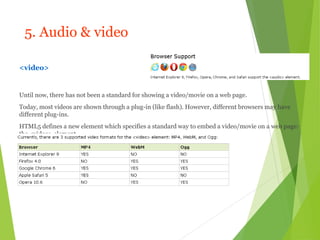
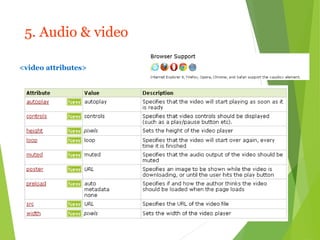
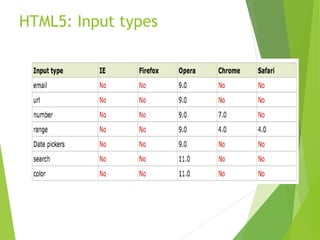
HTML5 is the newest version of HTML that adds new semantic elements, built-in audio and video playback, and features like the canvas element for drawing graphics. It simplifies the syntax of earlier HTML versions and aims to make web pages more semantic, reduce the need for plugins, and work across devices. New elements in HTML5 include <header>, <footer>, <nav>, <video>, <audio>, <canvas>, and new form input types. It is still a work in progress with partial browser support.