This document defines and provides examples of different types of real numbers:
- Rational numbers can be expressed as ratios of integers and include integers, natural numbers, whole numbers, and numbers with terminating or repeating decimals.
- Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as ratios and are non-terminating, non-repeating decimals like the square root of 2.
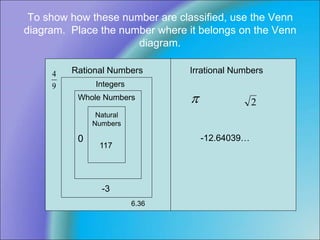
- A Venn diagram is used to classify examples like 117, 0, -12.64039..., -1/2, 6.36, π/2, and √9/4 as rational or irrational numbers based on these definitions.