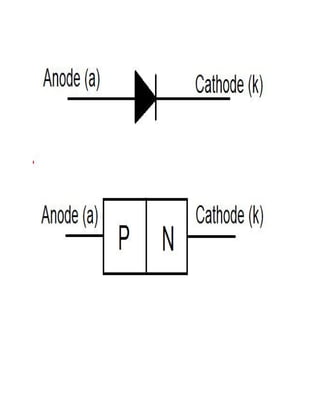
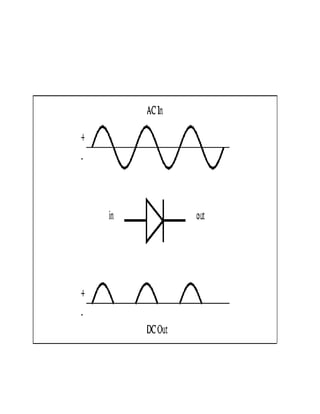
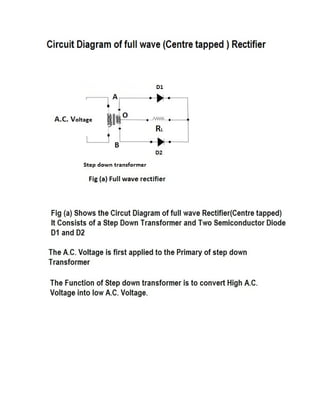
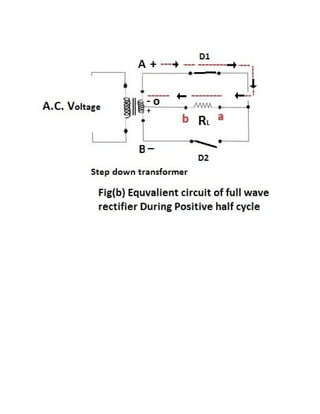
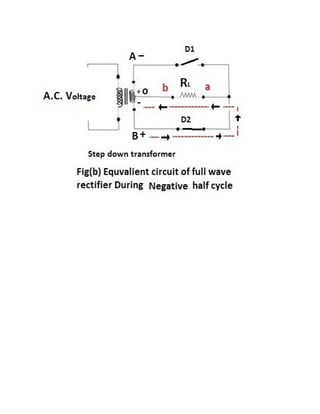
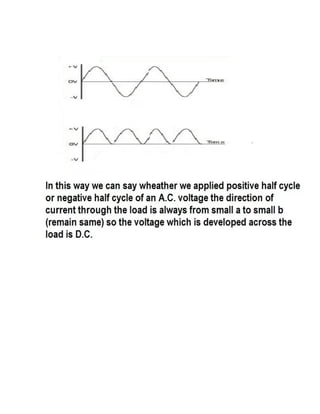
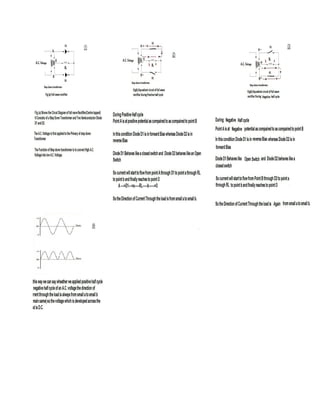
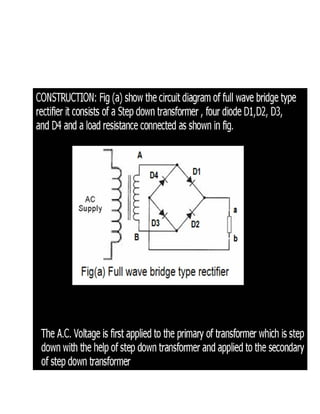
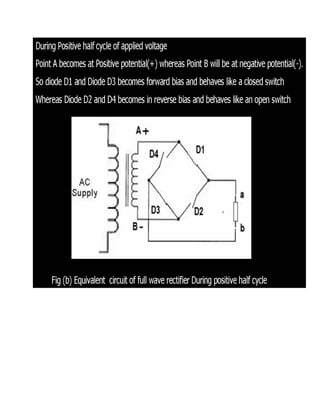
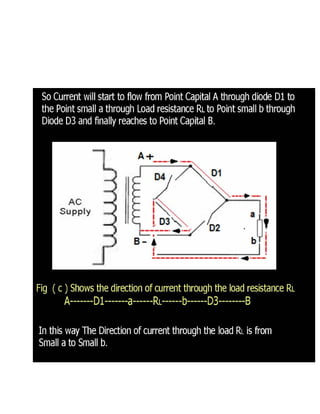
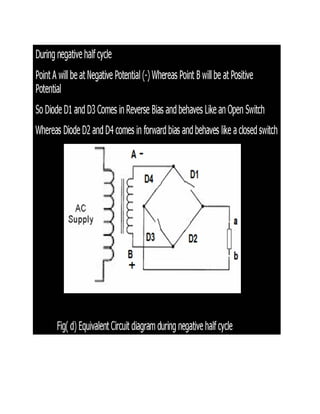
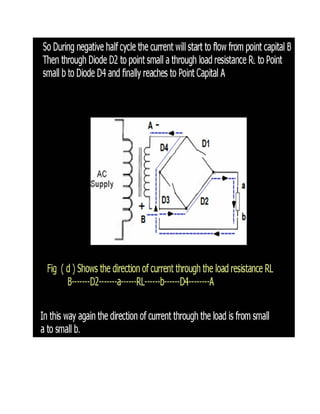
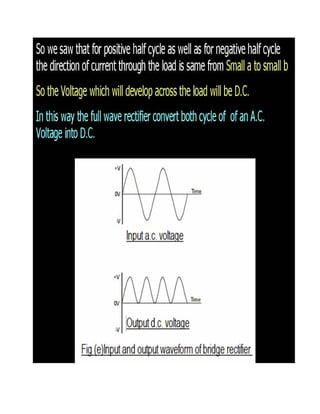
This document discusses rectifiers, which are devices that convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). It explains that AC current periodically changes direction, while DC current flows in one constant direction. A rectifier uses diodes, semiconductor devices that only allow current to flow in one direction, to filter the negative portions of the AC waveform. It describes half-wave rectification, where one diode only passes the positive half of the AC cycle, producing pulsing DC voltage. Full-wave rectification is also mentioned, using two diodes in a center-tapped transformer configuration to pass both halves of the AC cycle and produce less pulsing DC voltage.