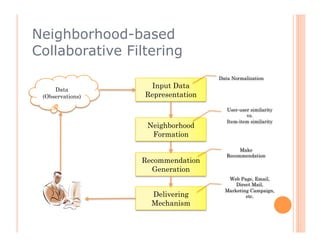
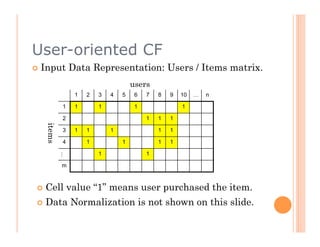
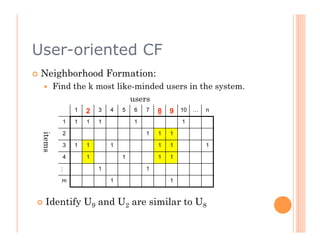
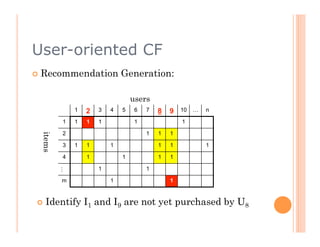
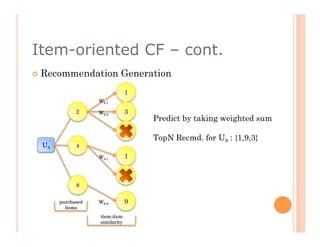
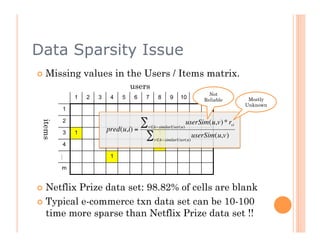
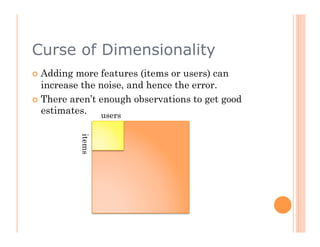
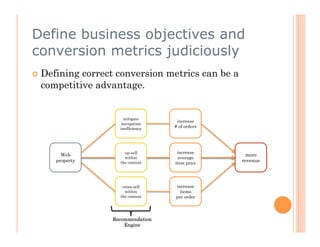
This document discusses collaborative filtering recommendation engines. It describes user-oriented and item-oriented collaborative filtering approaches. For user-oriented collaborative filtering, it finds similar users to a target user and generates recommendations based on the items those similar users purchased. For item-oriented collaborative filtering, it finds similar items to those a target user purchased and generates recommendations based on those similar items. The document also outlines challenges such as data sparsity, cold start problems, and scalability issues that recommendation engines may face.