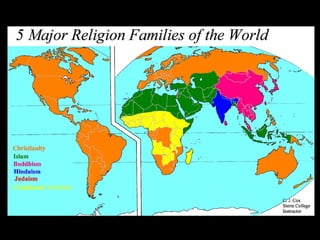
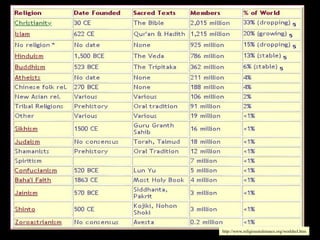
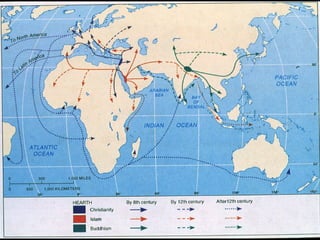
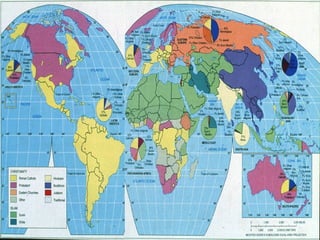
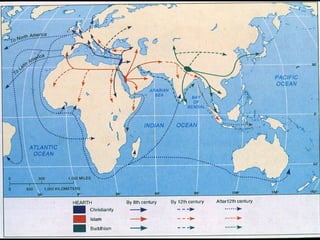
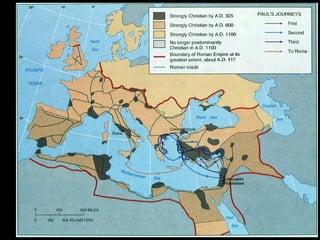
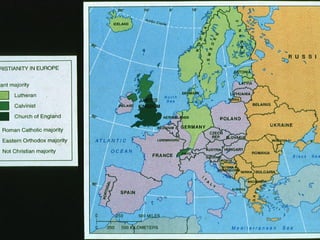
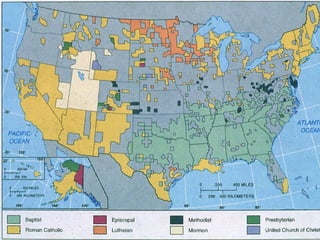
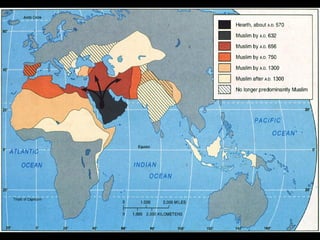
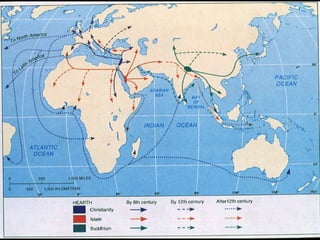
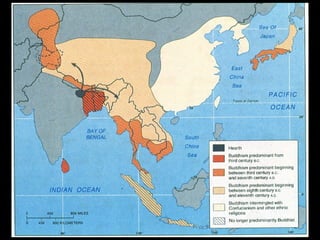
This document provides an overview of key concepts in the study of religion including definitions of religion, major world religions, and philosophical arguments regarding the existence of God. It discusses religion as involving a set of beliefs that provide explanations for human existence and purpose. Major universalizing and ethnic religions are outlined, and key terms like monotheism, polytheism, and secularization are defined. Philosophical arguments for God's existence like the cosmological, teleological, and ontological arguments are summarized. Objections to some arguments are also presented.