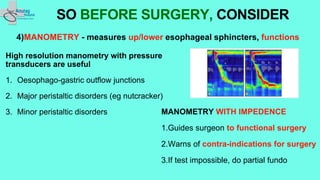
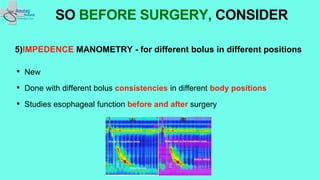
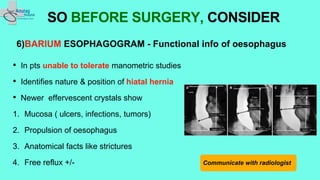
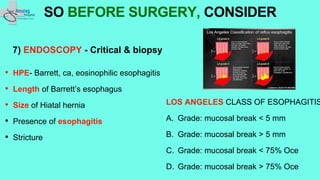
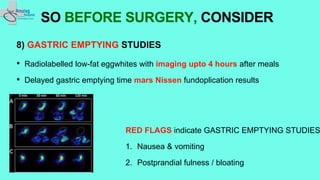
The document outlines essential preoperative tests and considerations for antireflux surgery, emphasizing the importance of proper diagnostics to ensure better outcomes. It discusses various testing methods such as pH monitoring, impedance testing, manometry, and endoscopy, and highlights cautionary measures before these tests, particularly regarding medication use. The summary also includes specific tests for conditions like Barrett's esophagus and large paraesophageal hernias.