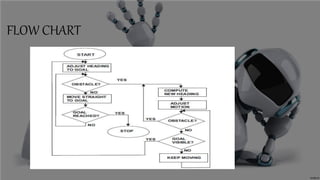
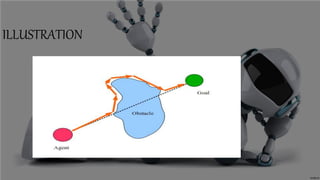
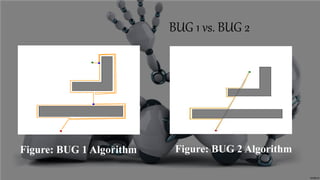
The document presents an obstacle avoidance algorithm for mobile robots that uses ultrasonic sensors to detect obstacles and then implements the Bug 1 and Bug 2 algorithms to navigate around obstacles in a reactive manner. It describes the Bug algorithms, compares Bug 1 and Bug 2, and discusses other algorithms like VFH and potential fields. Potential applications of obstacle detection algorithms discussed include mining vehicles, smart cars, and autonomous cleaning robots.