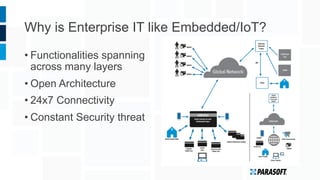
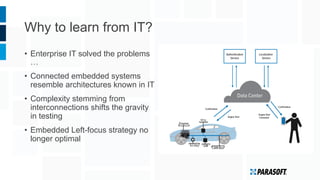
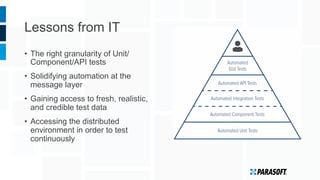
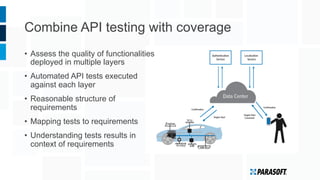
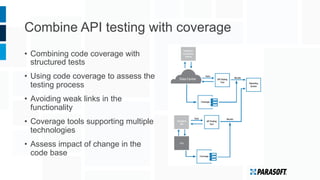
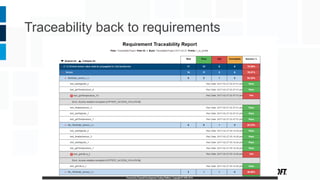
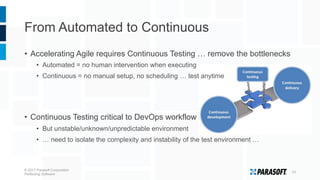
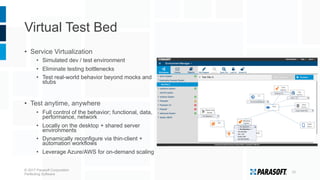
The document discusses how embedded software engineering can benefit from enterprise IT testing techniques amid increasing complexity in embedded systems. It highlights various strategies, including automated API testing, service virtualization, and integrating security testing early in the development cycle. Lessons from the IT industry emphasize the importance of traceability and continuous testing to address the challenges posed by interconnected embedded systems.