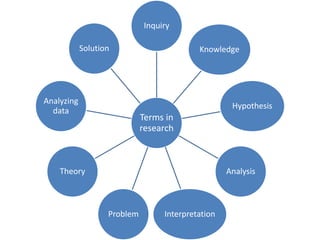
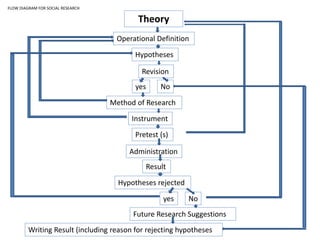
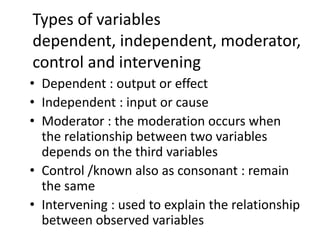
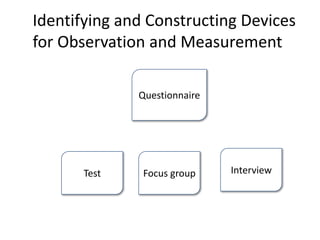
This document outlines the key steps and terms involved in the research process. It discusses defining problems, formulating hypotheses, collecting and analyzing data, and using scientific methods to evaluate theories objectively. The goal of research is to solve problems, verify applications of theories, and gain new insights by proving or disproving ideas.