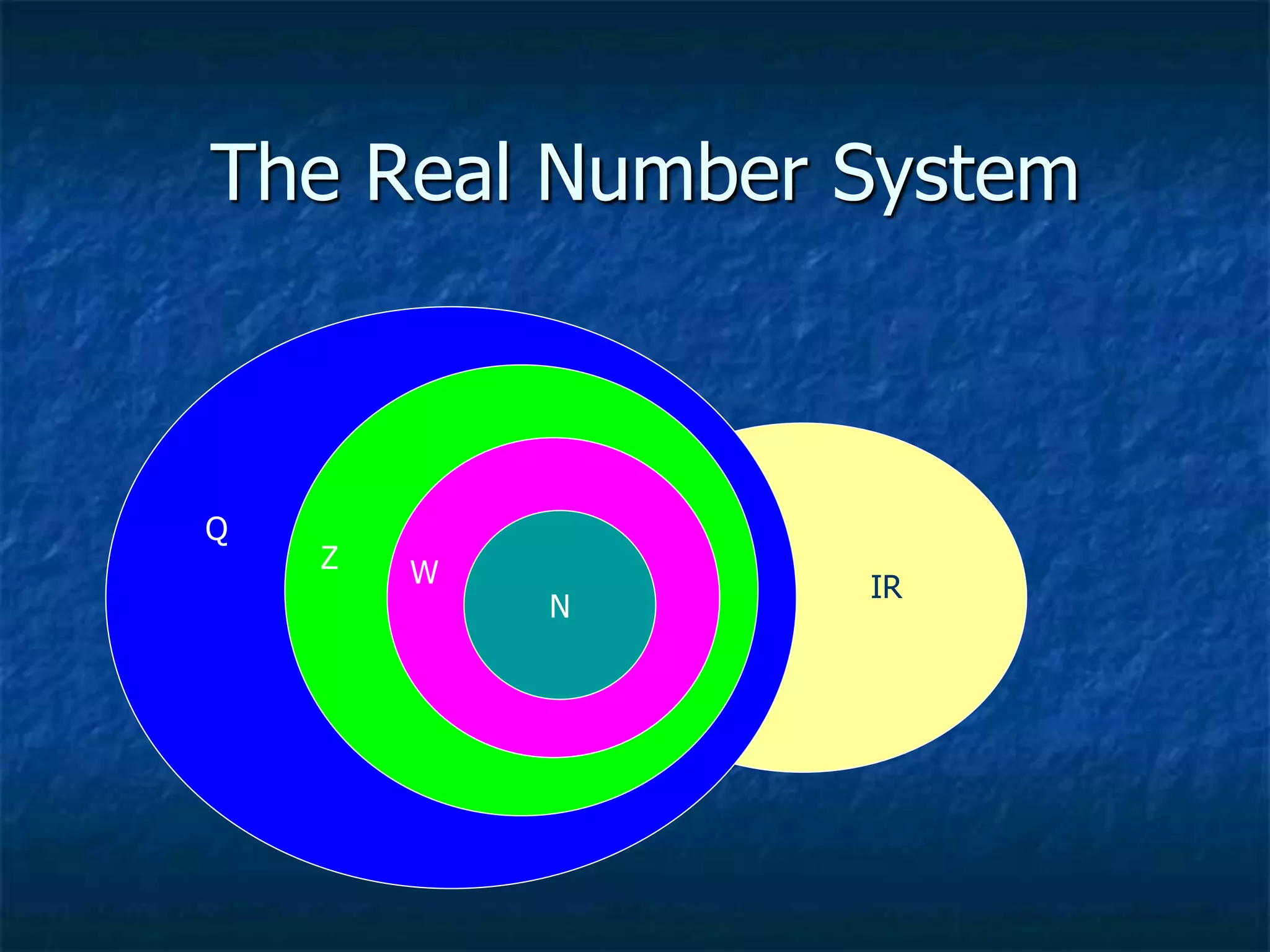
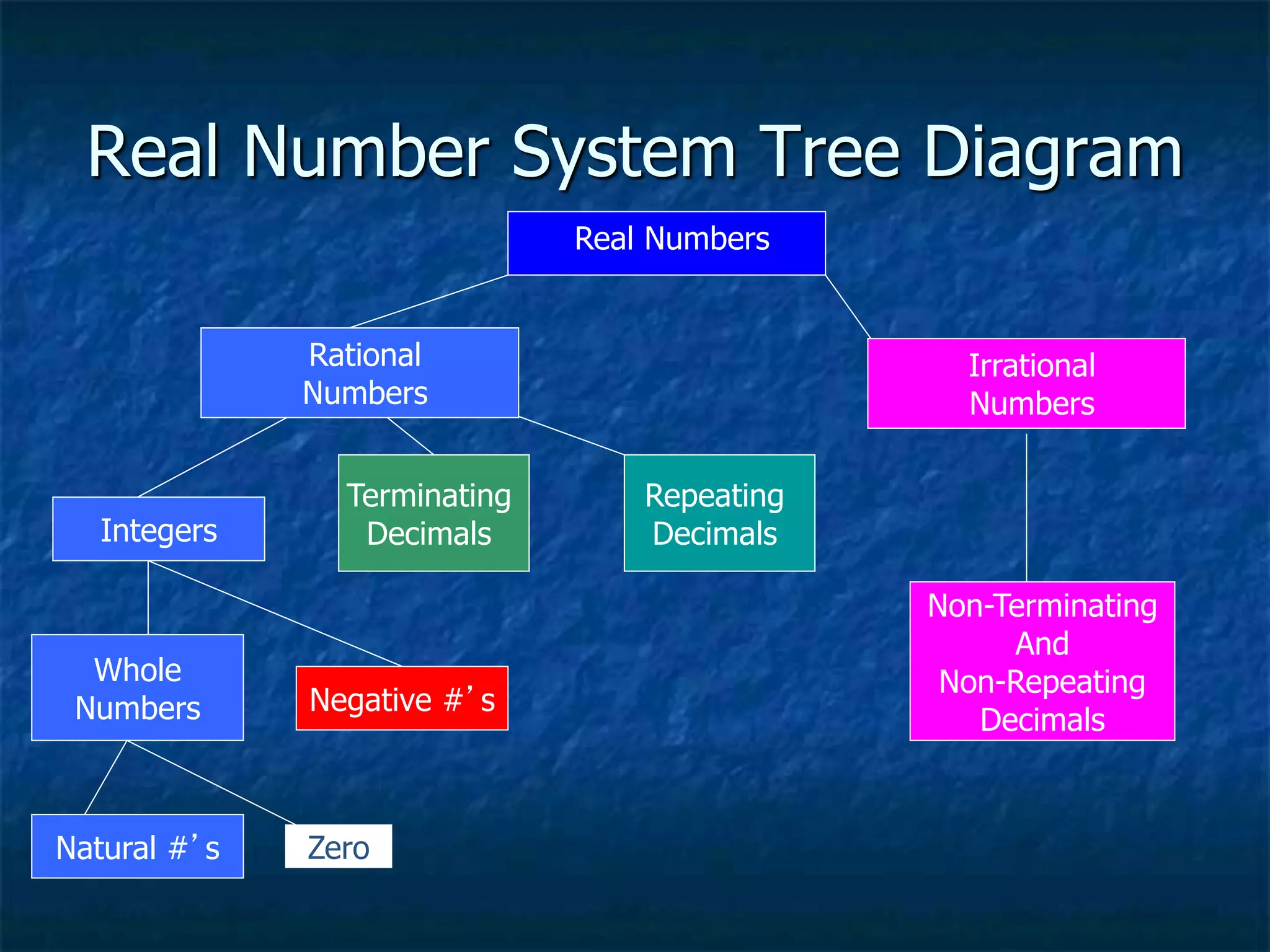
The real number system is composed of both rational and irrational numbers, encompassing five subsets: rational numbers, integers, whole numbers, natural numbers, and irrational numbers. Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions or terminating/repeating decimals, while irrational numbers include non-terminating and non-repeating decimals, like pi. The document also includes examples and exercises to distinguish between different types of numbers.