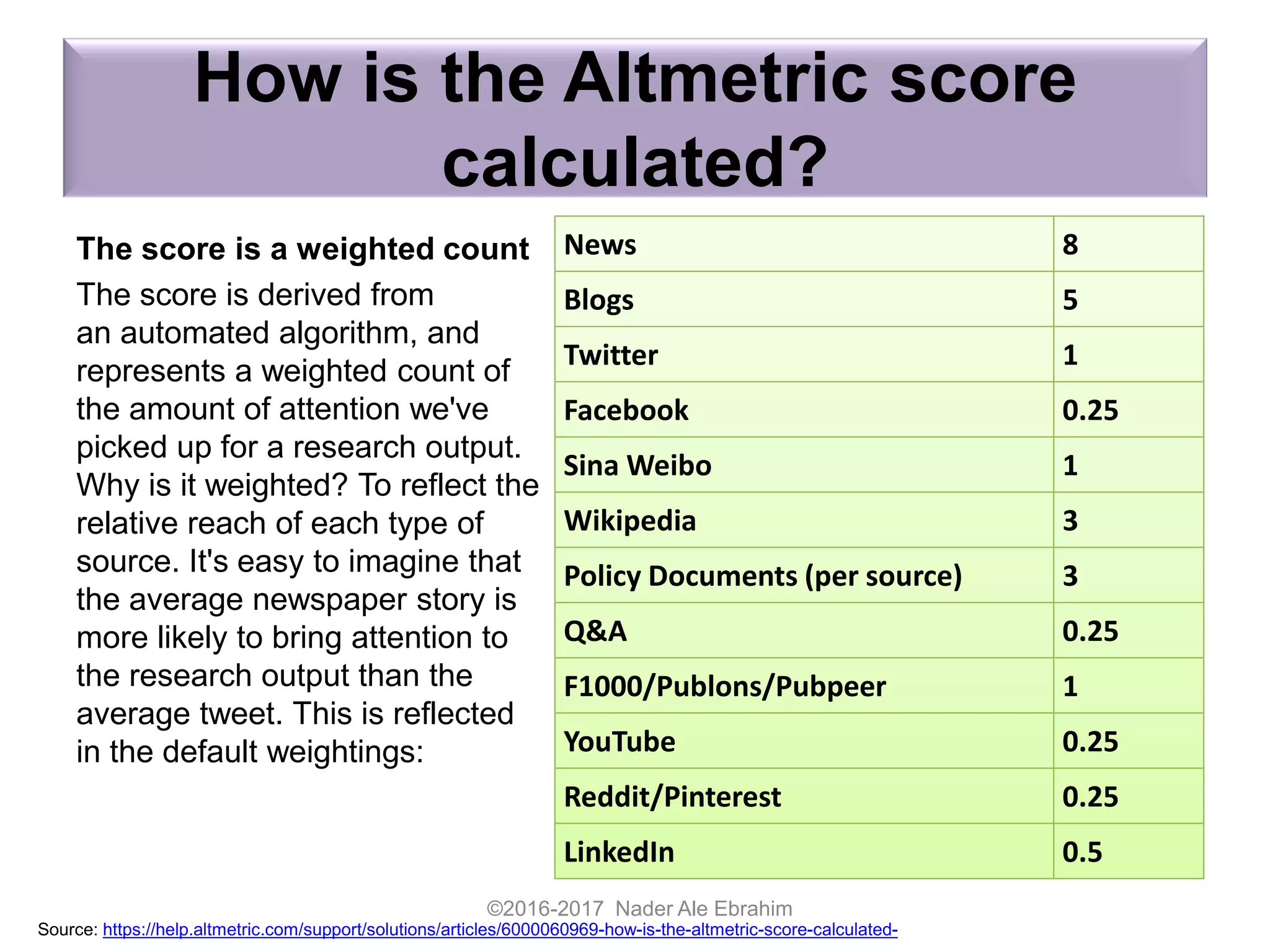
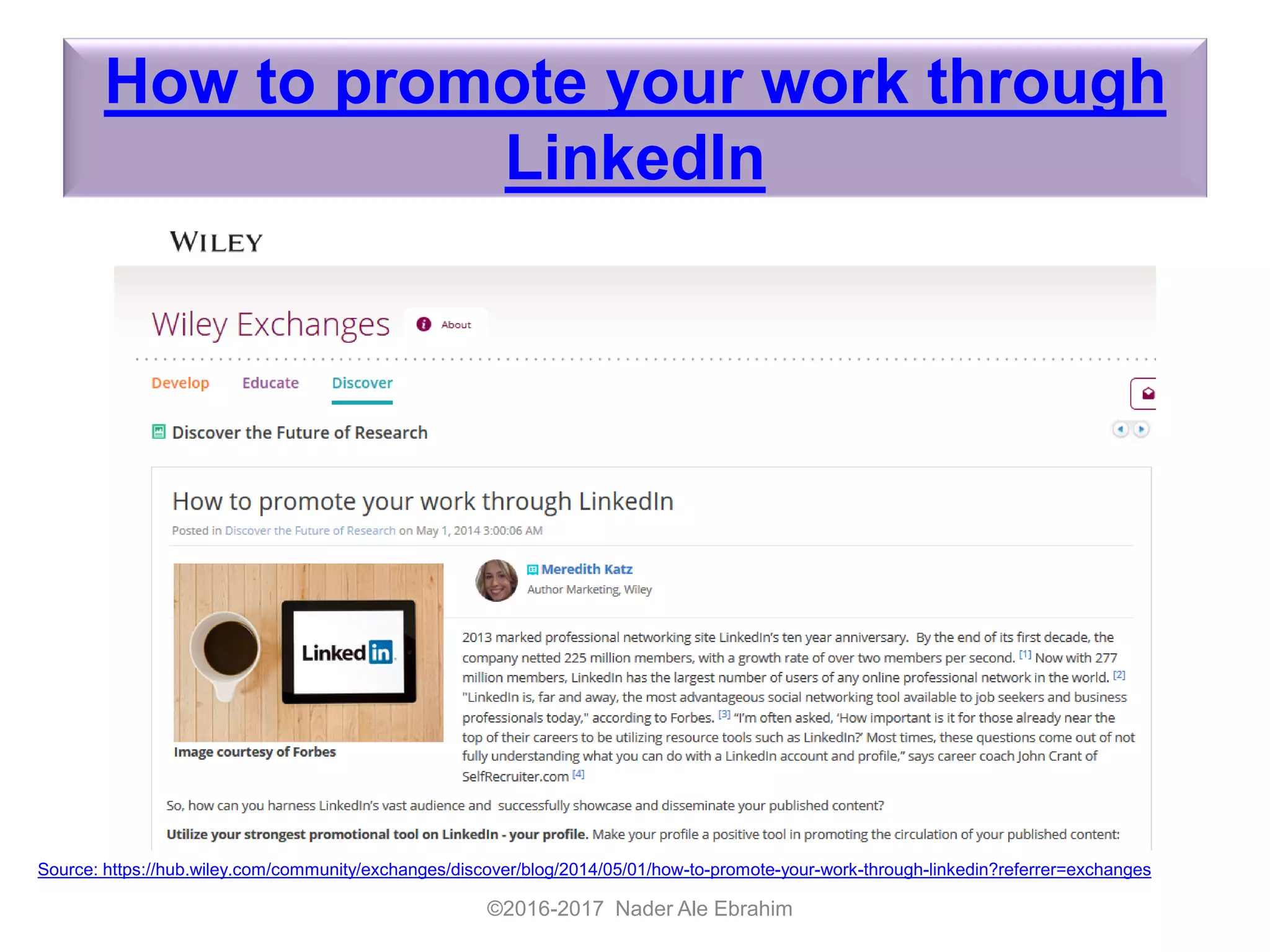
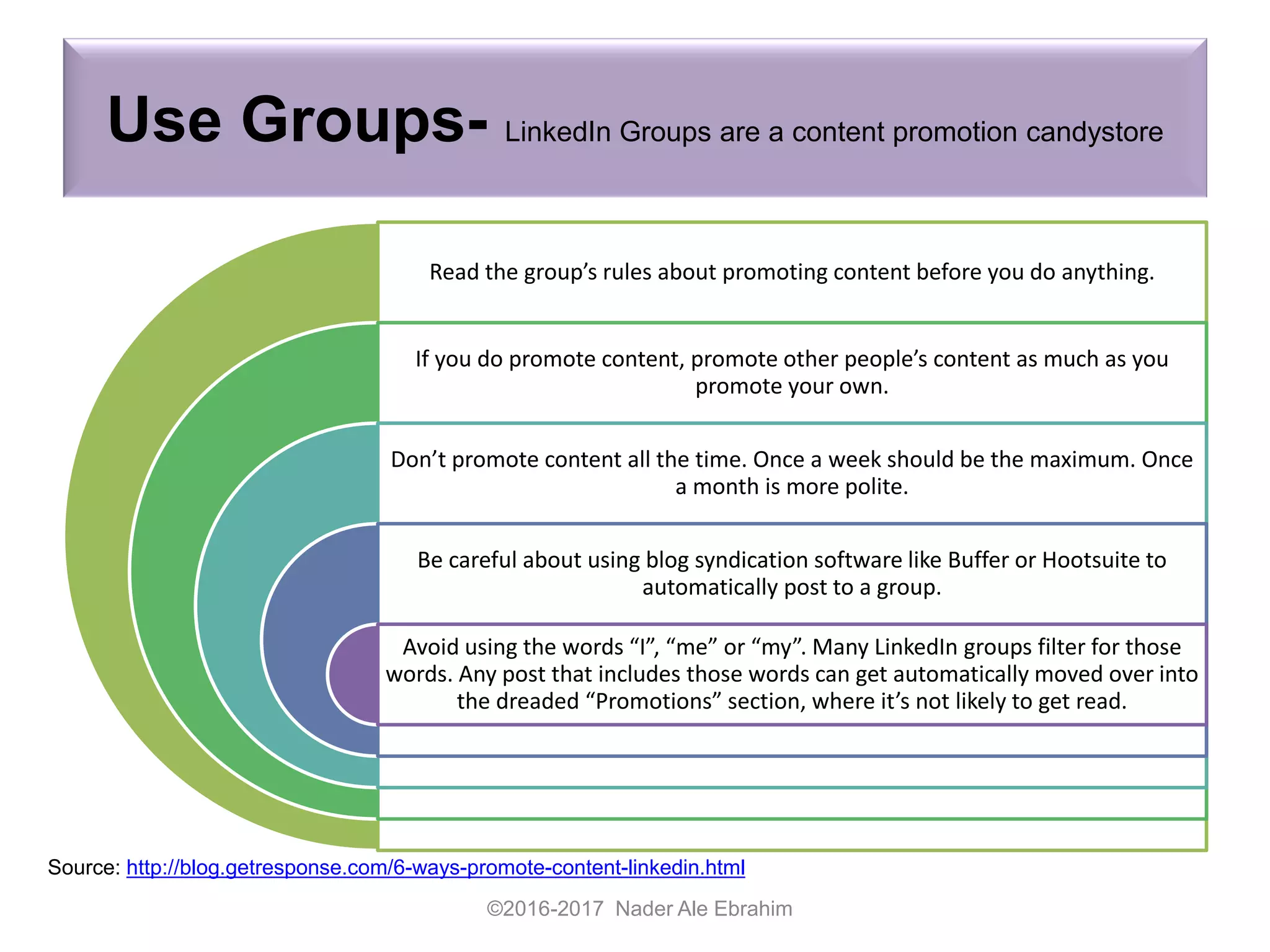
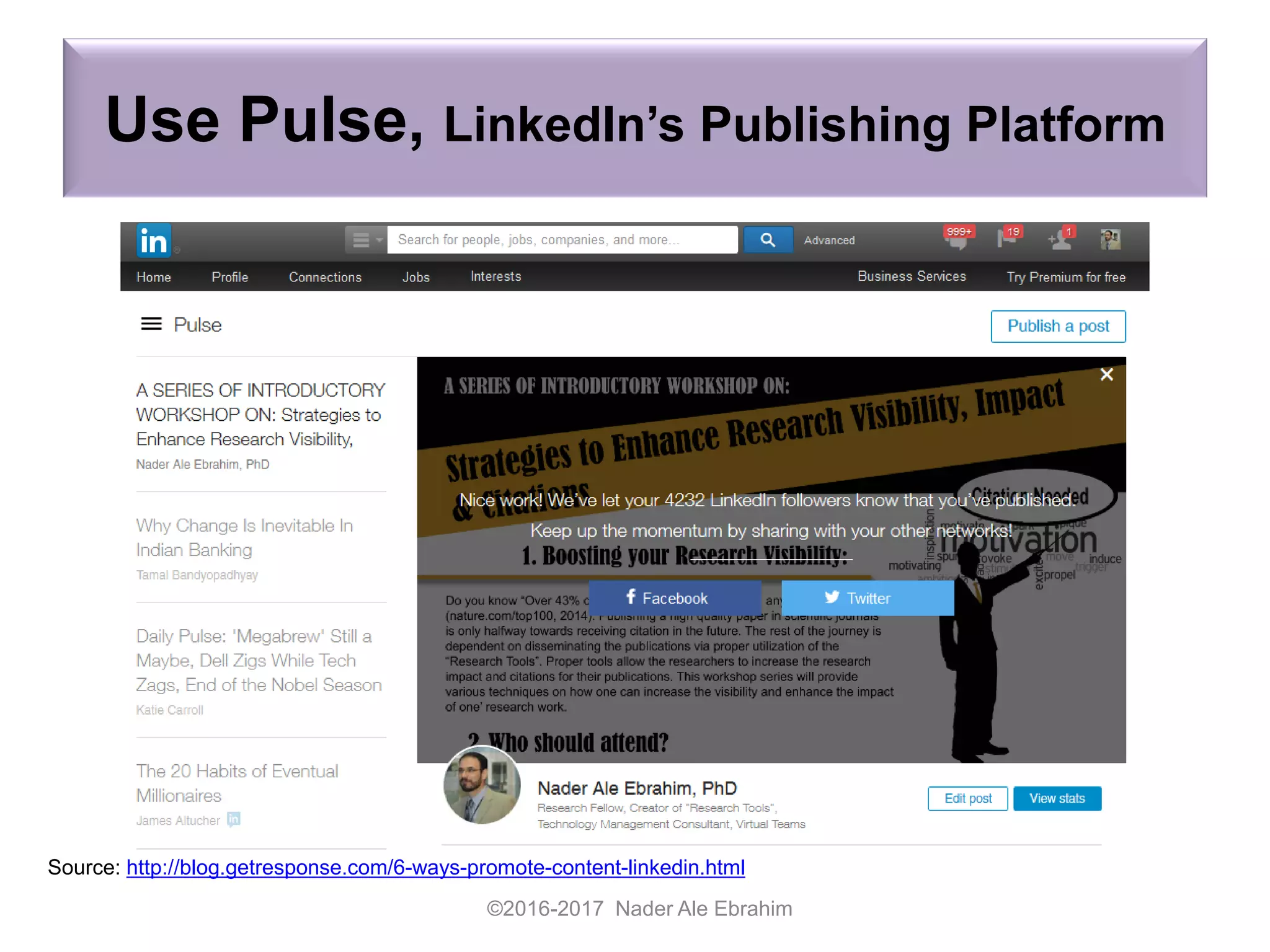
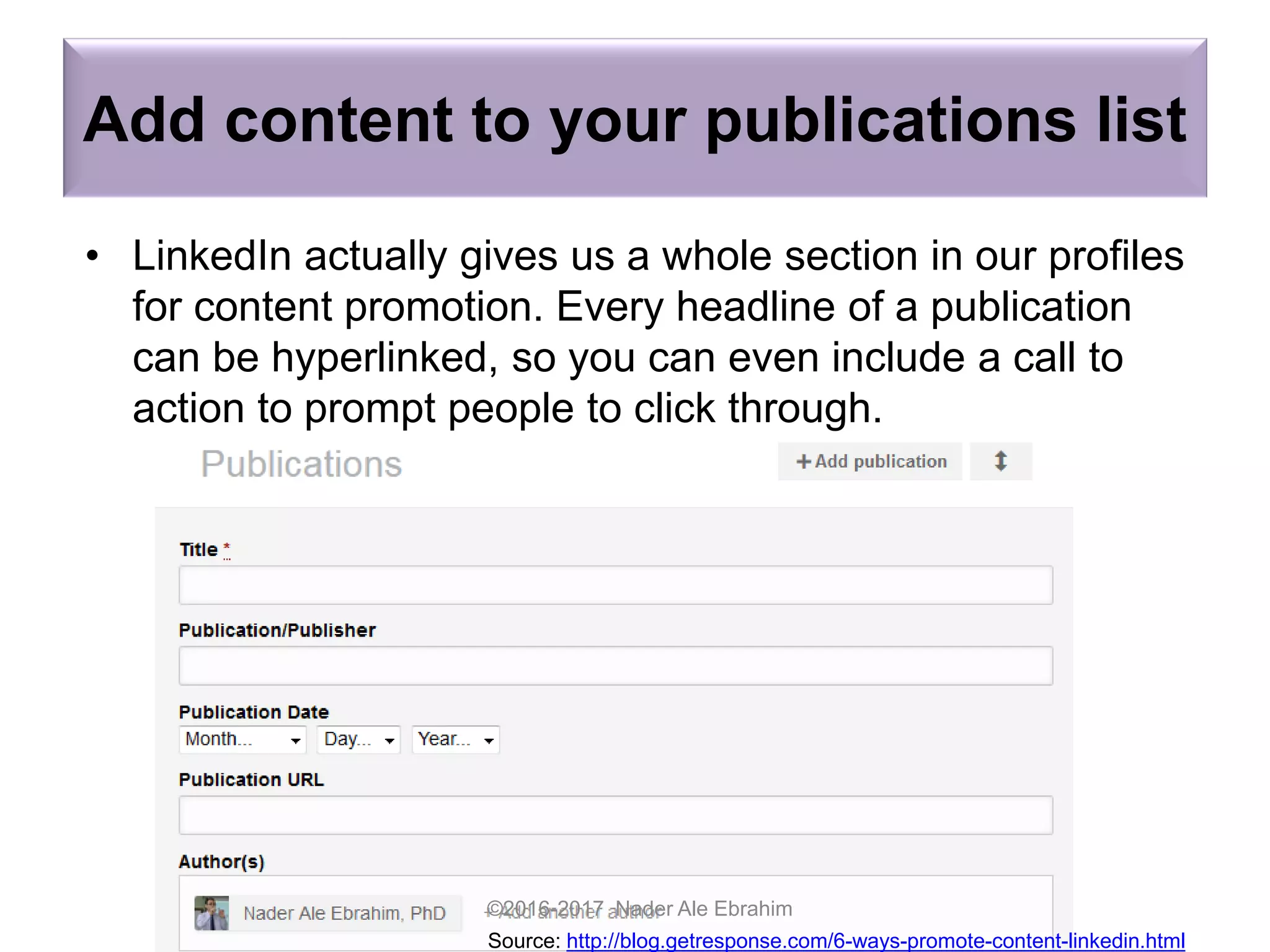
The document provides strategies for researchers to promote their work on LinkedIn and other academic social networks to enhance visibility, impact, and citation frequency. It emphasizes the importance of optimizing profiles, utilizing open access, networking, and sharing publications effectively to improve research outreach. Key recommendations include creating engaging content, participating in relevant groups, and maintaining an active online presence to connect with peers and potential collaborators.