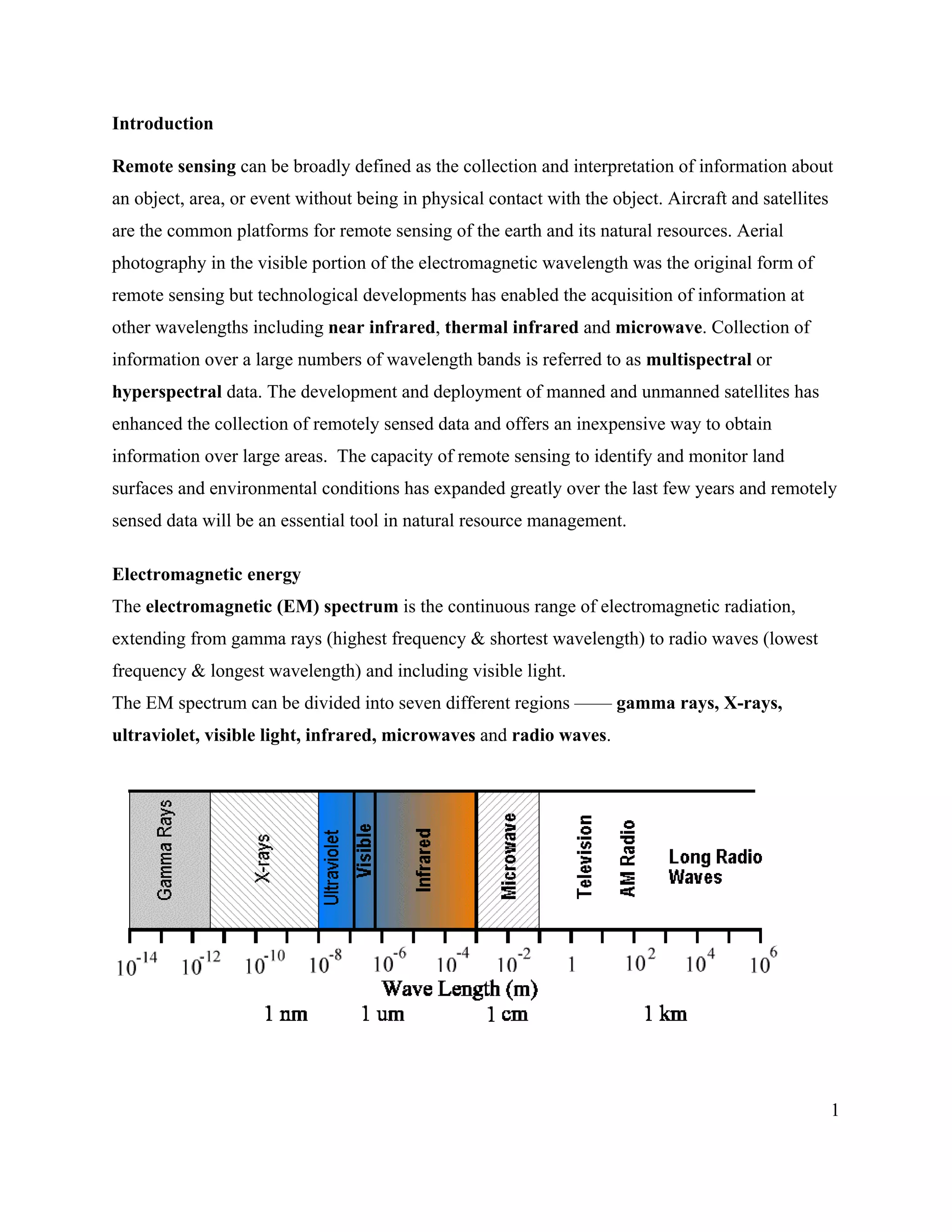
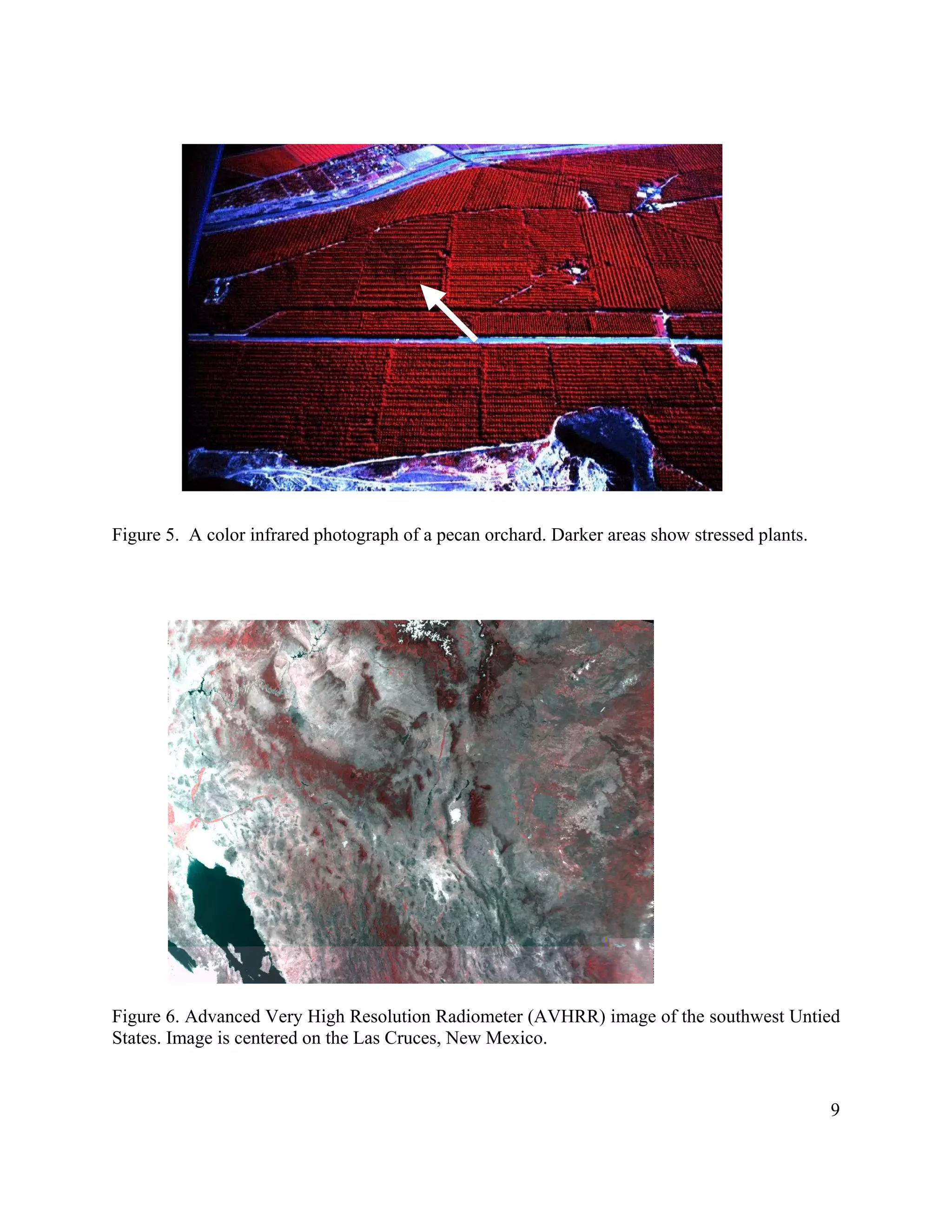
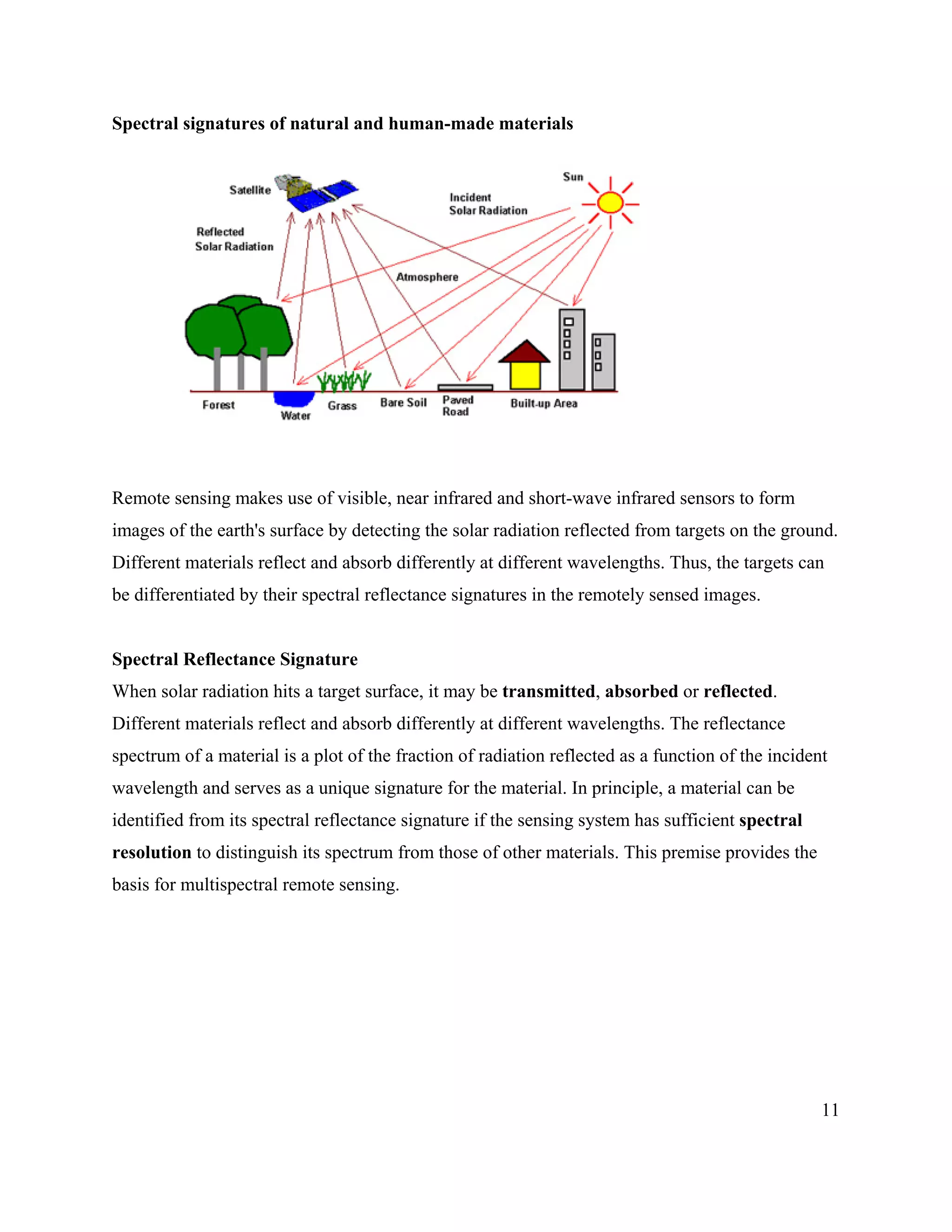
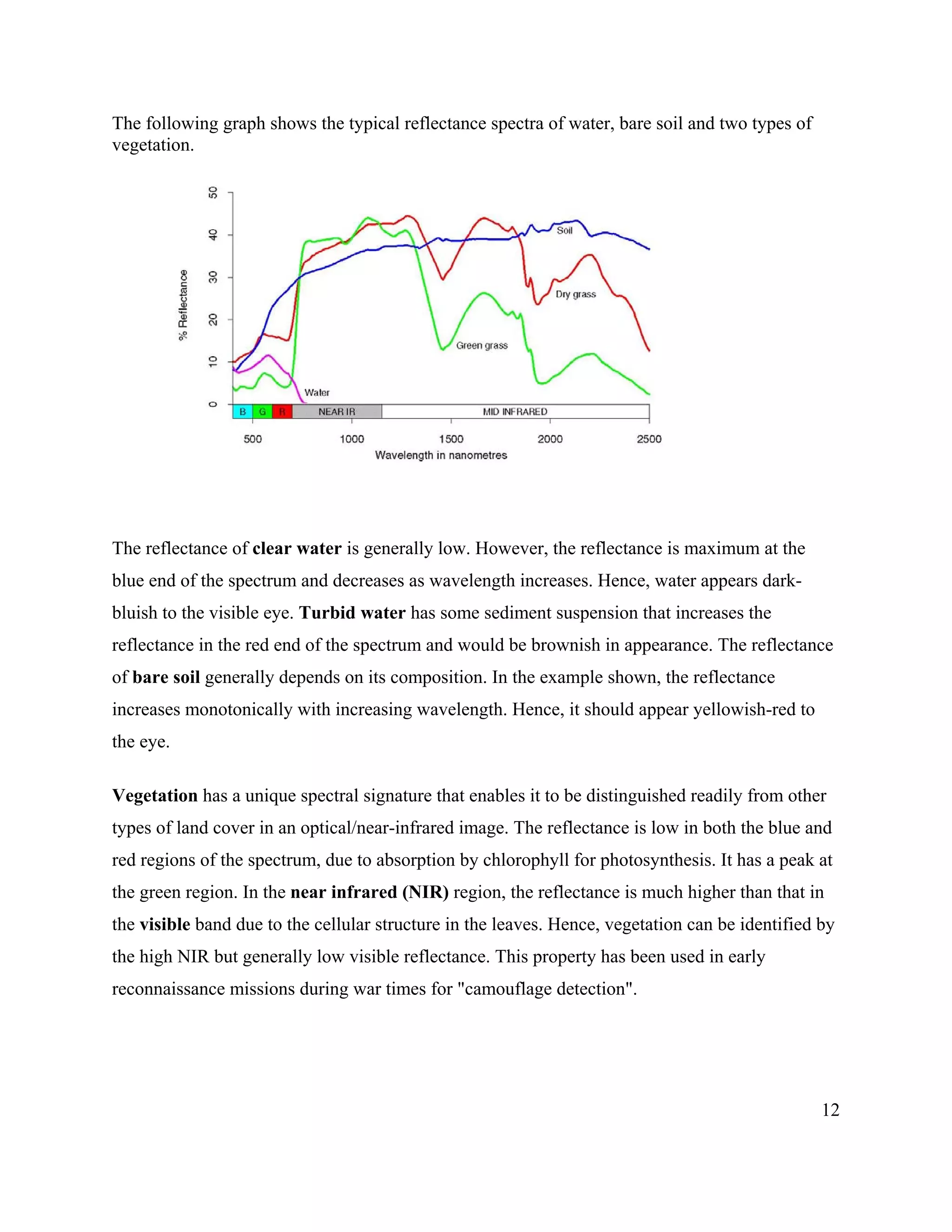
This document provides an introduction to remote sensing. It discusses electromagnetic energy, sensors and platforms, spectral signatures, geodesy, geographic information systems, image processing techniques, and applications of remote sensing such as forestry, vegetation monitoring, and geology. Key points include:
- Remote sensing involves collecting data about objects without physical contact using sensors on aircraft or satellites. Different materials have unique spectral reflectance signatures.
- Sensors can be passive (using external energy sources like sunlight) or active (with their own energy sources like radar). Spatial, spectral, and temporal resolution describe sensor characteristics.
- Common satellite platforms include Landsat, MODIS, and IKONOS. Geodesy relates to defining coordinate