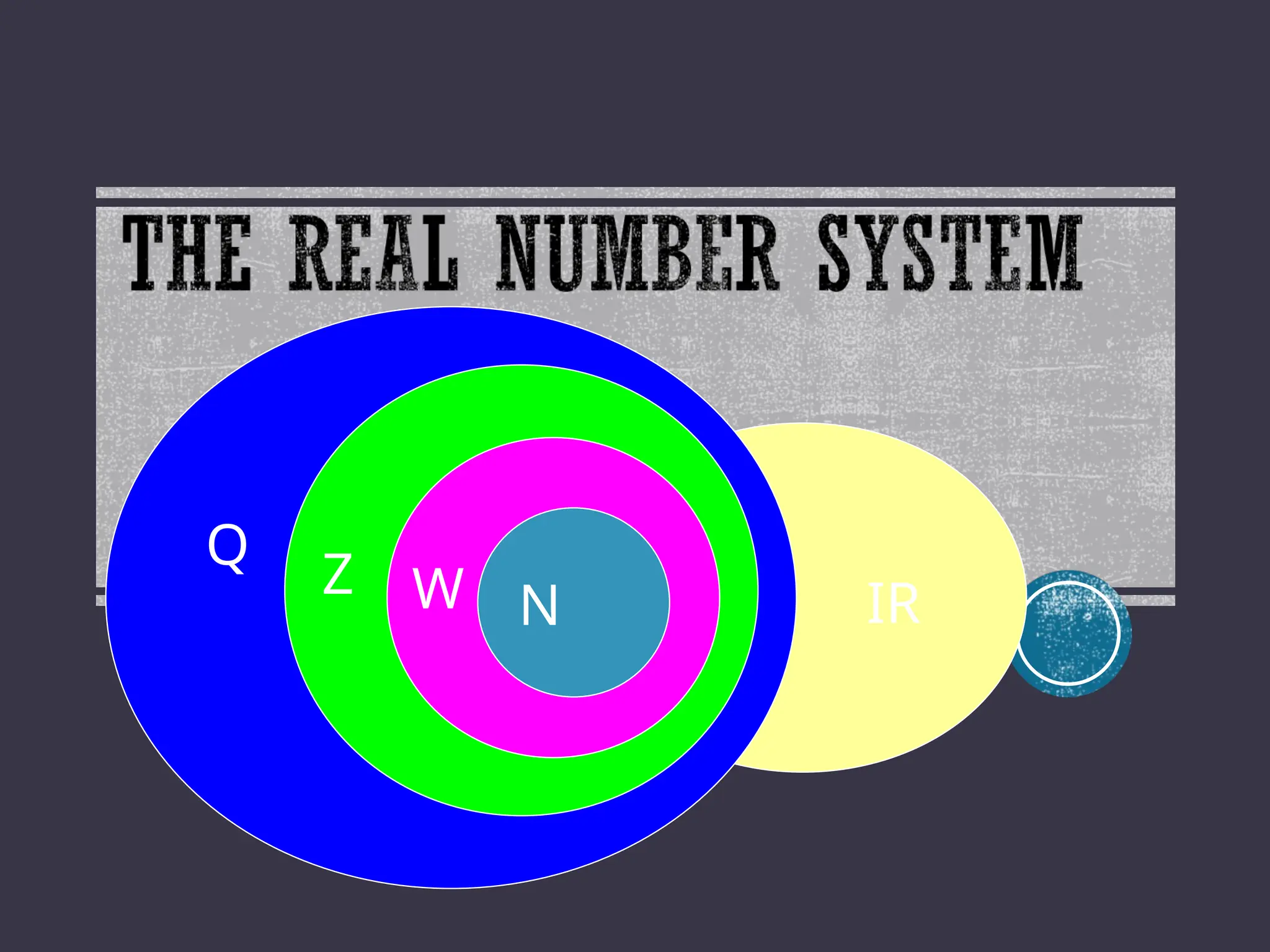
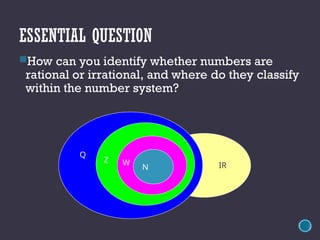
The document discusses the classification of numbers within the real number system, including rational and irrational numbers, as well as subsets like integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. It defines rational numbers as those that can be expressed as fractions, while irrational numbers are characterized by non-terminating and non-repeating decimals. The text emphasizes understanding how to identify and differentiate between these number types.