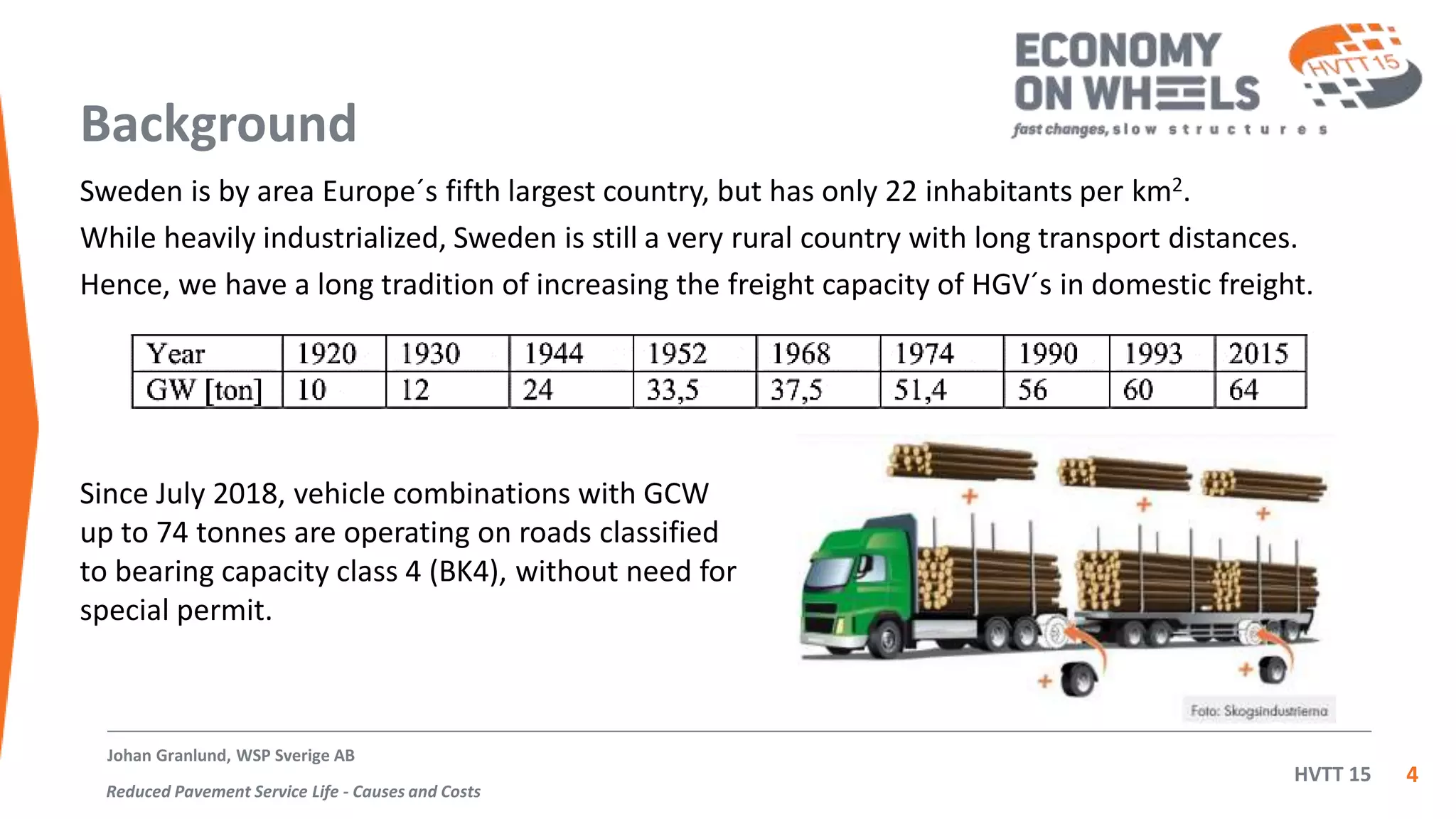
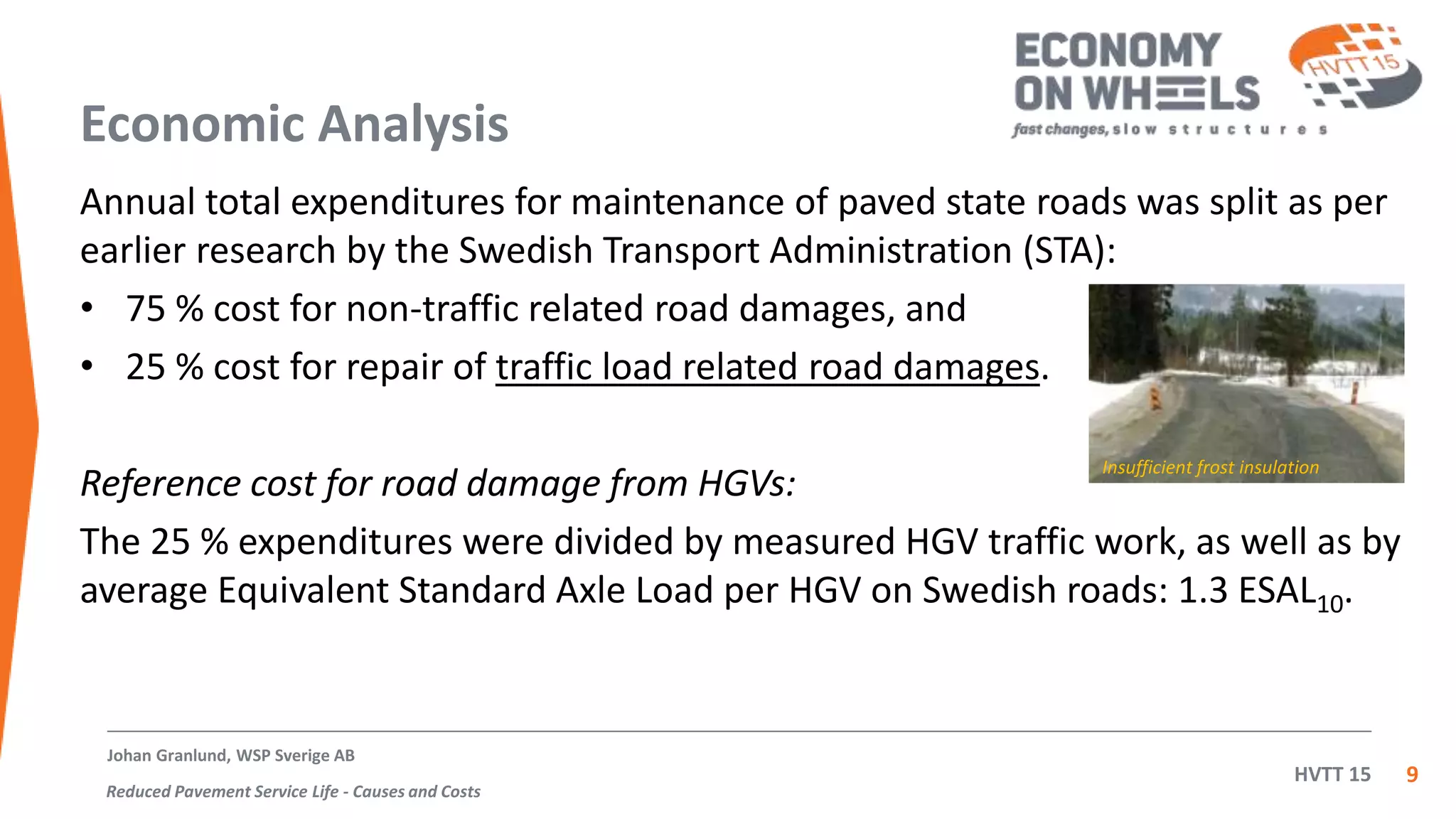
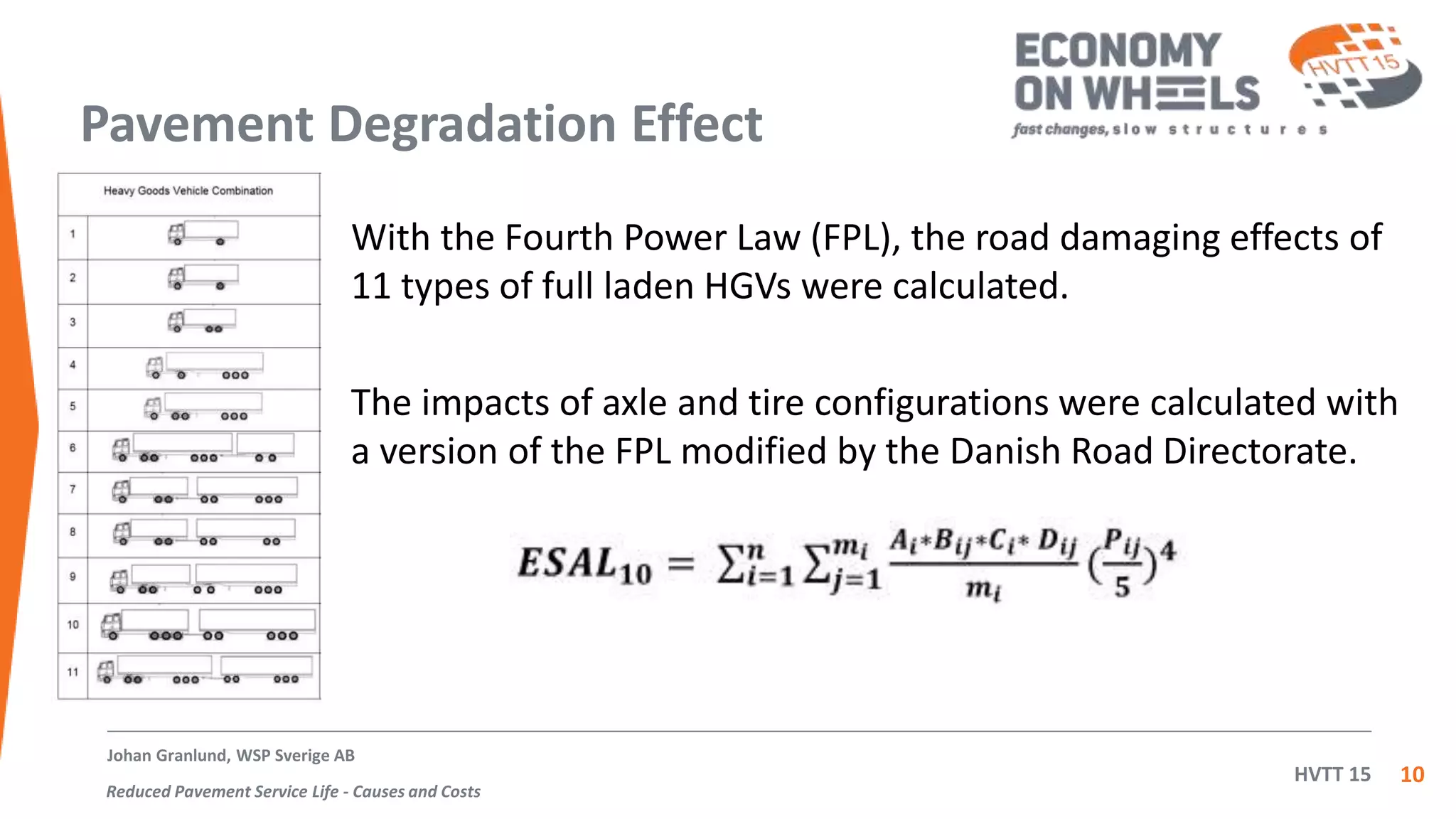
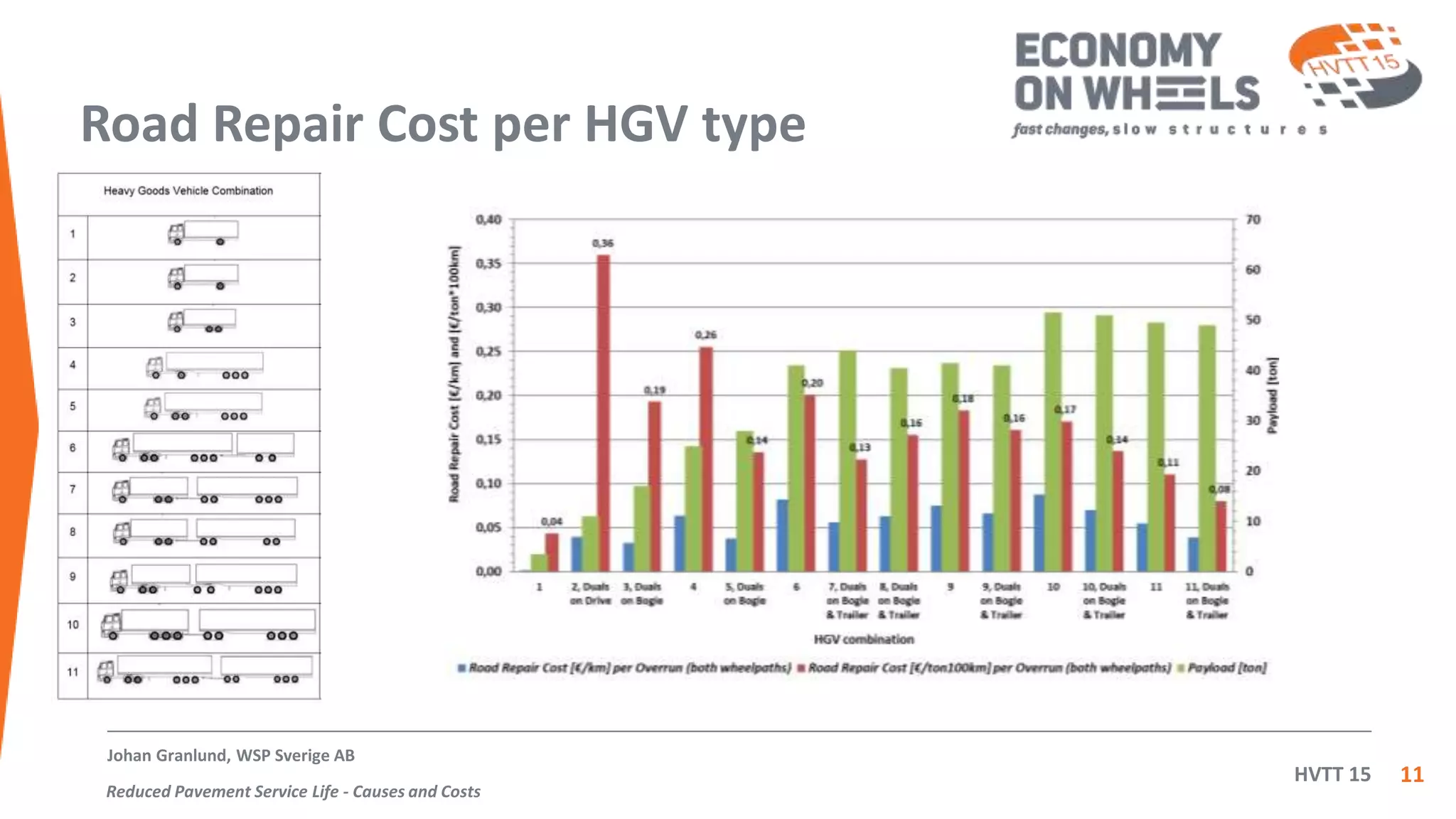
The document summarizes an inquiry conducted by the Swedish haulage industry in response to a government inquiry on road wear costs and taxation. The industry's inquiry found that: 1) 75% of pavement repair costs are due to non-traffic factors while 25% are due to traffic, 2) using a 4th power law, the road repair cost per ton-kilometer was calculated for 11 types of HGVs with two-axle lorries and EU semitrailer rigs found to cause the highest costs, and 3) 74-tonne high capacity vehicles cause the lowest road repair costs. After this finding, the government cancelled its proposed fee for road wear which was found to be 8 times higher than actual costs