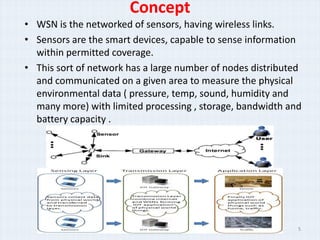
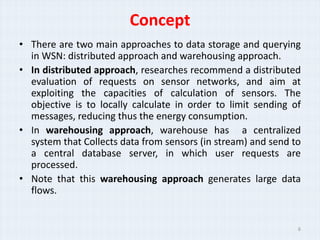
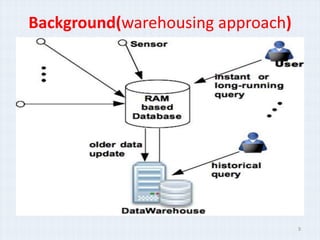
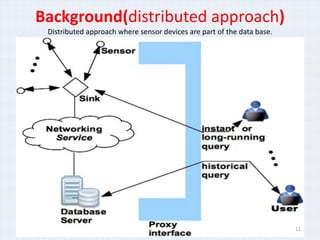
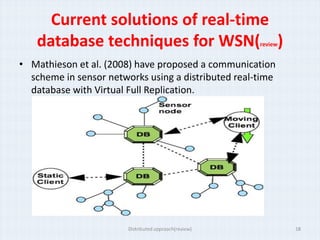
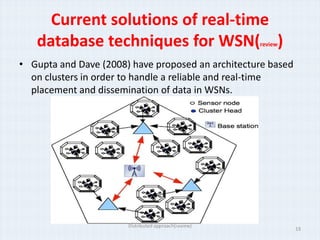
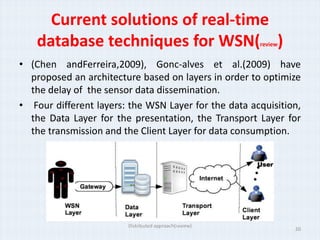
The document surveys real-time data management techniques for wireless sensor networks. It discusses the challenges of managing large amounts of real-time data in wireless sensor networks due to hardware constraints and limited resources. It describes two main approaches to data storage and querying: the warehousing approach where data is sent to a central database, and the distributed approach where sensor devices act as local databases. It then reviews several existing solutions that use each approach, including indexing techniques for centralized databases and distributed architectures using clustering or layers.