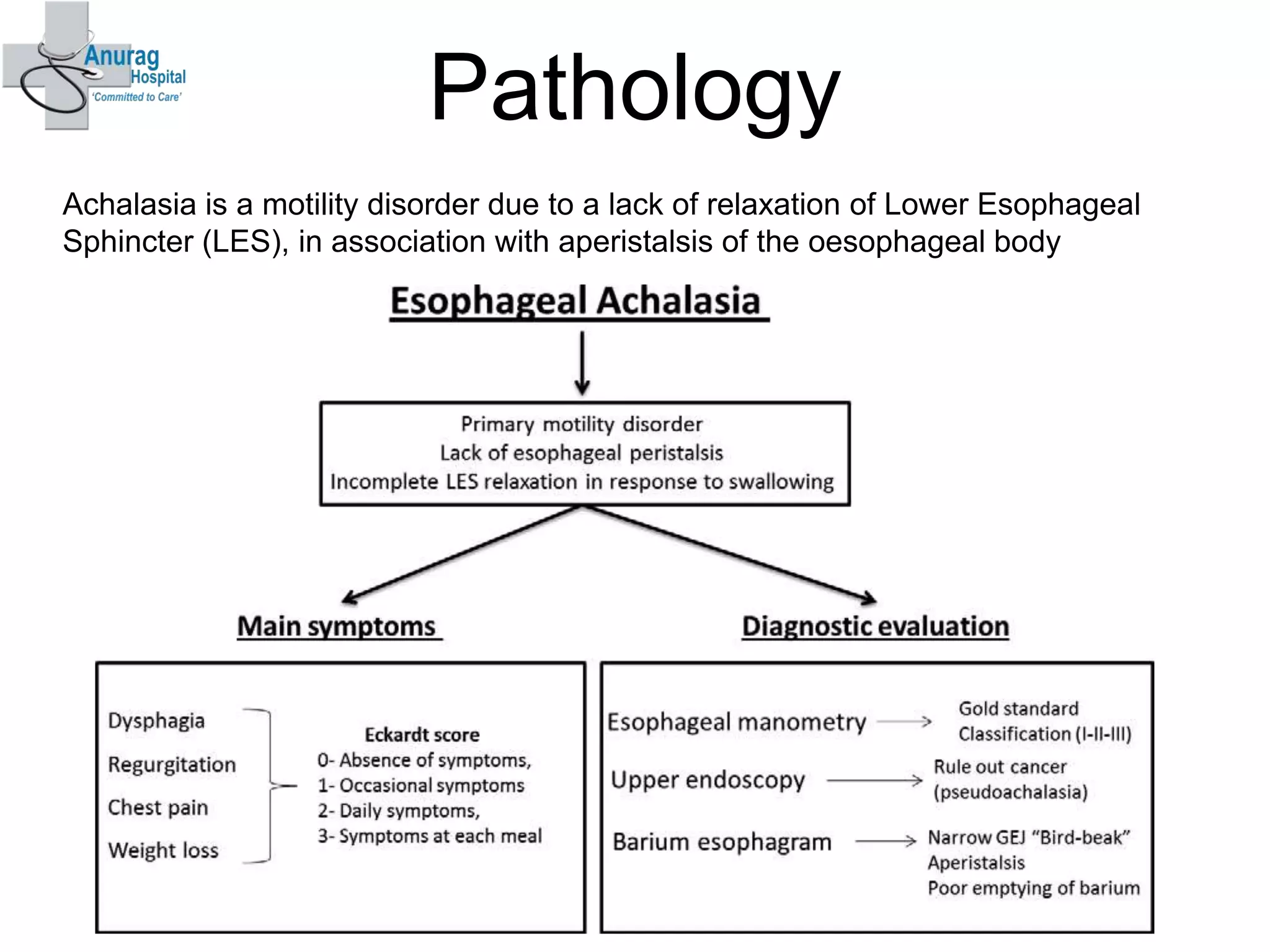
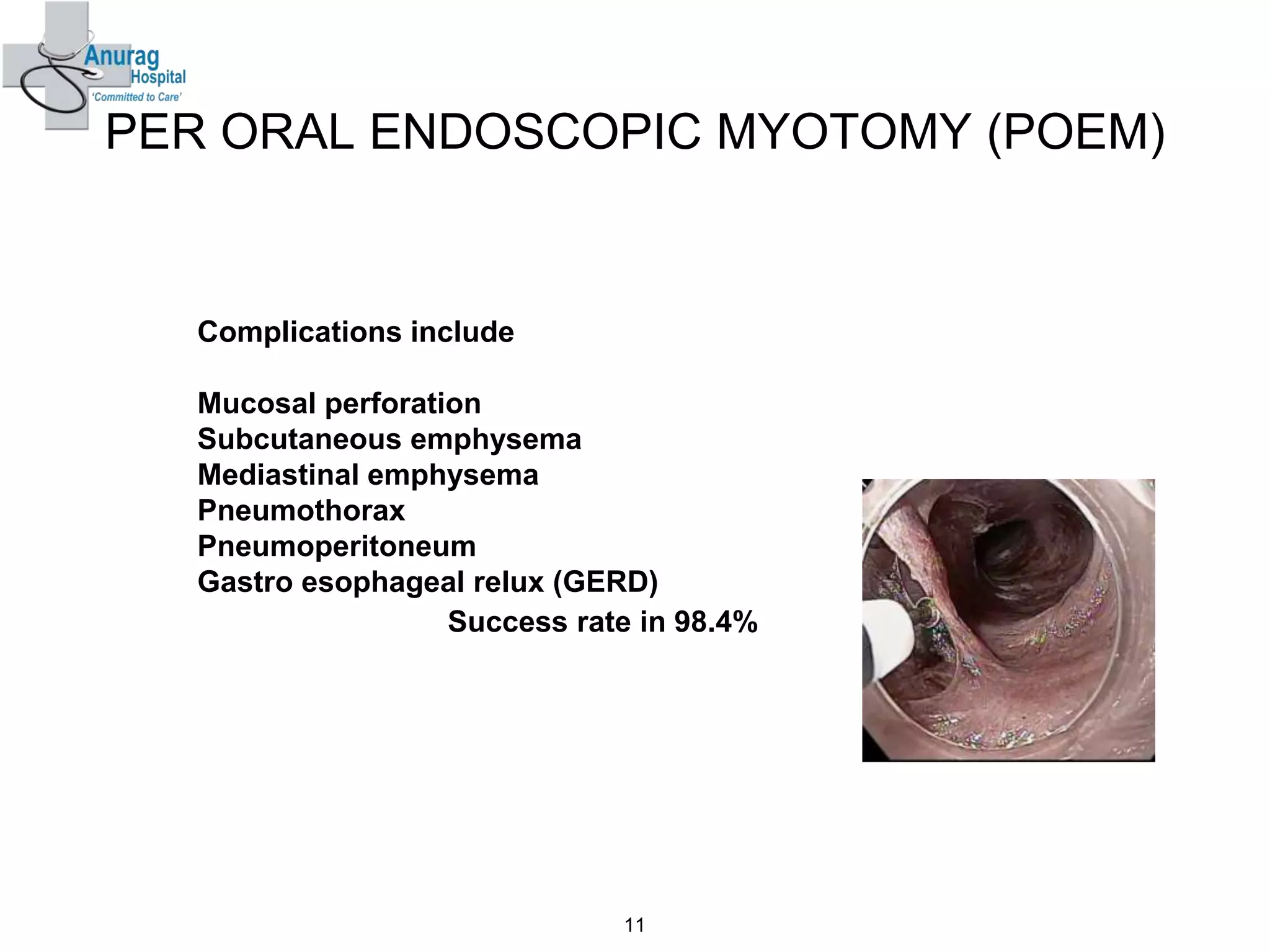
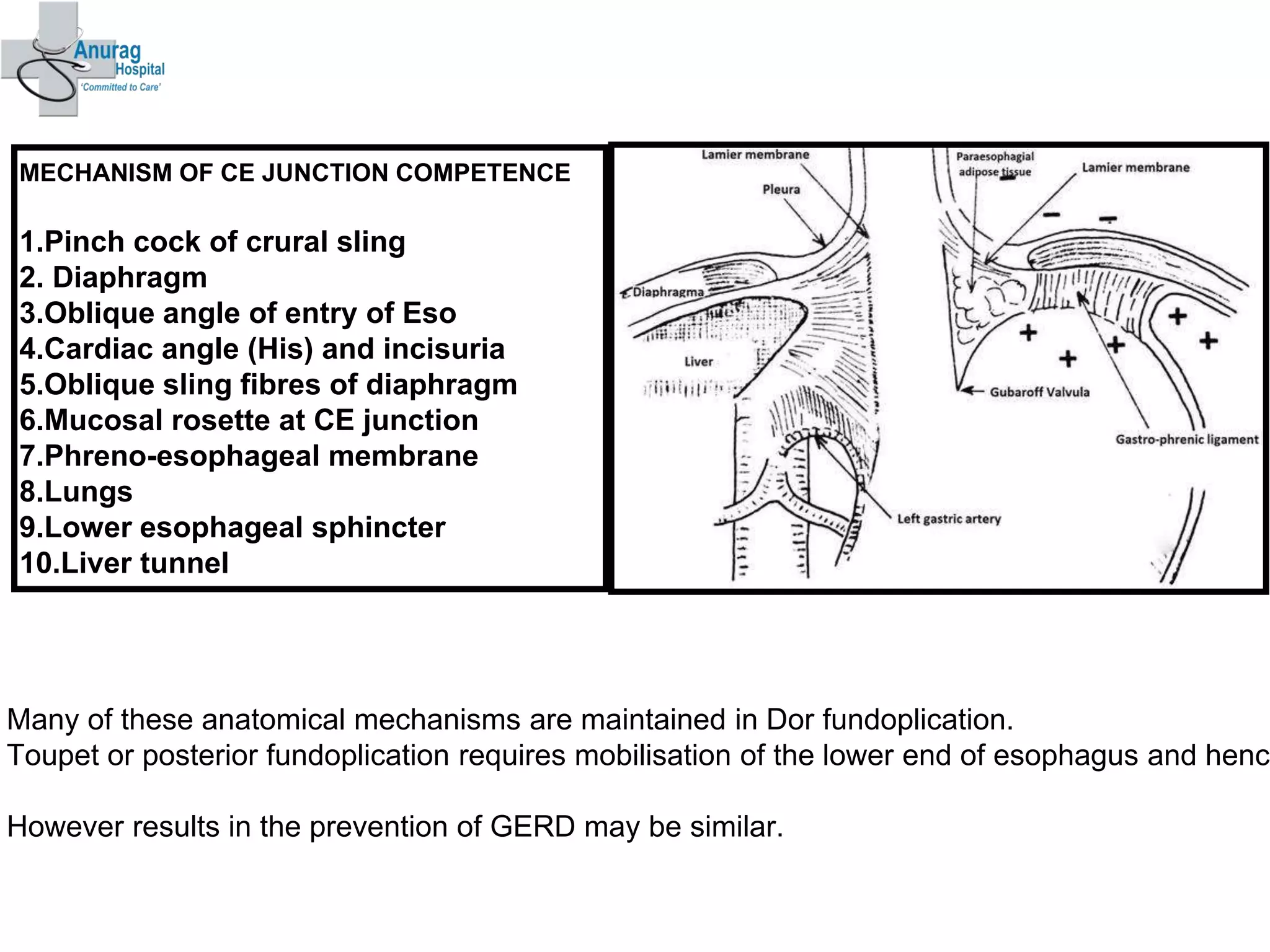
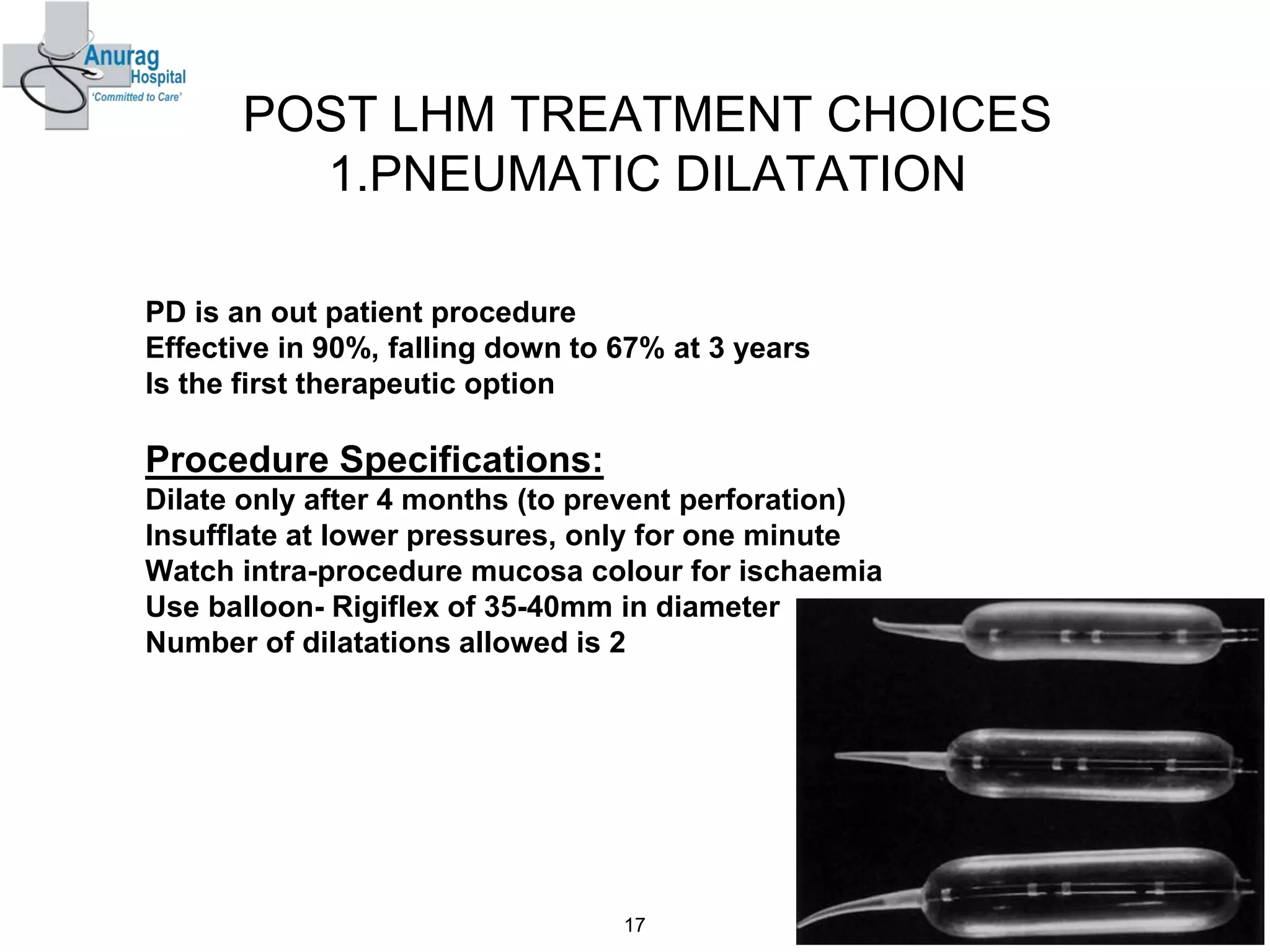
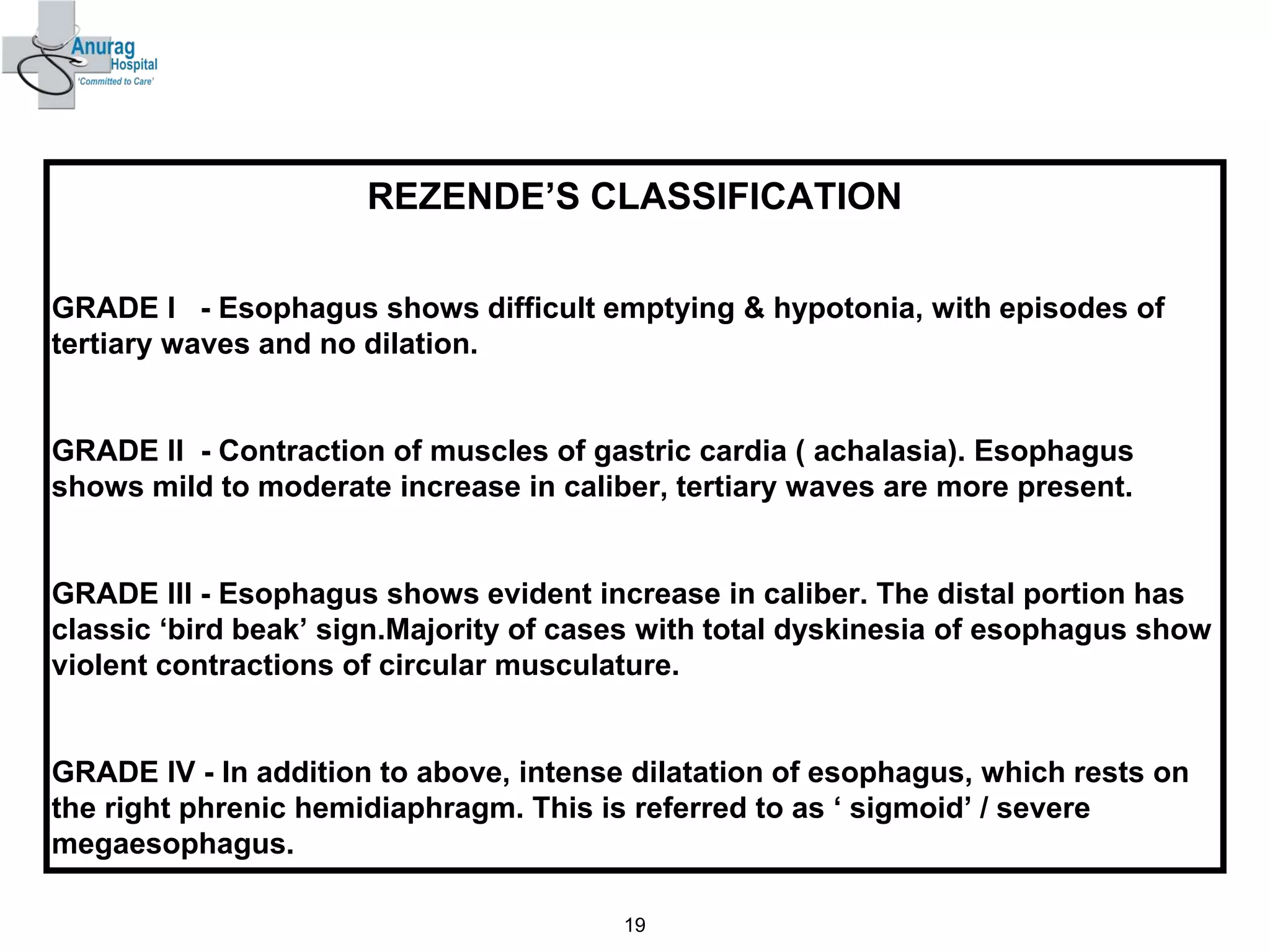
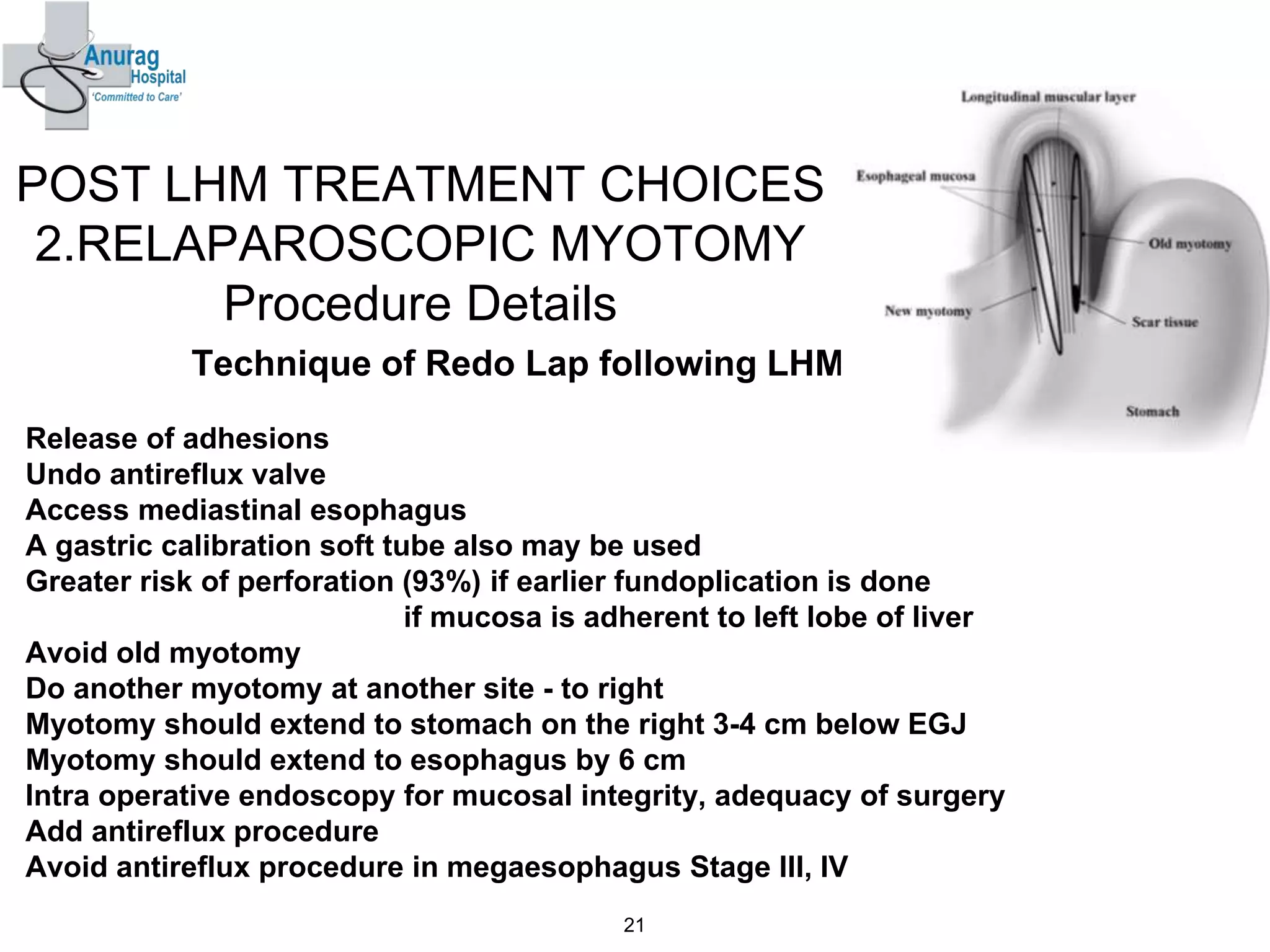
1. Surgical treatment for achalasia fails in 10-20% of patients due to recurrence of symptoms after surgery.
2. The main causes of recurrence after Heller's myotomy are incomplete myotomy at the lower esophageal sphincter and upper esophageal sphincter as well as fibrosis.
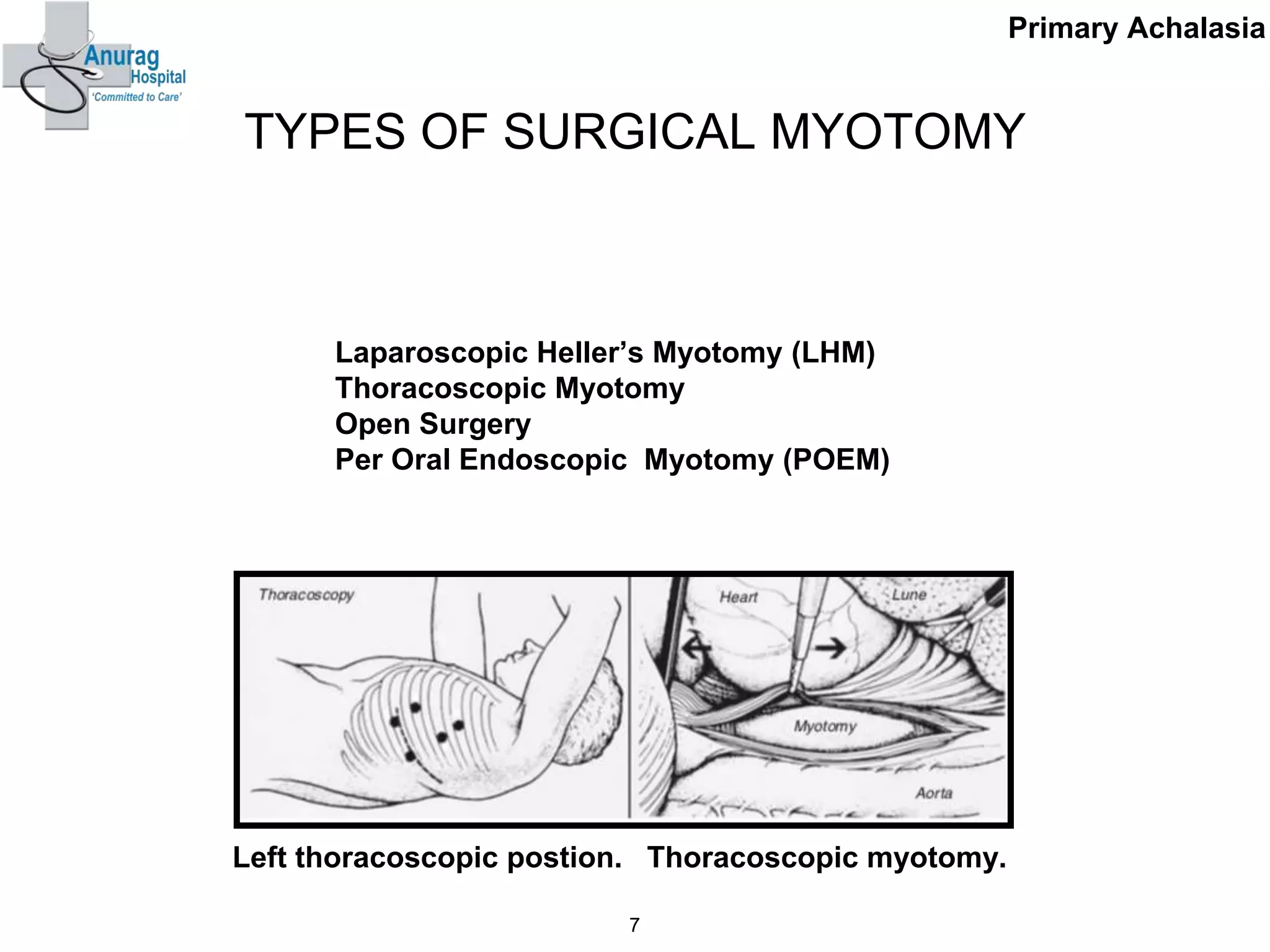
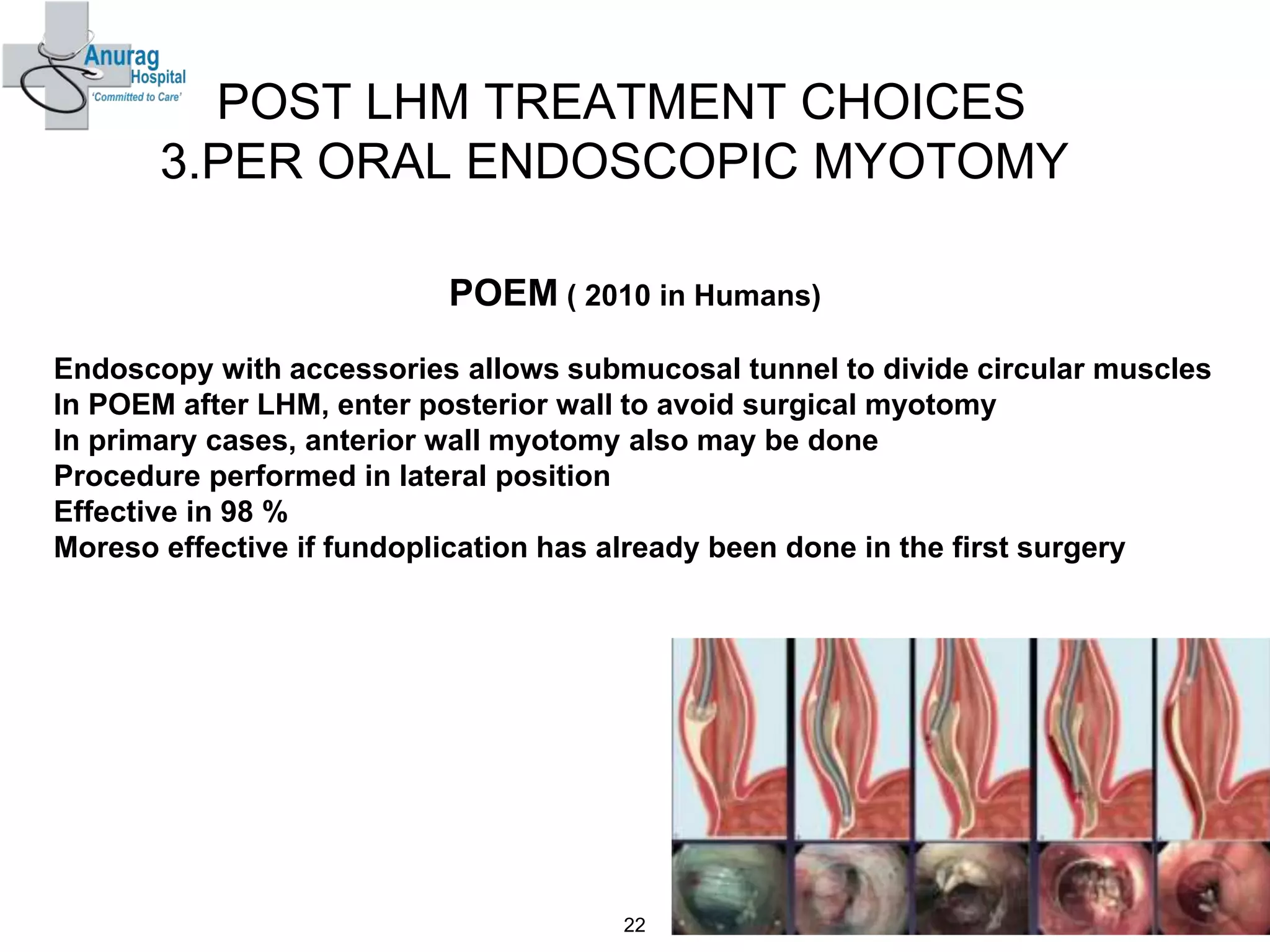
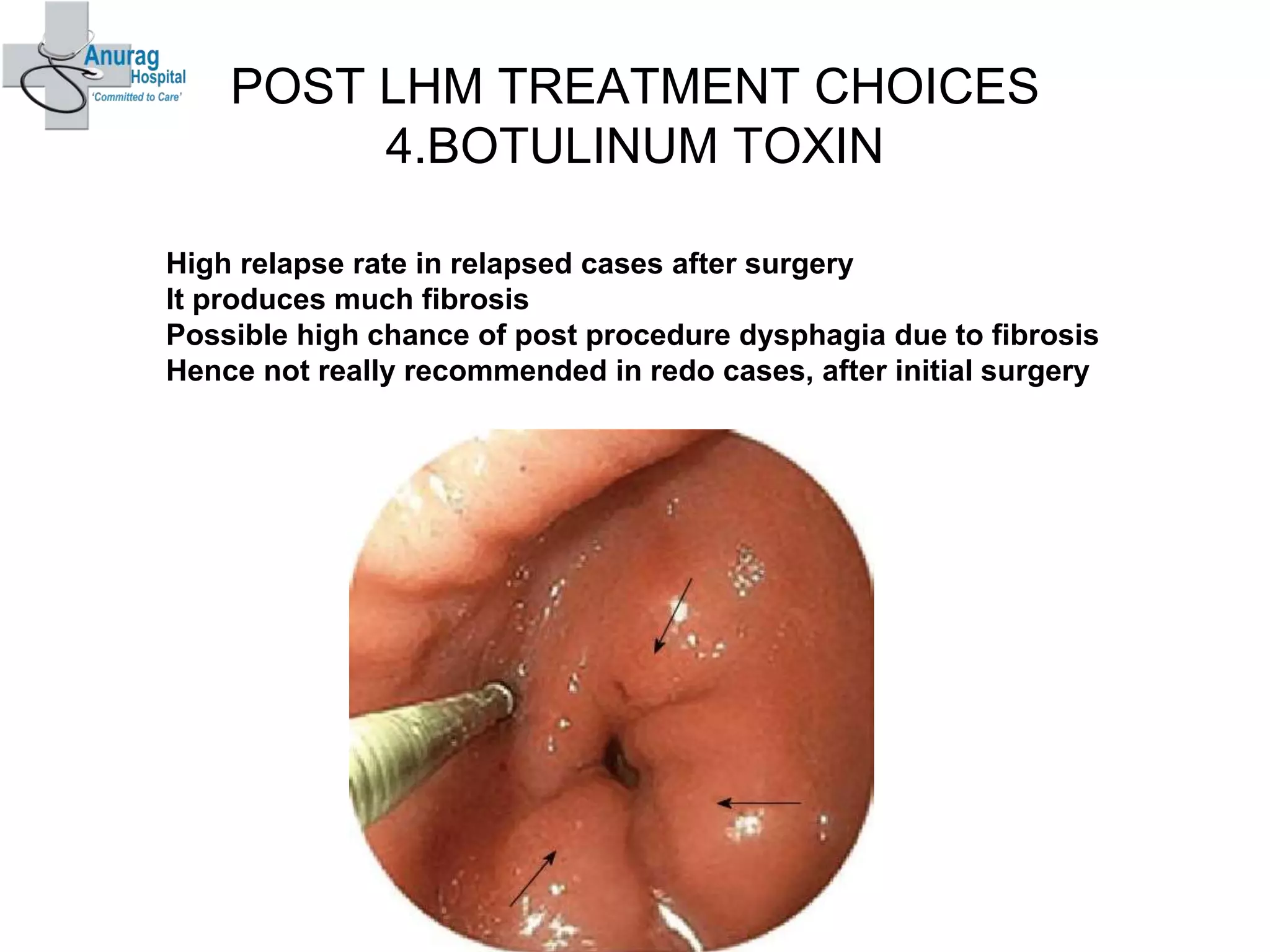
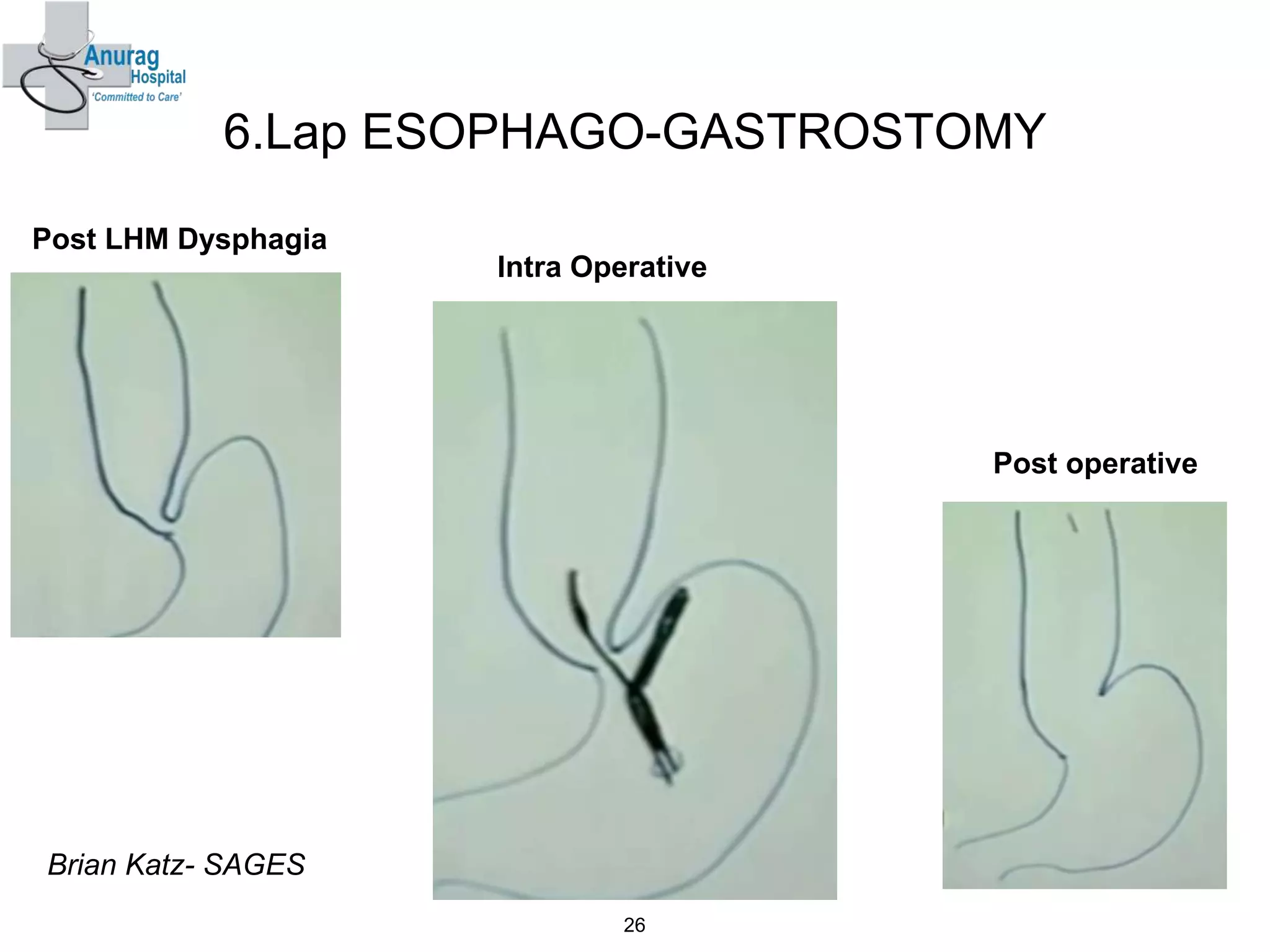
3. Treatment options for recurrence include pneumatic dilatation, repeat laparoscopic Heller's myotomy, per oral endoscopic myotomy, botulinum toxin injection, esophagectomy, and laparoscopic esophagogastrostomy.