The document discusses relations, functions, and their properties. Some key points:
1. Relations are subsets of the Cartesian product A x B. The number of relations from set A to set B is 2^mn, where m and n are the number of elements in sets A and B respectively.
2. Functions are a special type of relation where each element of the domain is mapped to only one element of the codomain.
3. Logarithmic and exponential functions are introduced along with their graphs and properties. Logarithmic functions are defined only for positive bases and arguments.
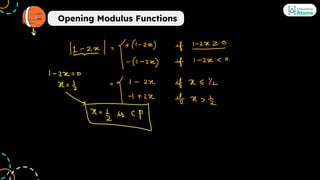
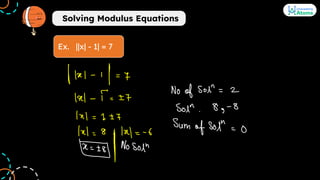
4. Modulus functions are discussed through their graphs and the concept of opening modulus. Methods to solve modulus equations are

























































![Equivalence Class
Let R = { (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 1) }
Equivalence class of 1 = [1] =
Equivalence class of 2 = [2] =
Equivalence class of 3 = [3] =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-58-320.jpg)





























































































![[ JEE-Advanced 2018 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-154-320.jpg)
![[ JEE-Advanced 2013, 4, (-1) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-155-320.jpg)

![A. 2f(x)
B. 2f(x2)
C. (f(x))2
D. -2f(x)
[ JEE-2009 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-157-320.jpg)






![Properties of G.I.F
1. x-1 < [x] ≤ x
1. [x + n] = [x] if n is integer
1. [x + [x]] = [x]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-164-320.jpg)







![Properties of {x}
1. 0 ≤ {x} < 1
1. x = [x] + {x}
1. {x + n} = {x} if n is integer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-172-320.jpg)

![Solve the equation
4[x] = x + {x}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-174-320.jpg)

![The number of solution(s) of the equation [2x] – 3 {2x} = 1, is / are](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-176-320.jpg)

![The number of solution(s) of the equation [x] + {–x} = 2x, is / are](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-178-320.jpg)

![If [x] be the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then
is equal to.
A. 0
B. 4
C. -2
D. 2
[ JEE-2021 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationsandfunctionsbb2-221118140734-e41bb2b2/85/Relations-and-Functions-BB2-0-pdf-180-320.jpg)





















