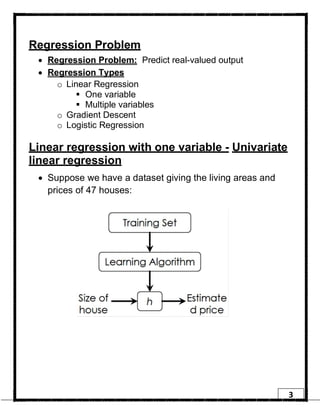
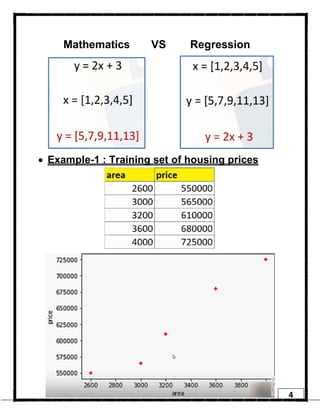
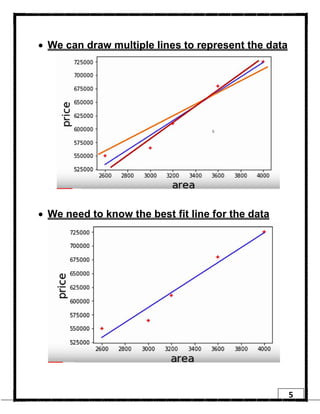
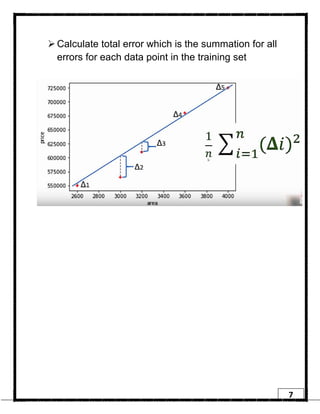
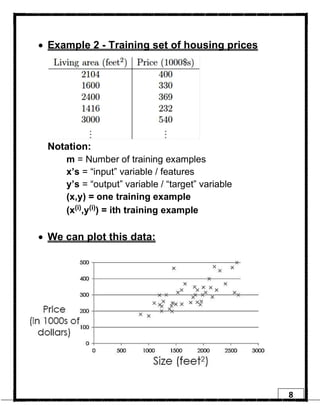
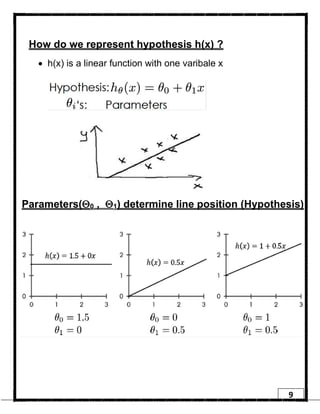
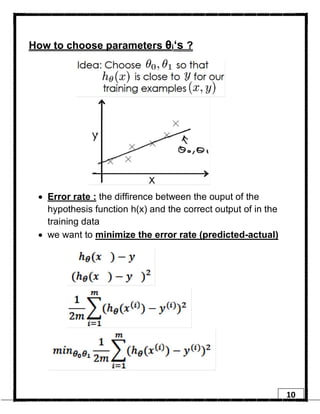
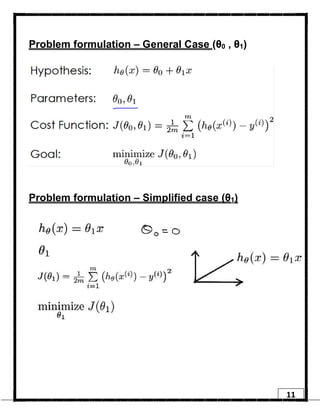
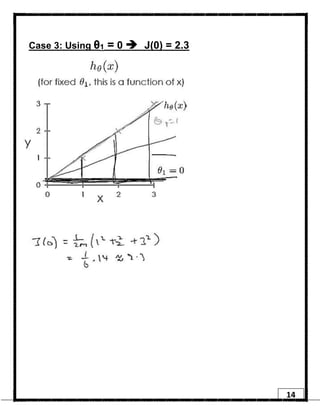
1. Regression is a supervised learning technique used to predict continuous valued outputs. It can be used to model relationships between variables to fit a linear equation to the training data.
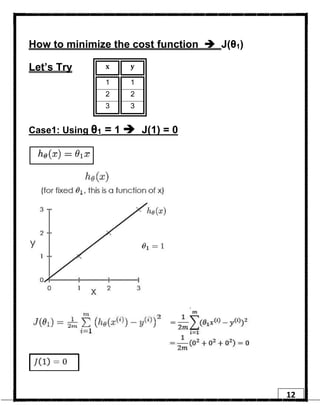
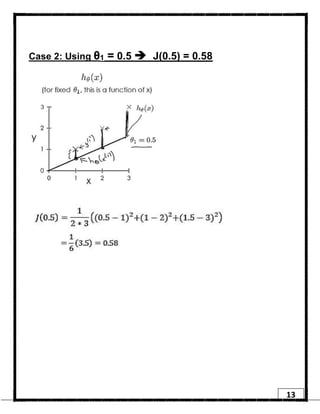
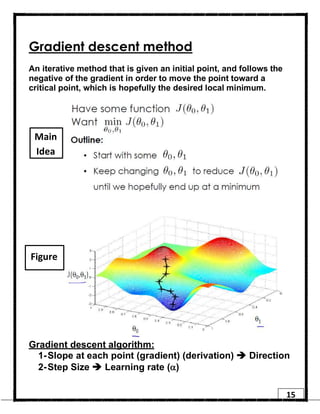
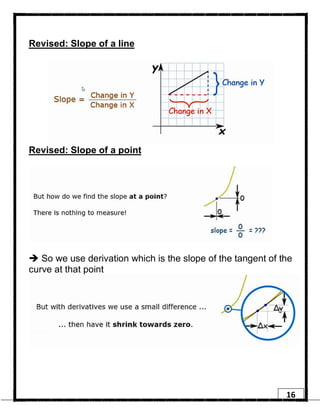
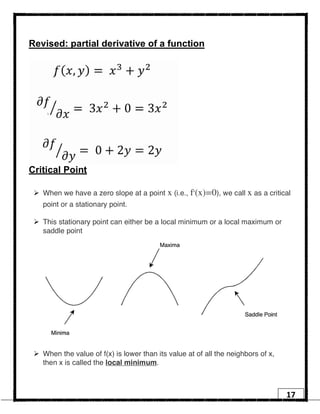
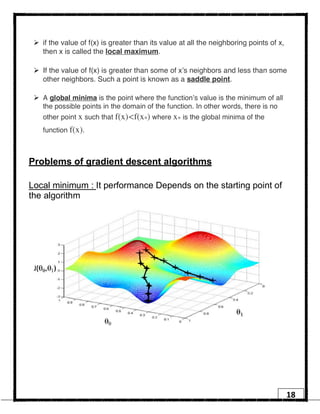
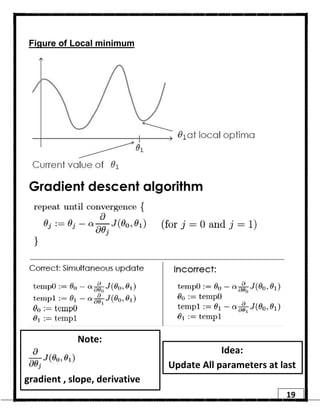
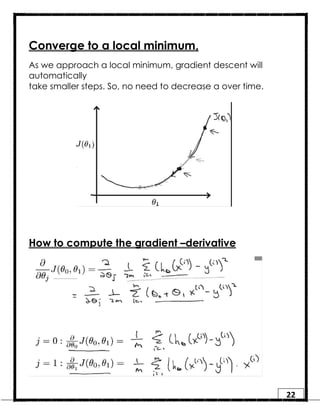
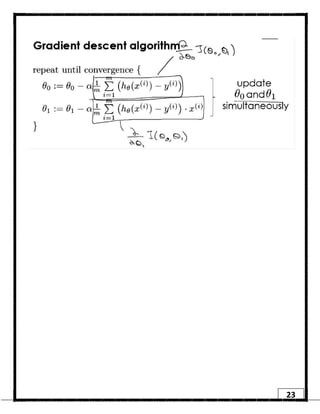
2. Gradient descent is an iterative algorithm that is used to find the optimal parameters for a regression model by minimizing the cost function. It works by taking steps in the negative gradient direction of the cost function to converge on the local minimum.
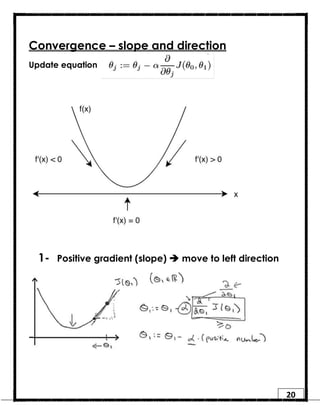
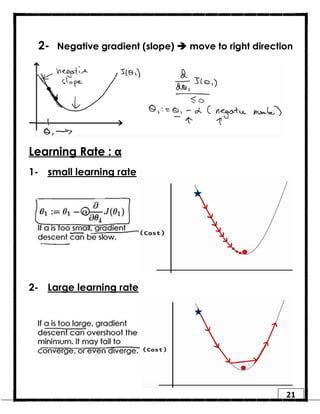
3. The learning rate determines the step size in gradient descent. A small learning rate leads to slow convergence while a large rate may oscillate and fail to converge. Gradient descent automatically takes smaller steps as it approaches the local minimum.