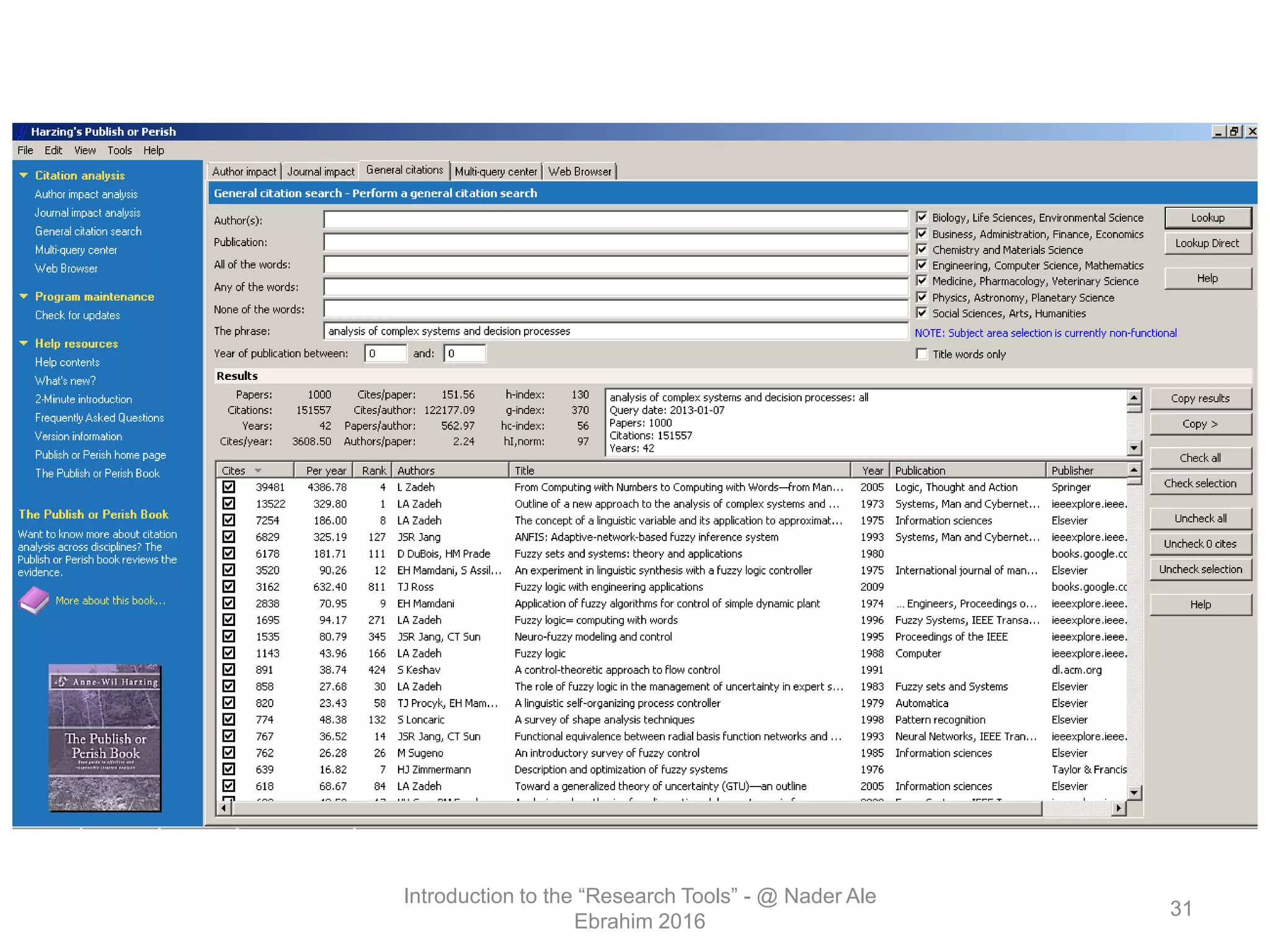
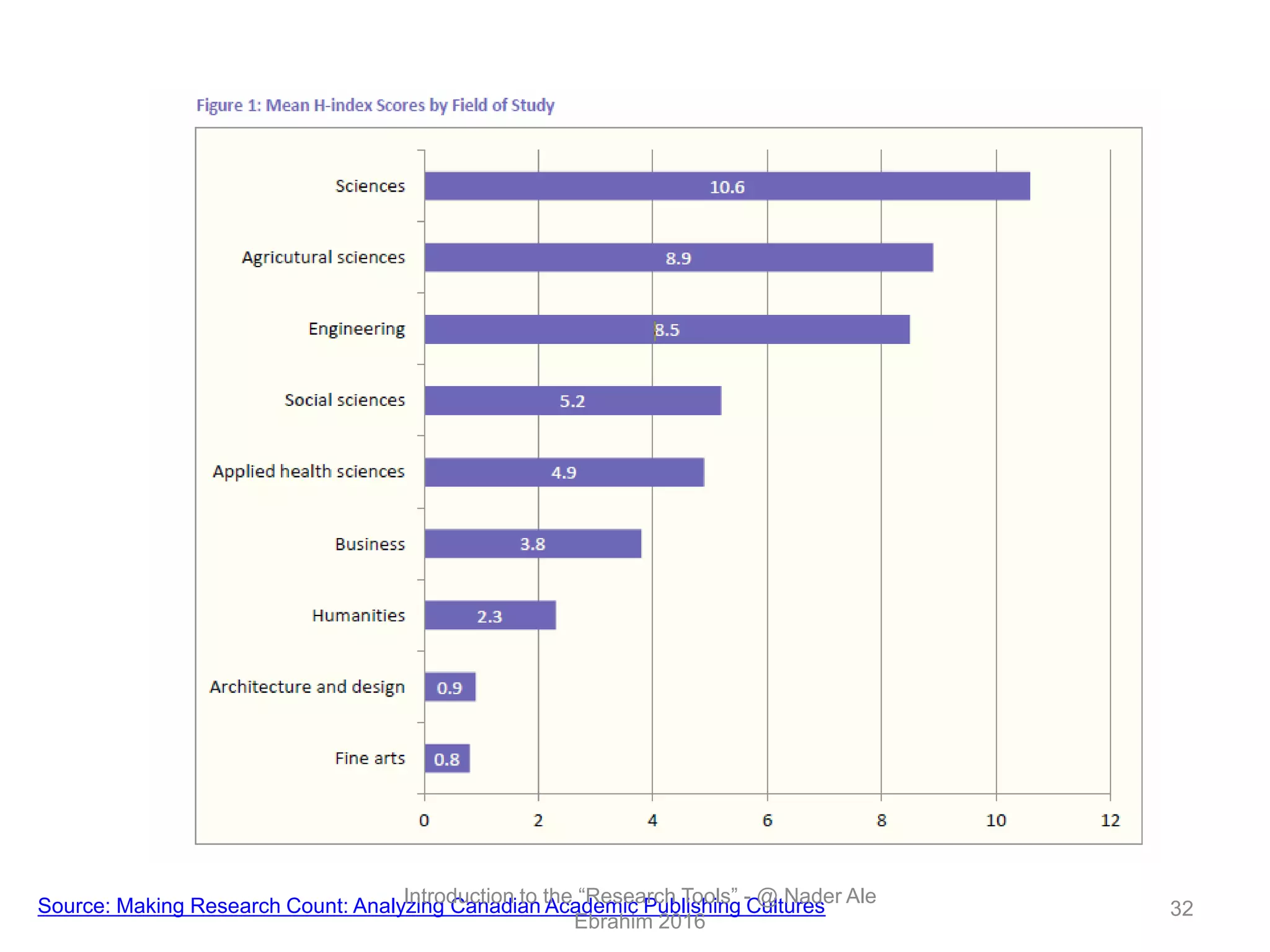
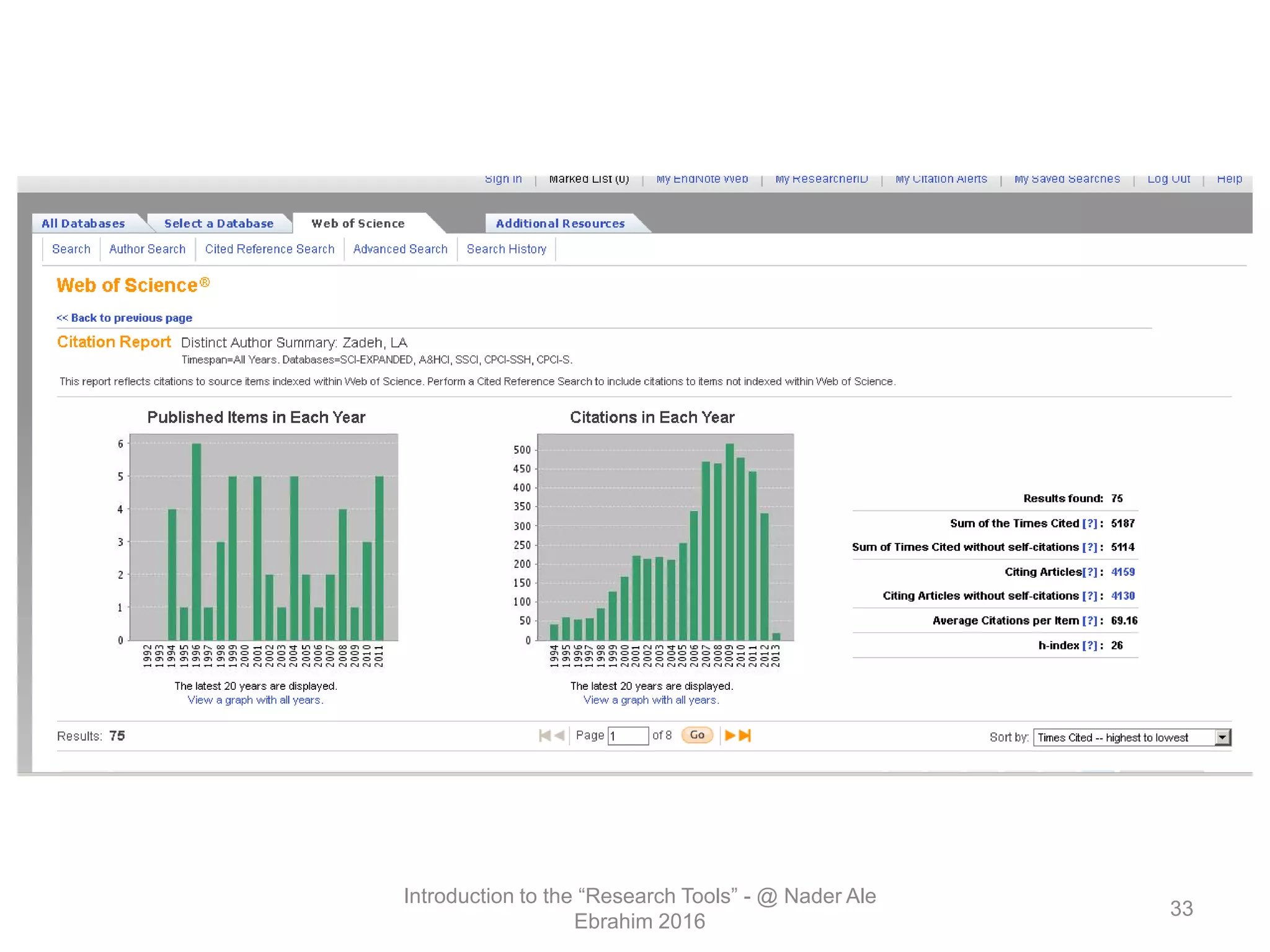
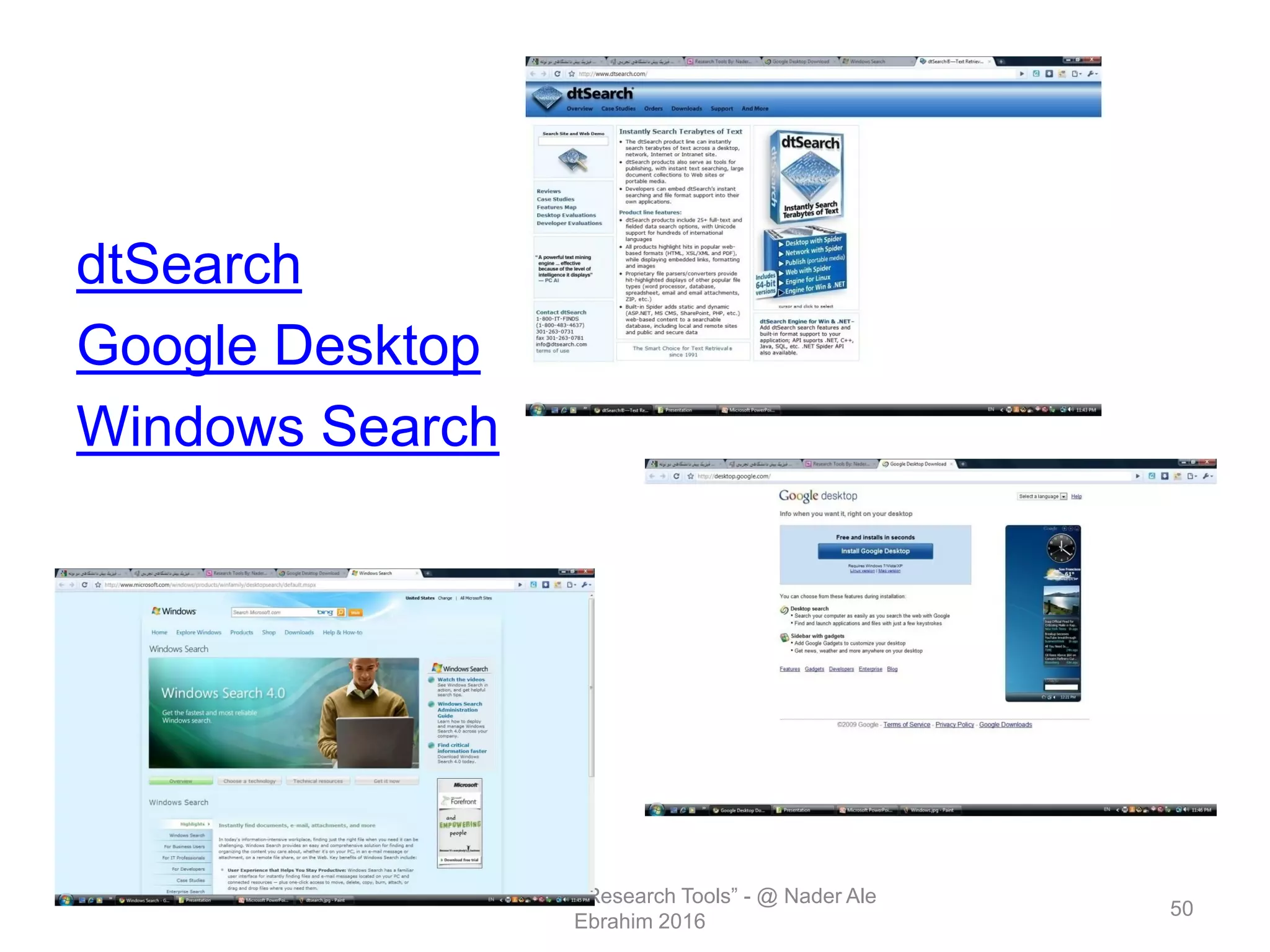
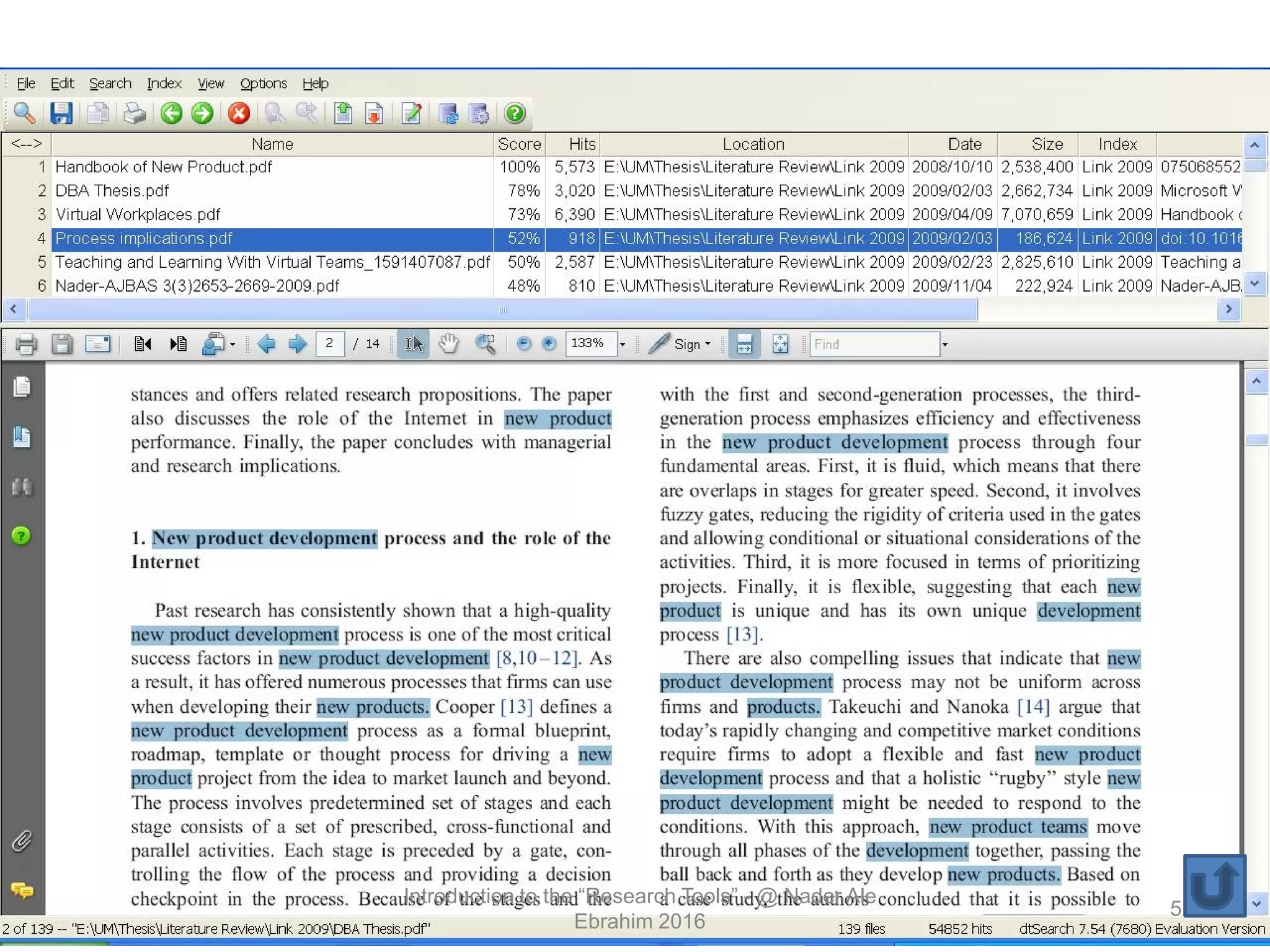
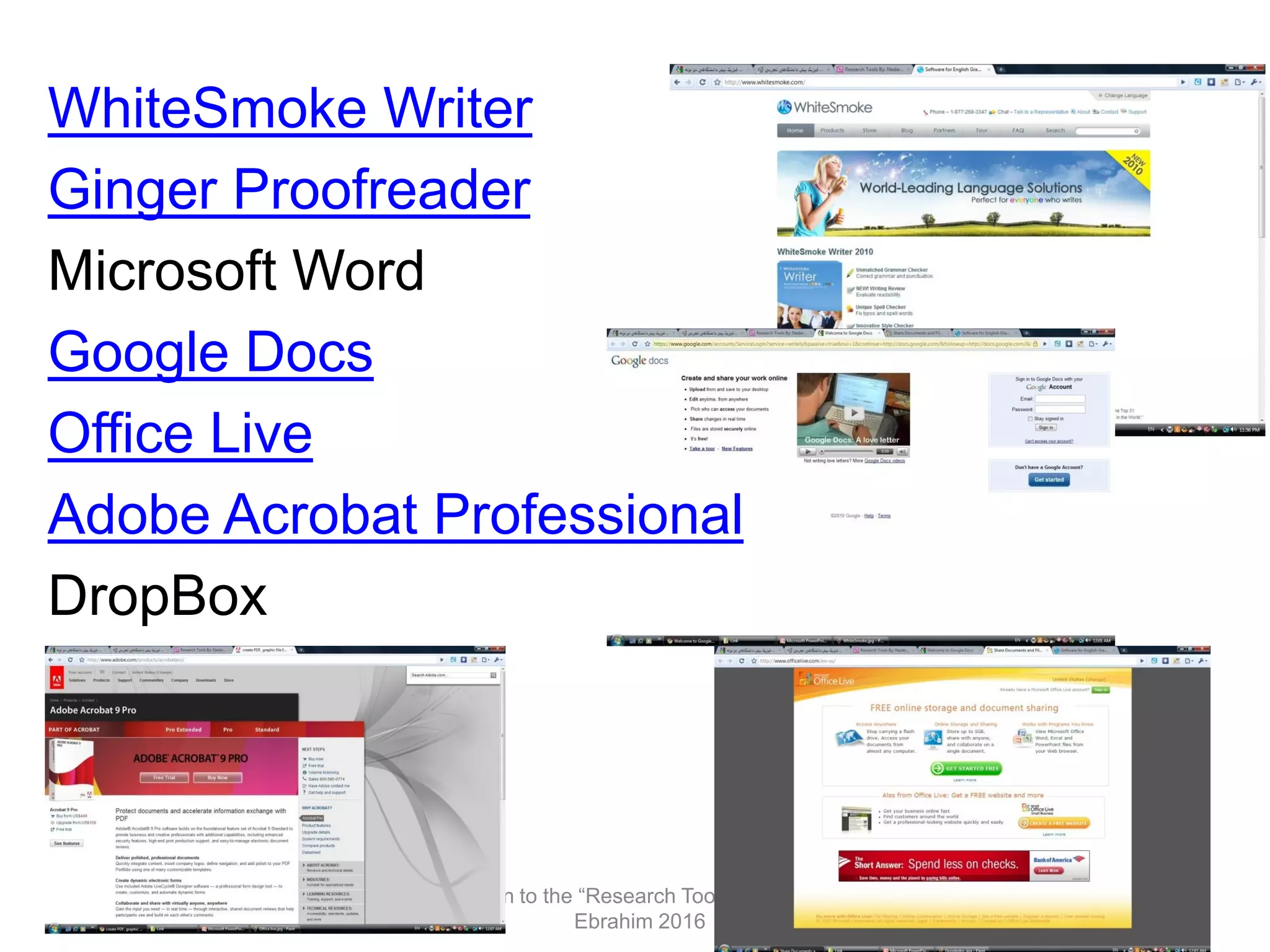
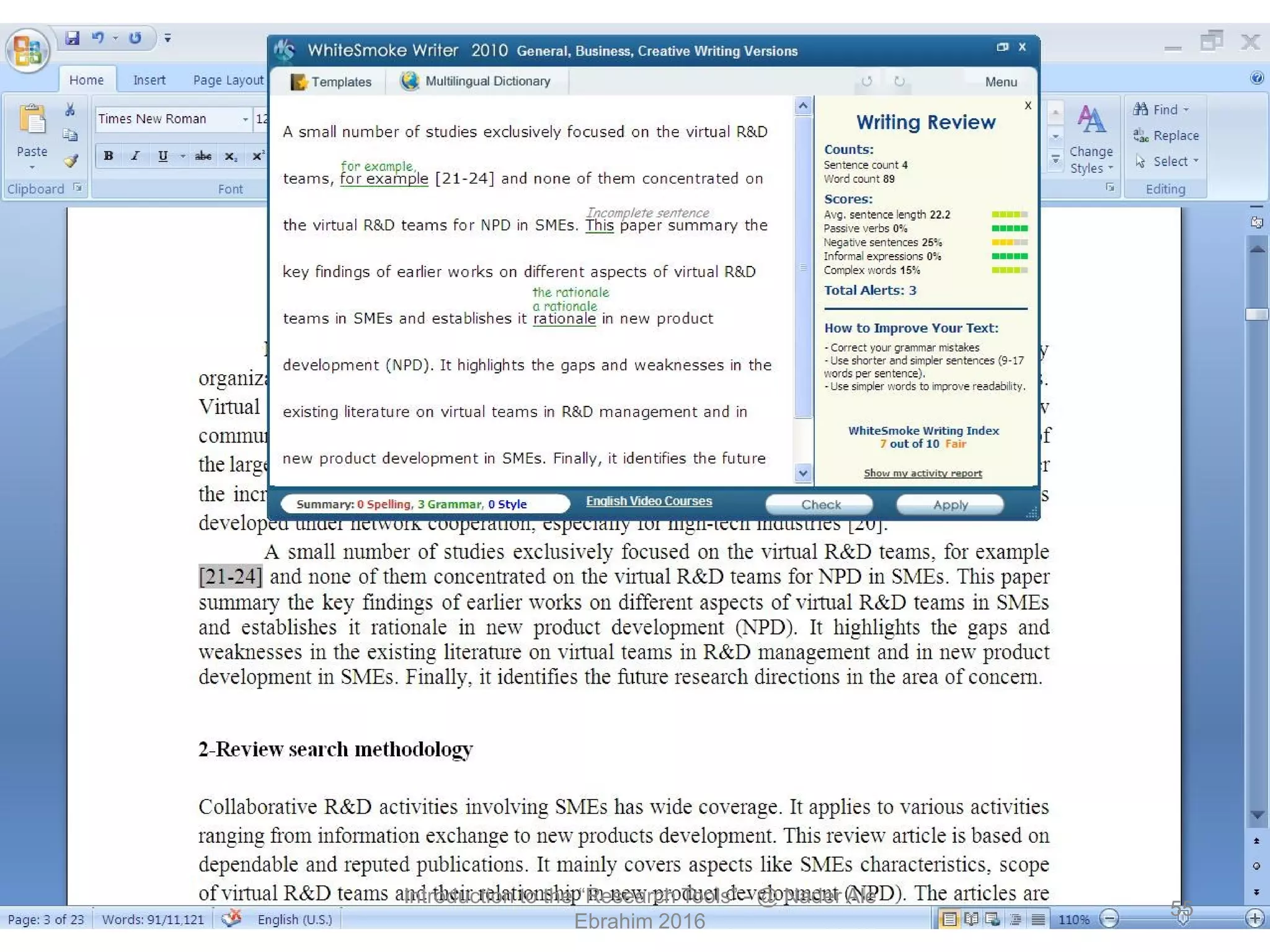
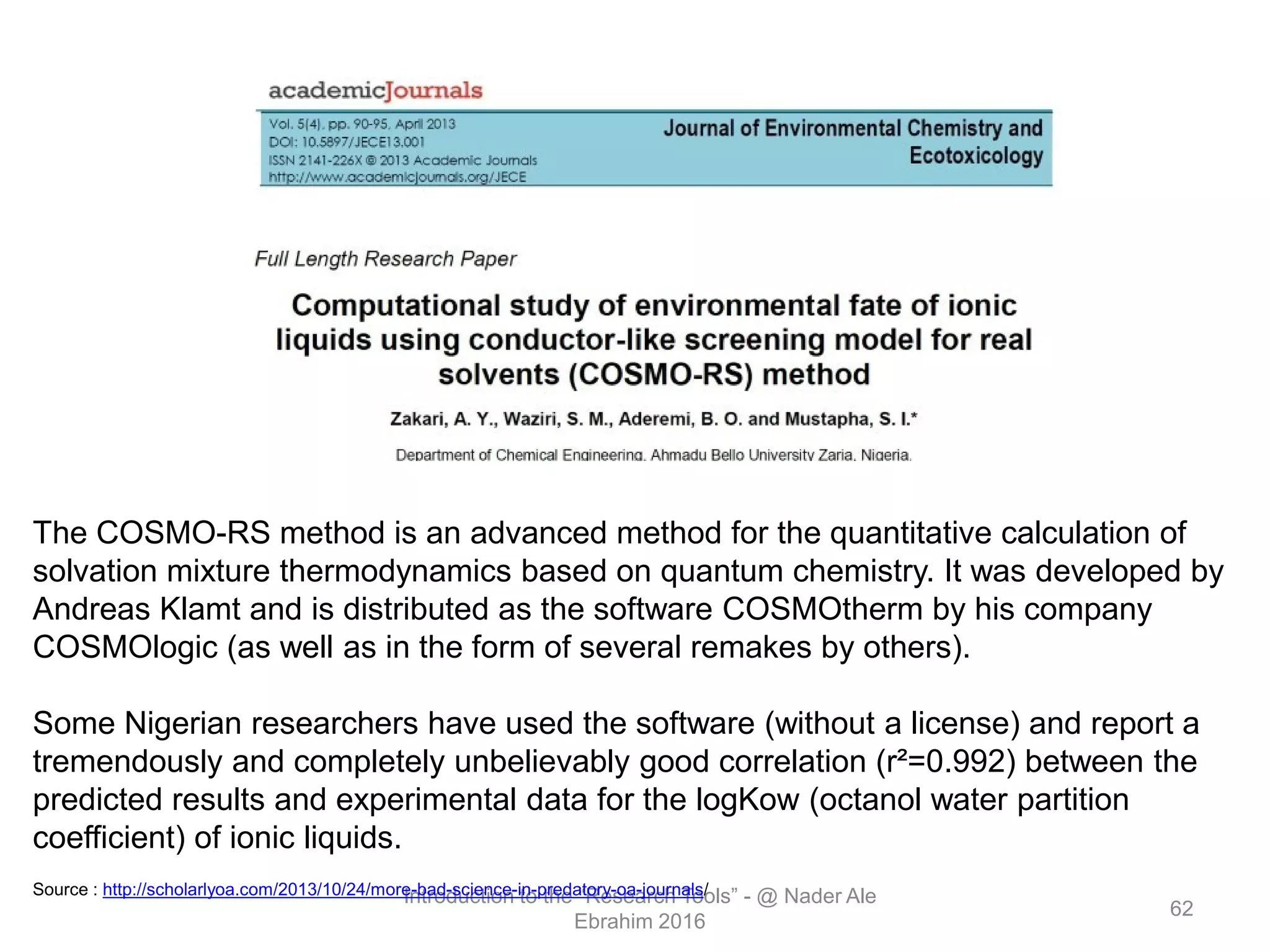
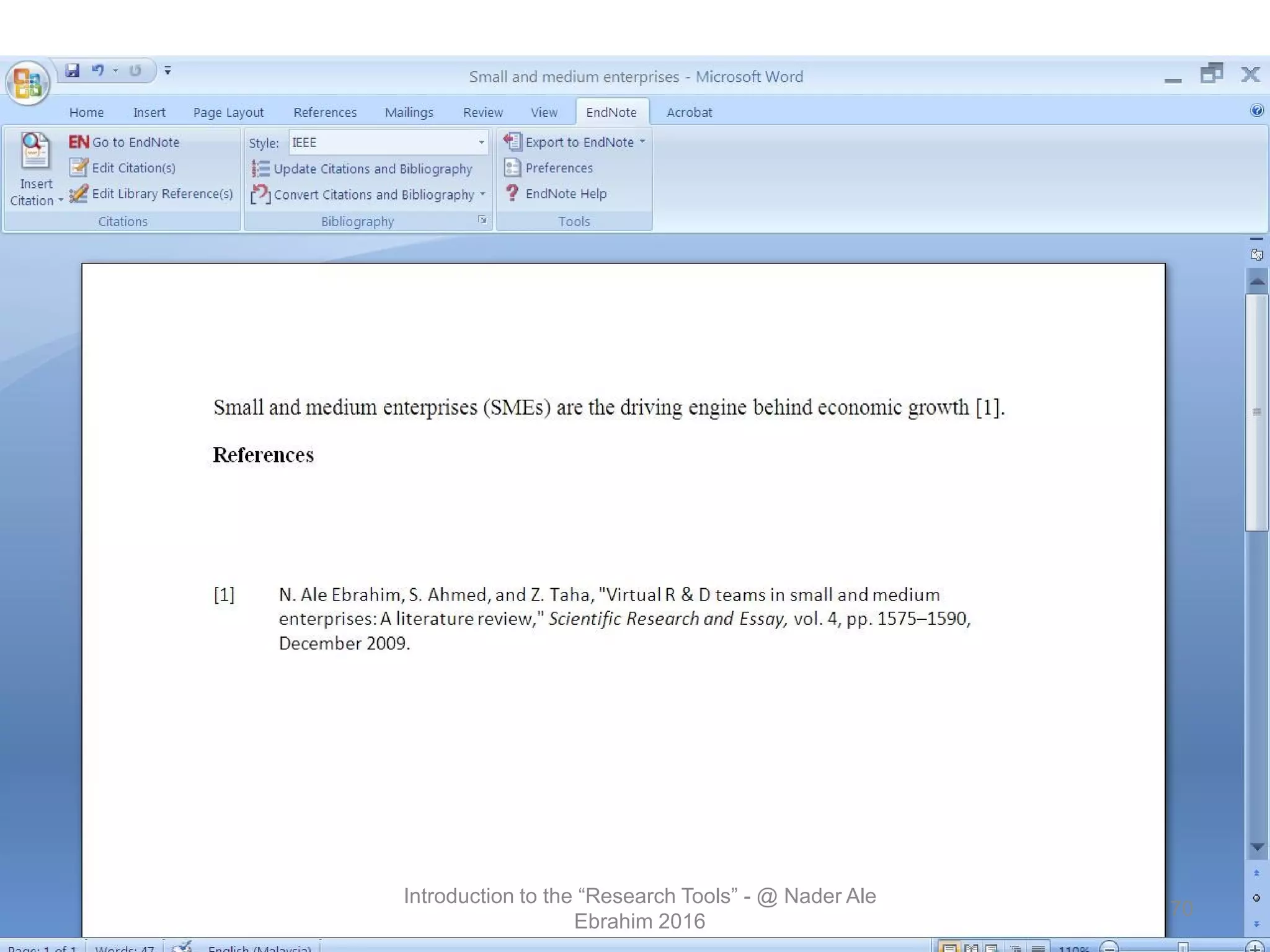
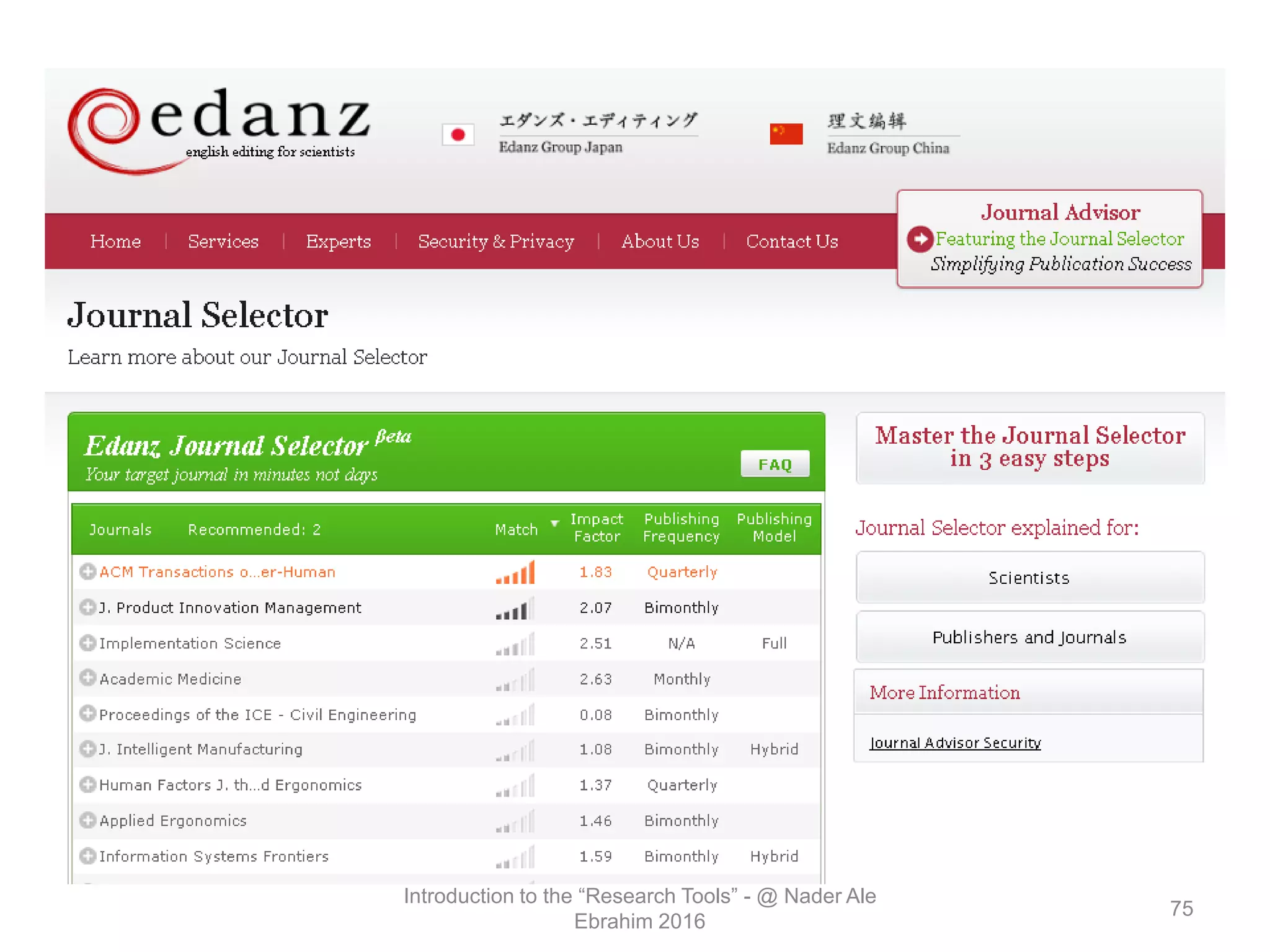
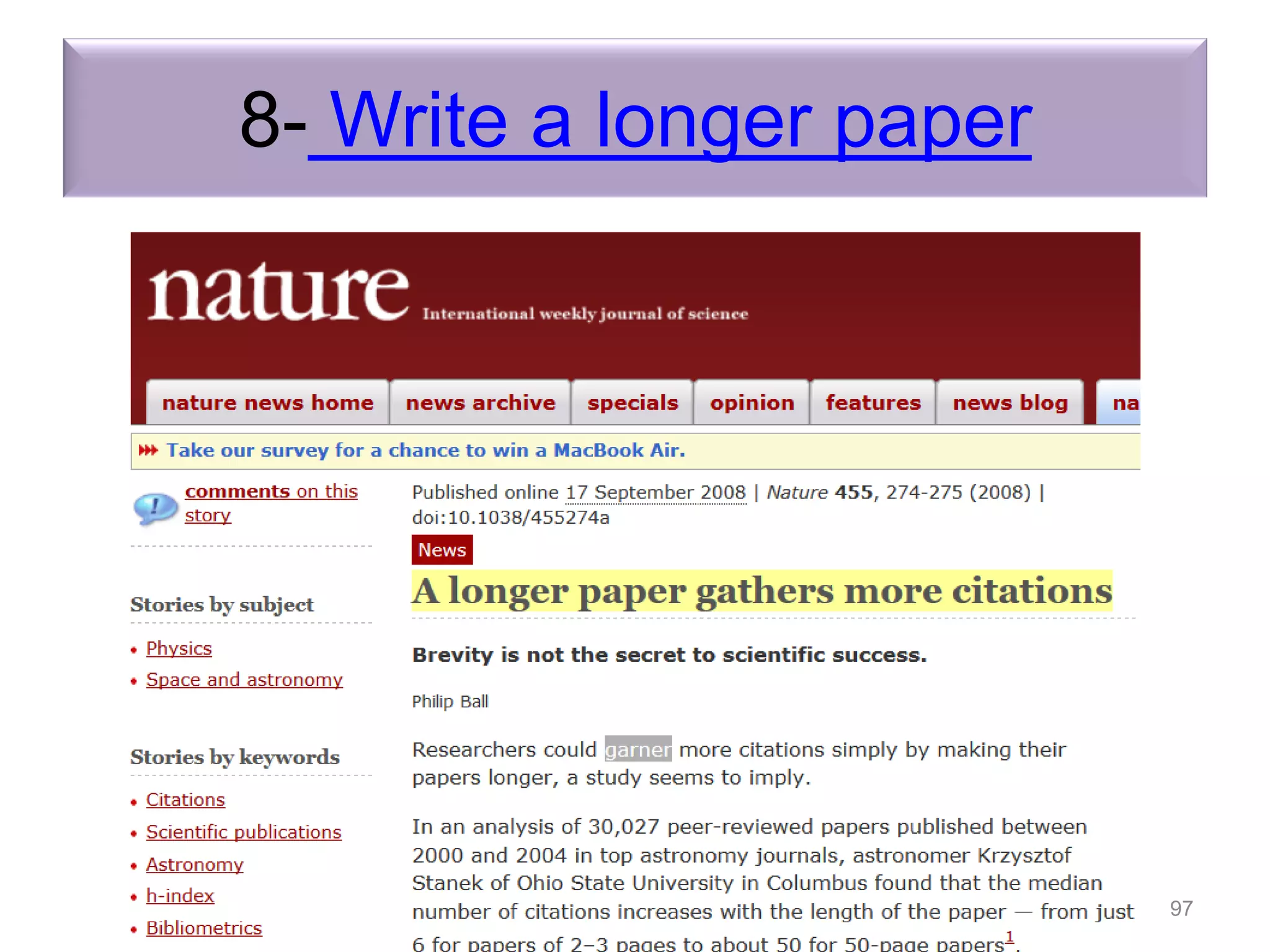
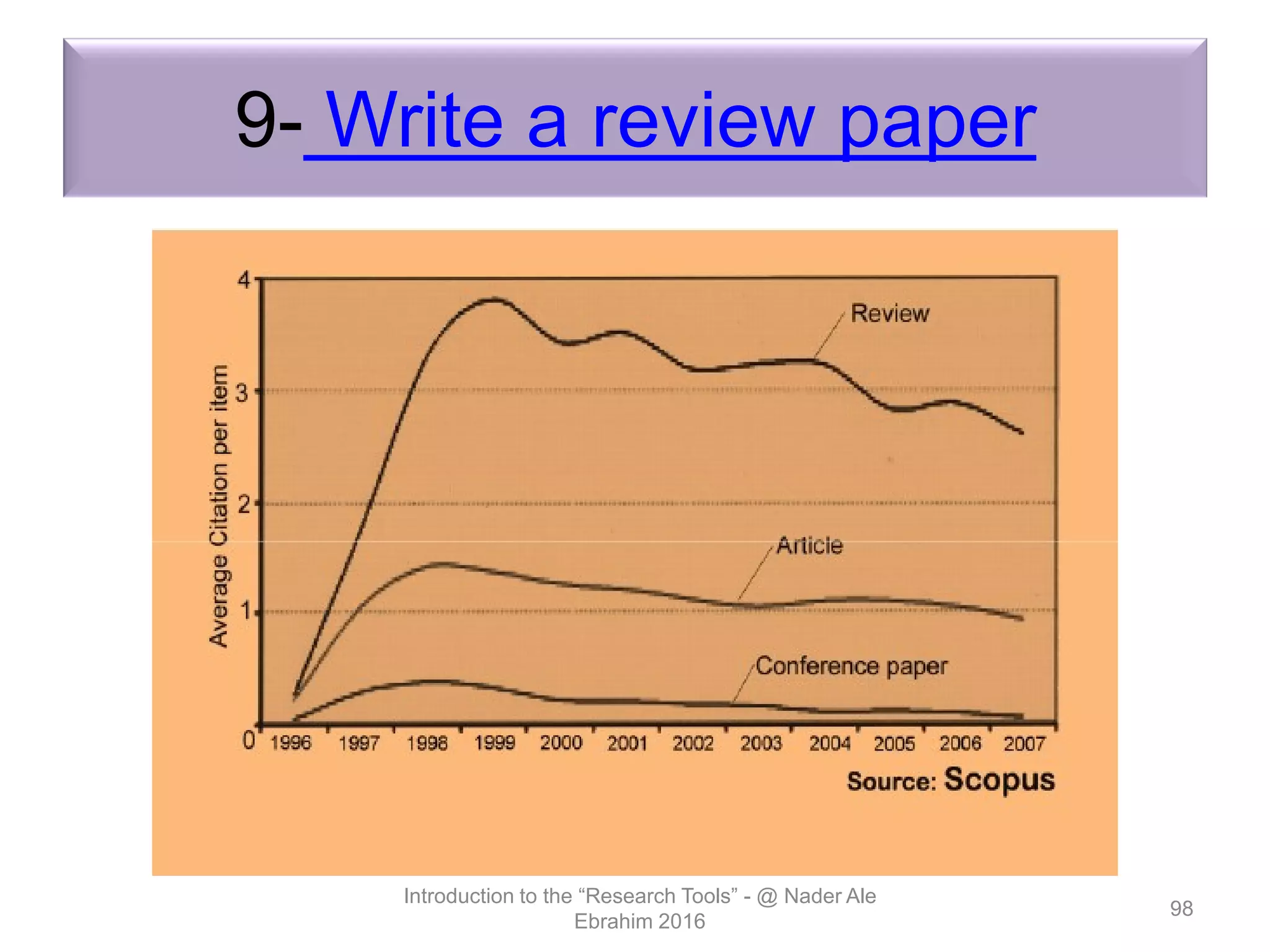
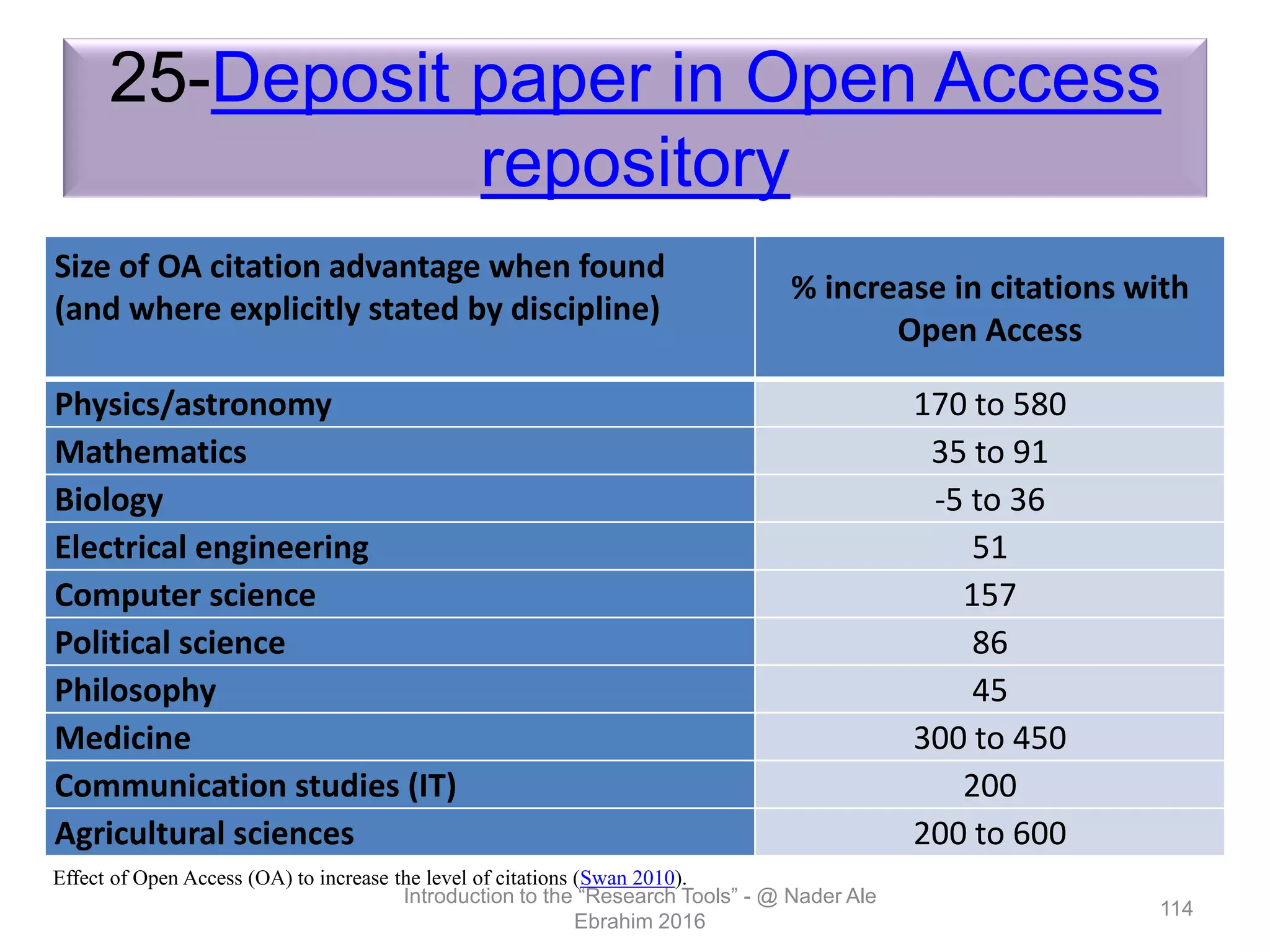
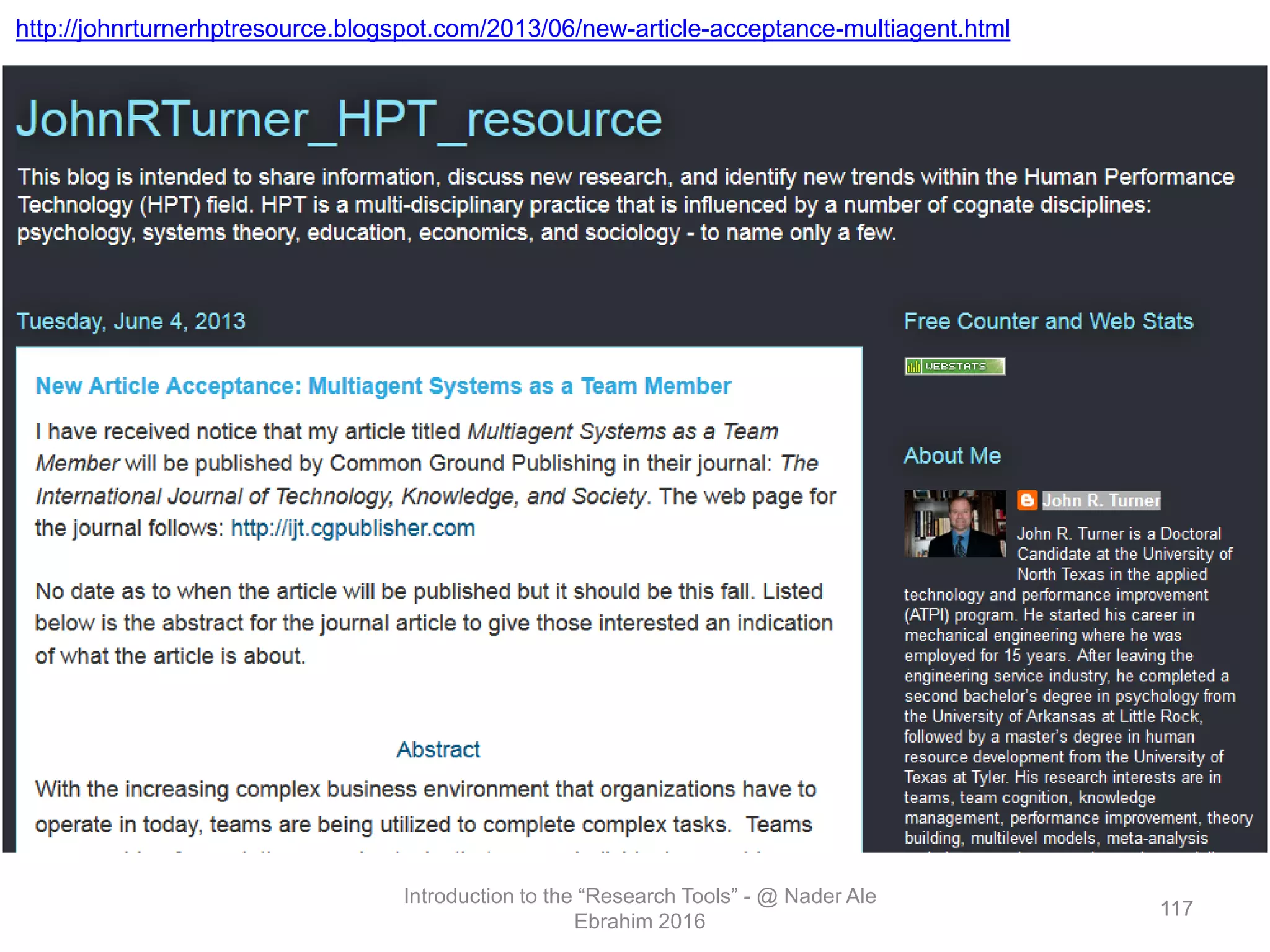
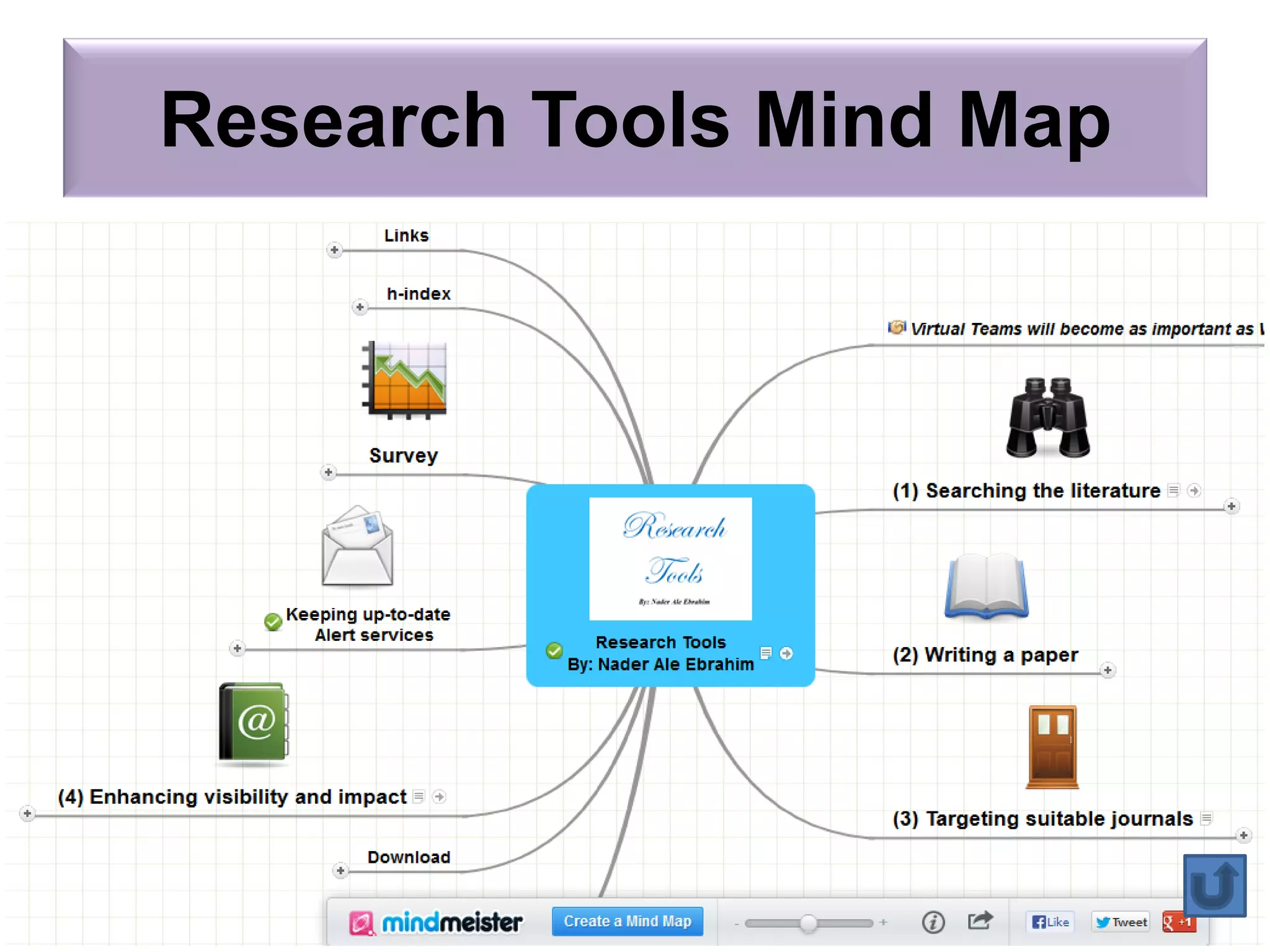
"Research tools" are defined as resources that aid researchers in various activities including literature search, paper writing, and enhancing research visibility. Dr. Nader Ale Ebrahim has compiled over 800 research tools organized in a web-based mind map to help students efficiently navigate the research process. The seminar aims to reduce research time through improved tool utilization, effective literature evaluation, and proper journal targeting for publication.




















![h-index (Jorge E. Hirsch)
• A scientist has index h if h of [his/her]
Np papers have at least h citations each,
and the other (Np − h) papers have at most
h citations each.
Introduction to the “Research Tools” - @ Nader Ale
Ebrahim 2016
28
H-index from a plot of decreasing citations for numbered papers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoresearchtoolsforresearchmethodologybynaderaleebrahim-160506034447/75/Introduction-to-the-Research-Tools-for-Research-Methodology-course-28-2048.jpg)