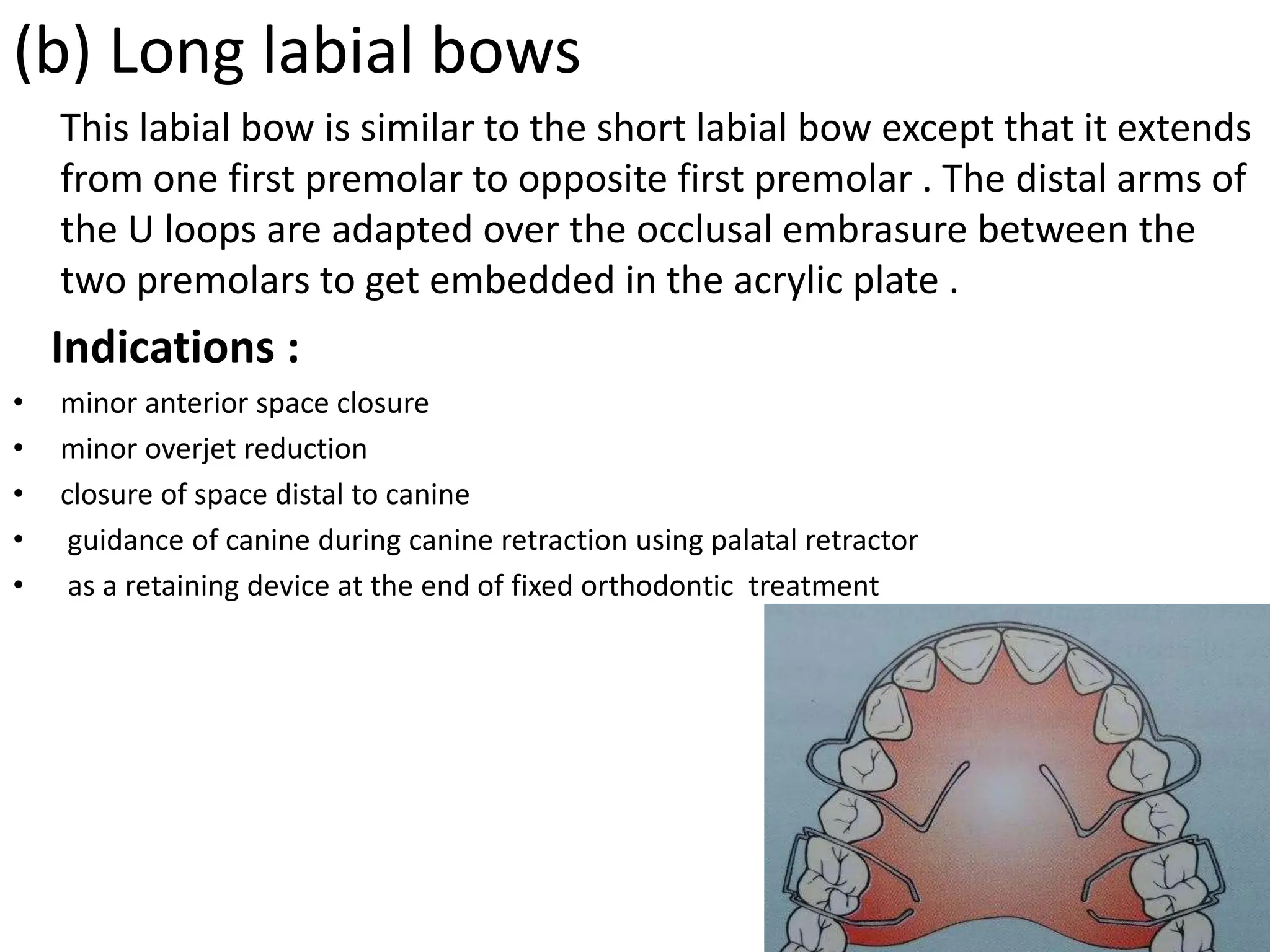
Removable orthodontic appliances can be inserted and removed by the patient. They were first developed in the 1830s using plaster models. Key advantages are that they allow for oral hygiene and are less expensive than fixed appliances. However, they have less control over tooth movement and require patient cooperation. Removable appliances use components like clasps for retention and bows or springs for applying forces. Common clasps include Adams, Jackson's, and circumferential clasps which engage tooth undercuts. Guidelines for appliance activation include providing paths for tooth movement and minimizing tipping.